Uses of Borax Powder
Borax or borax powder (chemical name sodium tetraborate decahydrate) has the chemical formula Na2B4O7.10H2O, or Na2[B4O5(OH)4].8H2O and has a wide variety of uses in metallurgy, household and laundry cleaning, chemistry, water softening, glass making, fertilizer, etc. A soft, light, colorless borax powder containing a crystalline structure and used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to make buffer solutions. It is a naturally occurring ore purified by recrystallization and made from boron compounds. Borax molecule was first prepared in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy, Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, and Louis Jacques Thenard. The physical properties or chemistry of borax are very similar to boric acid and both of them kill insects by targeting their stomachs and nervous systems.
![Borax powder, chemical name sodium tetraborate decahydrate, formula Na2[B4O5(OH)4] 8H2O structure and uses](https://www.priyamstudycentre.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/borax-molecule.png)
The IUPAC name of borax is sodium tetraborate decahydrate but it is also called simply sodium tetraborate or disodium tetraborate. The heating of crystalline solid borax first swells due to losing the hydrated water. But when further heating anhydrous substance gives meta-borate and boron trioxide.
In India, Egypt, Rome, and other ancient civilizations, it is used for the preparation of flux, glazes, and hard glass. Borax is found in dry lake beds in places of California’s Death Valley where the water evaporates and is purified by recrystallization. It is also made by heating a boric acid solution with sodium carbonate.
Structure of Borax
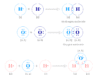
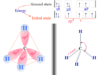
Borax is an inorganic salt consisting of the chemical elements boron, sodium, oxygen, and hydrogen in its formula or structure. Borax, commonly named sodium tetraborate decahydrate has the chemical formula (Na2B4O7.10H2O) or Na2[B4O5(OH)4].8H2O. The structure of the sodium tetraborate decahydrate anion has two tetrahedral units of BO4 and two planner units of BO3.
Each BO4 unit shares two oxygen with two planner BO3 units and one oxygen with the second BO4 unit to form a sodium tetraborate decahydrate structure. The fourth oxygen chemical bonding with the boron of the BO4 unit and a hydrogen atom.
The planner BO3 unit is sp2 hybridized but the tetrahedral BO4 unit is sp3 hybridized. These hybrid orbitals overlap with suitable orbitals of the oxygen and unpaired electrons.
Where is Borax Found?
Borax powder is an important chemical compound of boron found in pesticides or insecticides to kill ants or roaches, antiseptics or mouthwash in medicine, cleaner solution or water softener, and enamel for teeth. It was first discovered in the dry lake beds of Tibet and imported to Europe for refining.
Turkey, California (Searles Lake), Southwestern United States, Chile (Atacama desert ), Bolivia, Tibet, and Romania are the most important commercial depositors or suppliers of borax powder.
Borax Preparation
Borax is a naturally occurring ore purified by recrystallization and made from boron compounds. It is used to derive various closely related boron compounds that differ by their crystal water. It is commonly prepared from the mineral colemanite and closely related compound boric acid.
From Colemanite
Boiling the mineral colemanite with an alkaline solution of sodium carbonate uses for the preparation of crystalline solid powder of sodium tetraborate decahydrate.
Ca2B6O11 + 2Na2CO3 → Na2B4O7 + 2NaBO2 + 2CaCO3
Calcium carbonate is filtered out from the solution. The concentration of filtrate deposits crystals solid Na2B4O7.10H2O.
Another solution that contains metaborate (NaBO2) is again used for the conversation of Na2B4O7.10H2O by passing carbon dioxide (CO2).
4NaBO2 + CO2 → Na2B4O7 + Na2CO3
Borax From Boric Acid
Borax is also obtained by chemical reaction or heating of boric acid solution with sodium carbonate with specific heat. It can be crystalline by cooling the solution.
4H3BO3 + Na2CO3 → Na2B4O7 + 6H2O +CO2
Properties of Borax
The properties and structure of boron compounds in chemistry are very similar. Therefore, crystalline borax powder and boric acid have very similar chemical properties. These chemicals are dissolved in liquid mainly in water many other solvents such as glycerol, ethylene glycol, methanol, etc.
At normal temperatures, the crystalline borax powder contains ten molecules of hydrated water in its structure and molecular formula. At 62°C, it contains five molecules of hydrating water in its molecular structure.
| Chemical Names | Sodium tetraborate decahydrate Sodium borate decahydrate Sodium tetrahydroxy tetraborate hexahydrate |
| Chemical formula | Na2B4O5(OH)4·8H2O or Na2B4O7.10H2O |
| Molar mass | 381.36 g/mol |
| Appearance | Soft, light, colorless crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.73 g/cm3 |
| Solubility | Soluble in water to form a basic solution and many other solvents like glycerol, ethylene glycol, methanol, etc |
| Melting point | The decahydrate form decomposes at 75 °C and the anhydrous form melts at 743 °C |
| Boiling point | 1,575 °C (anhydrous) |
| CAS Number | 1303-96-4 |
Chemical Properties
The aqueous solution of borax is alkaline in nature with a pH of about 9.5. It changes the color of litmus paper and phenolphthalein indicator.
Na2B4O7 + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2B4O7
H2B4O7 + 5H2O → 4H3BO3
When borax reacts with water, it forms a weak boric acid and sodium hydroxide. Such weak acid is tritiated against strong acids using methyl orange as an indicator at a pH scale of 3.1 to 4.4.
Chemically, the sodium tetraborate decahydrate contains the [B4O5(OH)4]2− ion in its structure and it is converted easily to boric acid and other borates by using hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid.
Na2B4O7·10H2O + 2HCl → 4B(OH)3 + 2NaCl + 5H2O
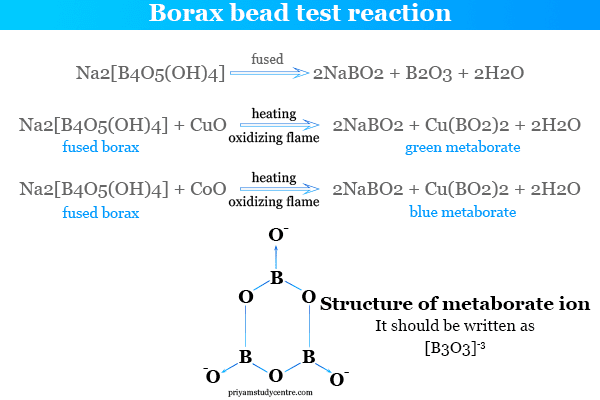
Borax Bead Test
When we heat borax first swells due to the loss of hydrating water. However, further heating produced the chemical compounds metaborate and boron trioxide.
The fusion of sodium tetraborate decahydrate with transition metal oxides (copper, iron, cobalt, nickel, or chromium oxide) forms a bead of metal borate that looks like a characteristic glossy color. It is used in chemistry for the quantitative chemical analysis of metal salts. Such a test is called the borax bead test in chemistry.
Metaborate of Transition Metals
Metaborate fusion with metal salts heated in oxidation flame forms ic-metaborate with a characteristic glossy color. However, the fusion of metal salts or heated in reduction flame forms us-metaborate with a characteristic glossy color.
The fusion of sodium tetraborate decahydrate with metal ingredients like copper oxide (CuO) in an oxidizing flame defines blue cupric metaborate but in a reducing flame it defines dull red cuprous metaborate.
| Metaborate of metals | Bead test colour | |
| oxidizing flame | reducing flame | |
| Copper | green, blue | dull red |
| Iron | yellow | dark green |
| Cobalt | dark blue | dark blue |
| Nickel | brown | colorless |
| Chromium | green | green |
Uses of Borax Powder
Borax powder is a naturally occurring ore that has a wide range of industrial uses in various fields such as metallurgy, household and laundry cleaning, chemistry, water softening, glass making, fertilizer, etc.
Uses in Metallurgy
Borax is a solvent for metal-oxide slags in metallurgy. Therefore, it dissolves many metallic oxides when fused with them. It is also used as a flux in welding and soldering.
From mining to processing of metals, borates can play an important role in metallurgical processes. Therefore, it can make excellent fluxes, removing metal oxides and dissolving impurities present in recovery metals.
Glass Making
Borax is the main component in glass making and pottery glazes in the ceramics industry. A soft, light, colorless crystalline solid substance, sodium tetraborate decahydrate is used mainly in the manufacture of optical and hard glass.
Water Softening
Water softening is a process in which we remove calcium and magnesium cations from hard water. Due to the facts of the low solubility of calcium and magnesium borates, borax is used as a cleaner or softener of water. It is used to introduce sodium ions to make water soft.
Ca2+ (Aq) + Na2B4O7 (aq) → CaB4O7 (s) + 2Na+ (aq)
Mg2+ (aq) + Na2B4O7(aq) → MgB4O7 (s) + 2Na+ (aq)
Borax is commonly suitable for removing the permanent and temporary hardness of water that we use for cleaning our clothes.
Uses of Borax in Chemistry
A soft, light, colorless crystalline powder borax is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to make buffer solutions. In biochemistry and analytical laboratories, such buffer solution is used for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of DNA and RNA molecules. It is also used in chemistry for the quantitative chemical analysis of transition metal salts.
Borax Medicinal Uses
In medicine, it is a good antiseptic. However, it is also used to manufacture enamel for teeth. A small amount of borax is used to make eye drops that control the pH level of your eyes and retain moisture.
Borax is one of the most important boron compounds used to make various cosmetic products and enamel glazes. However, it has many health issues when we swallow it by itself or breathe it.
Borax Uses for Cleaning
The pure and powder form of borax has many uses and it has been long used in household cleaning and stain removal. In household cleaning, it has uses mostly for cleaning drains and toilets, cleaning floors, removing stains from sinks, removing rust, deodorizing rugs and carpets, cleaning outdoor furniture, freshening shoes, etc.
Uses of Borax in Laundry
Borax has uses in laundry to whiten and brighten clothes. It can remove orders and soften hard water to reduce mineral deposits left behind on the fabrics of your clothes. Therefore, it is a popular laundry booster that is safe to use.
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and sodium tetraborate decahydrate are both used in laundry to brighten clothes. However, borax (pH = 9.5) is slightly alkaline than sodium bicarbonate (pH = 8). Therefore, among these two, sodium bicarbonate is the best choice for cleaning clothes in laundry.
Borax Fertilizer
Boron is an important micronutrient or plant nutrient that is needed for all crops to control flower and fruit shedding and increase the sweetness, size, and production. Borax fertilizers commonly contain 10.5% boron and are used to fulfill the deficiencies of boron in crops.
Other uses of Borax
- Borax can be used as the neutron-capturing shield for the safe storage and transportation of radioactive substances.
- Boric acid and sodium tetraborate decahydrate kill insects by targeting their stomachs and nervous systems. Therefore, it is used in toxic poisonous pests or insecticide control chemicals for killing ants or roaches.
- In the swimming pool, it is used as a buffering agent to control the pH of the swimming pool.
- It is used for the preparation of glaze for pottery, and stiffening candle-wicks.
- A mixture of sodium tetraborate decahydrate and ammonium chloride is also used as a flux for welding and soldering iron, gold, silver, and steel.
Toxicity
Borax is categorically safe to use as laundry boosters, hand soaps, and some kinds of toothpaste. Unlike many other sodium salts, it does not produce skin irritation.
However, it has many health issues when we swallow it by itself or breathe it. Short-term consumption can cause various health issues such as stomach irritation, vomiting, and diarrhea. When swallowed or eaten, it also causes serious side effects such as skin, eye, and respiratory irritation, digestive problems, fertility issues, kidney problems, death, organ damage, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Borax?
Borax is a commonly uses salt of boric acid that occurs with the chemical name sodium tetraborate decahydrate with formula Na2B4O7.10H2O, or Na2[B4O5(OH)4].8H2O. It is a soft, light, colorless crystalline mineral that has a wide variety of uses.
The IUPAC name of borax is sodium tetraborate decahydrate but it is also called simply sodium tetraborate or disodium tetraborate. Such inorganic salt consists of the chemical elements boron, sodium, oxygen, and hydrogen.
How to Make Borax?
Boiling the mineral colemanite with an alkaline solution of sodium carbonate uses to make sodium tetraborate decahydrate. It is also made from boric acid by heating with sodium carbonate.
What is Borax Used For?
Borax powder is a naturally occurring ore that has a wide range of industrial uses in various fields such as metallurgy, household and laundry cleaning, chemistry, water softening, glass making, fertilizer, etc. Due to its antifungal properties, it can be used to kill fungi or inhibit their growth. It is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to make buffer solutions.
Borax and boric acid have anti-insecticide properties and they kill insects by targeting their stomachs and nervous systems. It is also used as a solvent for metal-oxide slags in metallurgy. Therefore, it dissolves many metallic oxides when fused with them.
What is Borax Chemical Formula?
Borax powder (chemical name sodium tetraborate decahydrate) has the chemical formula Na2B4O7.10H2O, or Na2[B4O5(OH)4].8H2O. The IUPAC name of borax is sodium tetraborate decahydrate but it is also called simply sodium tetraborate or disodium tetraborate.