Neon on the Periodic Table
Neon (symbol Ne), a chemical element, inert gas, or noble gas of Group-18 of the periodic table discovered through its physical properties like the electromagnetic spectrum. The colorless, odorless, tasteless, monoatomic neon gas is used widely in fluorescent lamps. It occurs to the extent of 18 ppm by volume in dry air and 5 × 10−5 ppm by weight in igneous rocks. The name of the lighter gas, neon derived from the Greek latter neos meaning new. In solid-state, it forms a face-centered cubic crystal lattice.
Who Discovered Neon?
English natural philosopher and scientist Henry Candavis 1785. He observed that the small sample of air in the atmosphere contains a small volume of gas (1/120 part) even after repeated sparking with excess oxygen.
In 1898, British chemists Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers discovered three new elements neon, krypton, and xenon from the Greek words new, hidden, and strange by low-temperature distillation of liquid air.
Properties of Neon
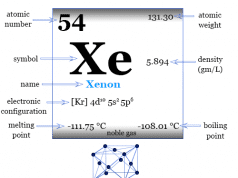
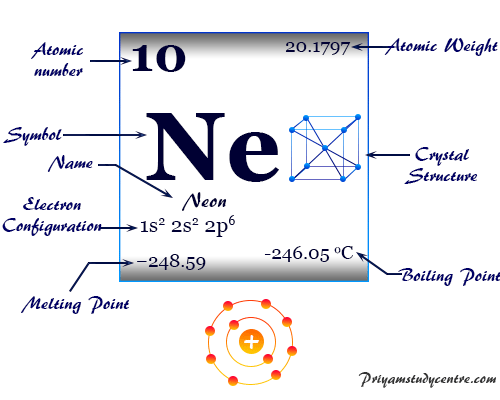
The inert gas, neon has the chemical symbol Ne, atomic number 10, and a heat capacity ratio (Cp/Cv) close to 1.66. Due to the filled valence orbital, the oxidation number or state is zero.
| Name | Neon |
| Symbol | Ne |
| Discovery | Sir William Ramsay and Morris Travers in 1898 |
| Name derived from | The Greek ‘neos’ means new |
| Properties of neon | |
| Atomic number | 10 |
| Atomic weight | 20.1797 |
| Electron per shell | 2, 8 |
| Electronic Configuration | [He] 2s2 2p6 |
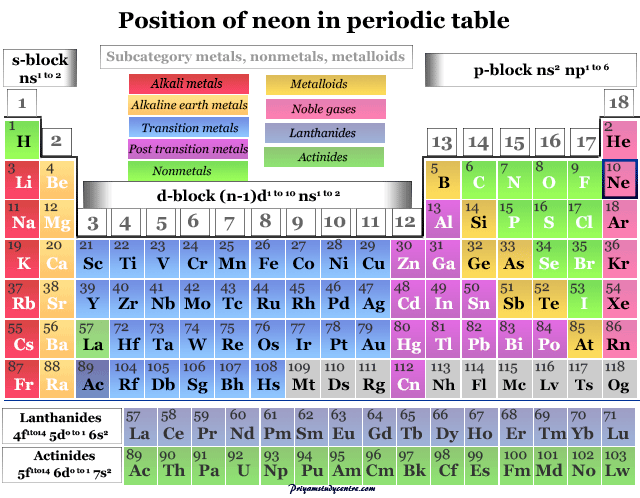
| Group | 18 |
| Period | 2 |
| Block | p-block |
| Common isotope | 20Ne |
| State at 20°C | Gas |
| Melting point | −248.59 °C, −415.46 °F |
| Boiling point | −246.046 °C, −410.883 °F |
| Density | 0.89990 g/liter at 1 atm |
| Critical point | 44.4918 K, 2.7686 MPa |
| Molar heat capacity | 20.79 J mol−1 K−1 |
| Oxidation states | 0 |
| Atomic radius (non-bonded) | 1.54 Å |
| Covalent radius | 0.62 Å |
| Electron affinity (kJ mol−1) | Unknown |
| Electronegativity | Unknown |
| Ionization energy | 1st: 2080.7 kJ/mol |
| 2nd: 3952.3 kJ/mol | |
| 3rd: 6122 kJ/mol | |
| CAS number | 7440-01-9 |
Where is Neon Found?
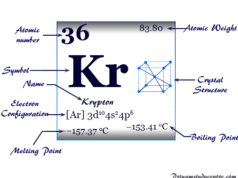
It is found to the extent of 18 ppm by volume in dry air and 7 × 10−5 ppm by weight in igneous rocks. Like other noble gases (helium, Argon, krypton), neon is mainly obtained as by-products of the liquefaction of air.
The rare gases can also be fractionated effectively by their preferential adsorption on charcoal at preferred temperatures. At −180 °C charcoal adsorbed argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. Worming the charcoal to −80 °C produced almost pure argon. After the adsorption of Ar and heavier rare gases, the lighter Ne and He are adsorbed at −225 °C.
Isotopes
Neon has three stable isotopes, 20Ne (90.92 percent), 21Ne (0.26 percent), and 23Ne (8.82 percent). 17 radioactive isotopes were also obtained from different types of nuclear reactions or thermonuclear reactions.
Chemical Compounds
Neon is the second-lightest noble gas after helium. It contains complete valence s and p-subshells to make a very stable configuration. The energy required for the promotion of an electron to the next vacant orbitals is quite large.
This fact suggests that the covalent bonding of the gas is very unfavorable. The formation of ionic compounds by chemical bonding with fluorine is unlikely due to the high positive entropy and free energy for the formation of ionic compounds. Therefore, No stable chemical compounds of Ne have been observed and the molecule of the element consists of single atoms.
Reactivity of Neon
Solid clathrate hydrate was produced from water ice and neon gas at high pressures and −30 °C temperature. The clathrate cannot be called a true compound since it is bound through hydrogen bonding. The noble gas molecules freely move through the materials. The gas is liberated when heating.
The ionization energy is highest for all noble gases of the periodic table but they do decrease down the group. The facts indicate that if the noble gases show any reactivity, they are present at the lower position of the group.
What is Neon Used for?

- It is widely used in electronics for filling photoelectric cells, voltage stabilizers, vacuum tubes, and high-voltage indicators. It is also used in wavemeter tubes, television tubes, helium-neon lasers, and similar instruments.
- The so-called neon lights or bright reddish-orange lights in advertisements contain a mixture of noble gases used in the various colors of fluorescent light.
- It is a non-conductor of electricity but under low pressure and high voltage, it starts conducting. Under these conditions, the ionization of atoms occurs.
- The exited ion while returning to its ground state emits a characteristic reddish-orange light which is used in conduction lamps or signs tables.
- Liquid neon is used as a cryogenic refrigerant for the refrigeration of helium gas molecules. It is more expensive than the other liquefied substances. Therefore, we cannot be used to attain lower temperatures like liquid nitrogen or helium due to the high price of neon gas.