Glycogen
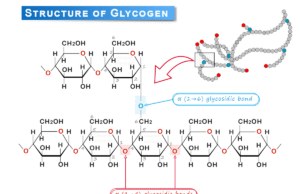
Glycogen Storage
Glycogen is a carbohydrate or an extensively branched polymer of glucose stored primarily in the cells of the liver, skeletal muscle, and brain....
Adenosine Triphosphate
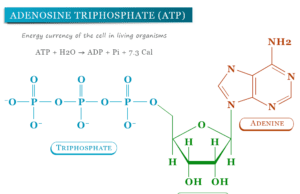
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in biology is a unique and most important high-energy biomolecule in living cells. The structure of adenosine triphosphate contains...
Electrical Energy
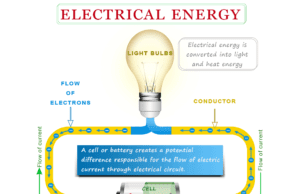
Electrical Energy and Power
Electrical energy is the energy obtained from the electric potential or kinetic energy of the charged particles (electrons) while electric power...
Natural Resources
Management of Natural Resources
Natural resources are living and non-living components and energy sources of nature that are used by humans to meet their requirements....
Chemical Reaction
Chemical Reactions Examples
A chemical reaction in chemistry is a process that transforms one or more substances or reactants to form new types of substances...
Peptides
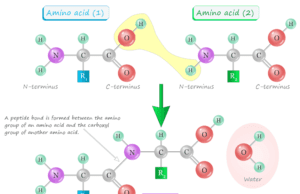
List of Peptides and What They Do?
Peptides are a continuous and unbranched list of amino acid biopolymers joined together by peptide bonds. A list...
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium Carbonate Na2CO3
Sodium carbonate also called washing soda or soda ash is an inorganic compound or salt with the chemical formula Na2CO3. In pure...
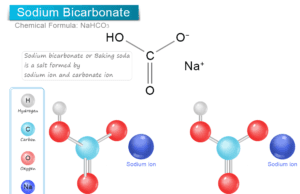
Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate Baking Soda
Sodium bicarbonate (chemical formula NaHCO3), also called baking soda or sodium hydrogen carbonate is a commonly uses effervescent salt or compound...
Calcium Oxide
Calcium Oxide Quicklime
Calcium oxide (chemical formula: CaO), also called quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound in our daily lives formed...
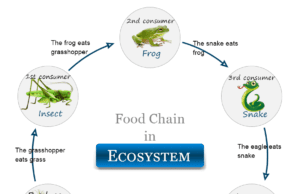
Ecosystem
Definition of Ecosystem
An ecosystem or ecological system is a structural and functional unit of the biosphere where regular energy input and matter circulation occur....