Osmosis
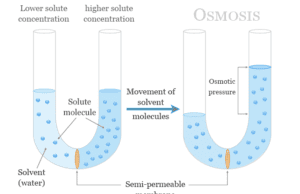
Osmosis and Reverse Osmosis
Osmosis is a natural process of movement or diffusion of solvent or water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a lower...
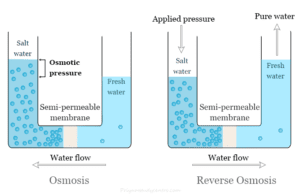
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration System
Reverse osmosis (RO) system is a multi-stage water filtration process that removes contaminants from unfiltered or feed water when pressure...
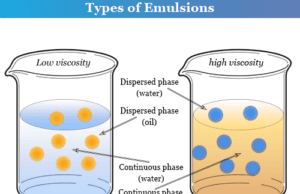
Emulsion
Emulsion Definition in Chemistry
Emulsion in chemistry is formed when a liquid is dispersed in another liquid that is not miscible to each other. Milk...
Colloid
Colloid Solution
Colloid solution is a two-phase heterogeneous system in which one phase is dispersed in a fine state ranging from 1 nanometer (nm) to...
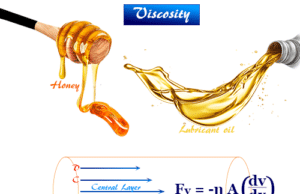
Viscosity of liquids
Measuring Viscosity of Liquids
Viscosity of liquids in chemistry is measuring the resistance to flow exhibited by fluids (liquids or gases) like glycerol, ester, oils,...
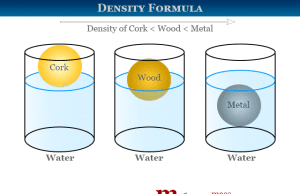
Density
Density Calculation Formula
Density calculation formula for solids, liquids, and gas molecules is the measurement of mass per unit volume at a given temperature and...
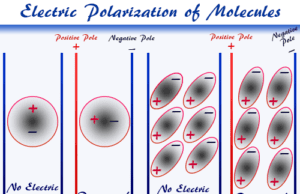
Electric Polarization
What is Electric Polarization?
Electric polarization occurs when a non-polar molecule is placed between two parallel plates with an applied electric field. The electric field...
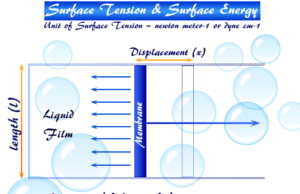
Surface Tension
Surface Tension of Liquid
Surface tension or surface energy is the most important characteristic property of liquid origin at the surfaces and is displayed when...
Dipole Moment
Bond Moment and Dipole Moment
Dipole moment formula in chemistry is used to find out or calculate the net bond moment and polar character or...
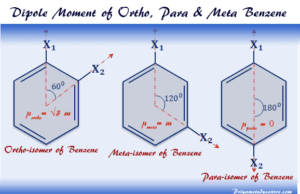
Dipole Moment
Dipole Moment of Molecules
Dipole moment molecules benzene and substituted benzene (xylene) in chemistry can be calculated by different theoretical or experimental formula. For example,...