What is Iron Deficiency Anemia?
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of nutritional disorder that occurs when your body doesn’t have an adequate amount of healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells contain an iron-containing protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen from the lungs to all body parts. A deficiency of iron, folic acid (folate), and vitamin B12 may impact your body to make healthy red blood cells.
Fatigue and tiredness are the most common symptoms of iron deficiency anemia, but a person does not experience any symptoms at an early stage of deficiency.
Iron deficiency can be prevented by eating sufficient iron-reached foods or supplements. If your doctor suspects that you are bleeding internally, some additional tests or treatments are necessary to prevent iron deficiency.
Meat, nuts, spinach, and foods made with iron-fortified flour are high sources of iron in our daily diet. Iron and vitamin C supplements may be recommended for people who suffer from iron deficiency.
Anemia may be caused by lack of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in your blood. Similarly, iron deficiency anemia is caused by a lack of iron in your blood. It may affect the growth and development of your children and fetus during pregnancy.
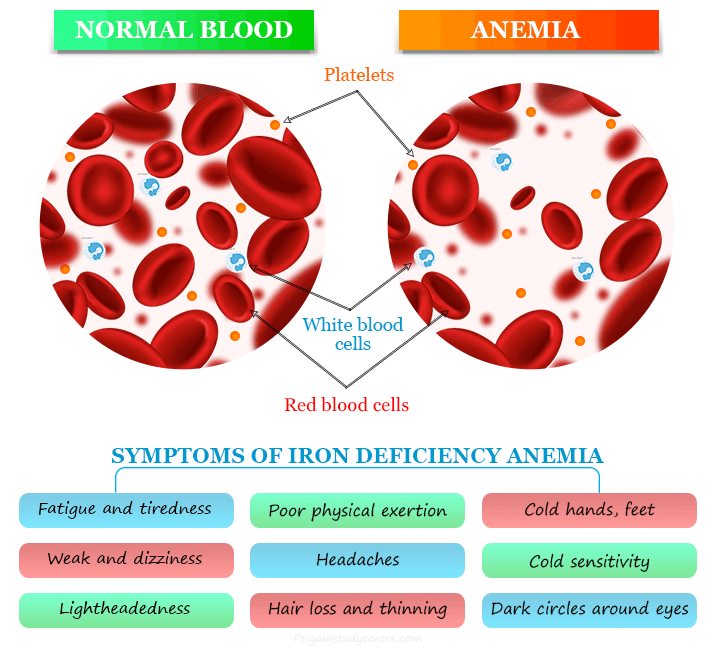
Iron Deficiency Anemia Symptoms
Anemia is derived from the Greek word anaimía meaning lack of blood. It occurs when low levels of healthy red blood cells in your whole blood. Anemia has many types but iron-deficiency anemia is the most common because most anemia cases in women and men occur due to iron deficiency.
Fatigue and tiredness are the most common symptoms of iron deficiency but early stage it does not show any particular symptoms. The common signs and symptoms of iron deficiency anemia in men and women may include:
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Weak and dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Poor physical exertion
- Headaches
- Decreased ability to concentrate
- Cold hands, feet, and dry lips
- Cold sensitivity
- Dark circles around the eyes
- Hair loss and thinning
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when a woman has insufficient stores of iron which help in manufacturing hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein that enables red blood cells to carry oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body.
If your body does not have sufficient iron to make hemoglobin, oxygen does not travel easily from the lungs to other parts of the body that causing fatigue and other health-related problems.
Causes of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Like other vitamins and minerals, iron is an important mineral that is used in the formation of red blood cells in the body. It is a critical component of hemoglobin and most of the iron found in the body is bound to hemoglobin. When your body contains sufficient iron to meet its biological functions, the remainder is stored mostly in the bone marrow and liver for later use.
Iron deficiency anemia may be caused commonly by blood loss, insufficient dietary intake, or poor absorption of iron from food. Women with a deficiency of iron-rich foods such as eggs, meat, and dark green vegetables are at a greater risk of developing iron deficiency. Therefore, vegetarians have more risk of developing the condition of iron deficiency anemia.
Blood Loss
Blood loss may happen due to heavy periods, childbirth, uterine fibroids, stomach ulcers, colon cancer, and urinary tract bleeding.
Menstrual bleeding
Menstrual bleeding or heavy periods is the most common cause of iron deficiency anemia in women. It is commonly faced by women of reproductive age. Women with menorrhagia or heavy menstrual periods are at risk of iron-deficiency anemia because they are losing a larger amount of blood during menstruation than being replaced from their daily diet.
Gastrointestinal bleeding
The gastrointestinal tract in the human body may include the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, rectum, and anus. Gastrointestinal bleeding is a leading cause of iron deficiency anemia in men and post-menopausal women.
Gastrointestinal bleeding may also occur due to the regular use of some groups of medicine such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, clopidogrel, and anticoagulants. It is a symptom of many digestive systems disorders such as von Willebrand disease and polycythemia vera.
Insufficient Dietary Intake
Another common cause of iron deficiency is unhealthy nutrition. Insufficient dietary intake or poor absorption of iron-rich foods and supplements can also cause iron deficiency in your body. Therefore, iron deficiency anemia can be prevented and treated by eating sufficient amounts of iron-rich foods or iron supplementation.
A huge number of people have been affected by iron deficiency anemia due to a lack of dietary iron. Women and young children are most commonly affected by iron deficiency.
Iron Deficiency in Pregnant Women
A pregnant woman has a high risk of iron deficiency anemia because their bodies need more iron to support their increased blood volume. Therefore, pregnant women need much iron reached foods and supplements during their pregnancy period.
Iron Deficiency in Children
The daily needed iron for a person depends mainly on their age and gender. Children required a lot of iron because they are growing rapidly. Teenage girls and women need more iron than men because they suffer from menstrual bleeding.
A baby has lots of storage iron when they birth but the storage iron may run out after 4–6 months of age. Infants who intake cow’s milk too early may also be suffering from anemia due to gastrointestinal blood loss.
Iron Deficiency due to Blood donation
Risk of iron deficiency anemia developing for frequent blood donors because they lose roughly 200 mg of iron with each whole blood donation. Therefore, blood banks screen people for anemia before donating blood. A person loses less iron when he/she donates platelets or white blood cells.
Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Your doctor can diagnose iron deficiency anemia by following tests,
- Red blood cell size and color: During iron deficiency, the size of red blood cells is smaller and the colour of red blood cells is paler than normal.
- Hematocrit: Our blood is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets suspended in plasma. Hematocrit is the percentage by volume of red blood cells or hemoglobin in human blood. Normal levels are generally ranging between 35.5 and 44.9 percent for adult women and 38.3 to 48.6 percent for adult men. Therefore, hematocrit levels may use to diagnose iron deficiency anemia in men and women
- Hemoglobin: Lower than normal hemoglobin levels indicate anemia and it causes various health problems. Therefore, a diagnosis of hemoglobin may be used to identify an iron deficiency. The normal hemoglobin levels range from 13.2 to 16.6 g/dL for men and 11.6 to 15 g/dL for women.
- Ferritin: It is a protein that helps store iron in your body. A low ferritin level usually indicates a low level of stored iron in the human body. Therefore, your doctor may diagnose iron deficiency by measuring ferritin levels in your body.
If you have underlying conditions your doctor may use additional tests such as endoscopy, colonoscopy, ultrasound, etc.
Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Treatment for iron deficiency anemia depends on its causes. For example, if iron deficiency anemia is caused due to blood loss, we need to treat the cause of your blood loss. Those who suffer from iron deficiency anemia should limit physical activity until the anemia problem may resolve.
It can be treated and prevented by intake a healthy diet that reached with vitamins and iron. It may also resolve by taking iron supplementation and the source of bleeding or an iron-absorption problem.
Eat iron-rich foods
Adding more iron-reached foods such as meat, eggs, peanut butter, spinach, kale, and beans to your daily diet may help to fight against iron deficiency anemia.
Heme and nonheme are the two main dietary forms of iron found in our daily diet. Plants and iron-fortified foods provide nonheme iron for our body whereas animal foods contain both forms for our good health.
The absorption of iron from food sources is very low. You can absorb higher levels of heme iron than nonheme iron. The most common iron reached foods may include:
- organ meats and meat such as beef, pork, and poultry
- dark leafy greens vegetables such as spinach, collard greens, and kale
- dried fruit such as raisins and apricots
- legumes such as peas, beans, etc
- seeds and nuts
- iron-fortified foods, such as breakfast cereals
You may avoid taking medications, supplements, or foods that contain calcium for higher absorption of iron. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is beneficial because it helps to enhance iron absorption.
Bell peppers, oranges, grapefruit, kiwifruit, broccoli, strawberries, and grapefruit may help to boost the absorption of iron from daily foods which we eat.
Iron Supplements
Your doctor may treat iron deficiency by providing oral iron supplementation which is available in multiple forms. Some oral iron supplements are in the form of pills and some are drops for children.
For better absorption of iron in your body you may intake iron on an empty stomach because low gastric pH levels may facilitate higher absorption of iron.
Medicine that immediately relieves heartburn symptoms may reduce the absorption of iron. Therefore, you may intake iron supplements before two hours or after four hours of taking any antacids.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) may improve the absorption of iron in your body. Therefore, your doctor might recommend taking iron tablets with a glass of orange juice or a vitamin C supplement for better treatment of iron deficiency anemia.
Treating underlying causes of iron deficiency
If the supplementation of iron doesn’t increase iron levels in your blood, you need to treat anemia by treating the source of bleeding or an iron absorption problem. After investigating the causes of bleeding, we need to take proper medications.
- Menstrual periods with abnormally heavy or prolonged bleeding may cause iron deficiency in women. There are many effective treatments that are used for abnormally heavy or prolonged bleeding.
- Peptic ulcers may decrease iron levels in your body. Doctors may use various antibiotics and other medications to treat peptic ulcers.
- Your doctor may use surgery to remove a bleeding polyp, a tumor, or a fibroid to treat the cause of the iron deficiency.
- Your doctor may also give iron intravenously or blood transfusions to treat iron deficiency anemia.
Always talk with a doctor if you have any signs and symptoms of iron deficiency because if untreated it may cause various health complications such as heart problems, depression, a higher chance of infections, pregnancy issues, etc.
Iron deficiency is a more common and oldest medical disorder in women than in men. People who are pregnant or have heavy menstrual periods have the highest risk of iron deficiency anemia.