Essential Vitamins and Minerals
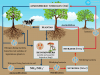
Vitamins and minerals are lists of essential micronutrients that use our body to carry out a range of normal biological functions. Most of these list of vitamins and minerals or essential elements are not produced in our bodies and we need to intake these micronutrients from various food sources. Vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K are essential organic compounds that are required in our diet in small amounts to perform various biological functions for normal growth and health. Like vitamins, the minerals that are essential for good health may include calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, chloride, magnesium, iron, zinc, iodine, sulfur, cobalt, copper, etc. The minerals are inorganic elements that are essential for bone, blood coagulation, neuromuscular irritability, acid-base equilibrium, fluid balance, and osmotic regulation.

Vitamins and Minerals List
Most people should be able to intake vitamins and minerals by taking a balanced diet but many people choose vitamin and minerals supplements for better health. The list of 13 vitamins that are needed to maintain our good health may include,
- Vitamin A
- D Vitamin
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
- Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C)
- Thiamine (vitamin B1)
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2)
- Niacin (vitamin B3)
- Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5)
- Vitamin B6
- Biotin (vitamin B7)
- Folic acid (folate, vitamin B9)
- Vitamin B12
The most common list of macrominerals that are used to control various biological functions in human bodies may include,
- Calcium
- Chloride
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- potassium
- Sodium
- Sulfur
The trace minerals that help to control various biological functions in human bodies and also maintain good health may include,
- Chromium
- Copper
- Fluoride
- Iodine
- Iron
- Manganese
- Molybdenum
- Selenium
- Zinc
Sources of Vitamins
The list of vitamins that are needed for our good health and their important sources are given below in the table,
| Vitamin | Sources |
| Vitamin A | Cheese, eggs, oily fish, fortified low-fat spreads, milk, yogurt, and liver products are the main sources of vitamin A |
| Thiamine (vitamin B1) | It is found in peas, some fresh fruits, nuts, whole grain bread, some fortified breakfast cereals, and liver |
| Riboflavin (vitamin B2) | Riboflavin is found mainly in milk, eggs, fortified breakfast cereals, mushrooms, and plain yogurt |
| Niacin (vitamin B3) | Meat, fish, wheat flour, and eggs are important sources of niacin (vitamin B3) |
| Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) | It is found mainly in chicken and beef liver and kidneys, eggs, mushrooms, and avocado |
| Vitamin B6 | Vitamin B6 is found in a wide variety of foods such as pork, poultry, some fish, peanuts, soya beans, wheatgerm, oats, etc |
| Biotin (vitamin B7) | A very low level of biotin (vitamin B7) is found in a wide range of foods |
| Folic acid (folate, vitamin B9) | Good sources of folate are broccoli, brussels sprouts, leafy green vegetables, chickpeas, beans, liver, etc |
| Vitamin B12 | Meat, fish, milk, cheese, eggs, and some fortified breakfast cereals are reached sources of vitamin B12 |
| Vitamin C | Vitamin C is found in a wide variety of fruits and vegetables such as citrus fruit, oranges, peppers, strawberries, blackcurrants, broccoli, brussels sprouts, and potatoes |
| Vitamin D | Oily fish, red meat, liver, egg yolks, cow’s and soy milk, and fortified foods |
| Vitamin E | Plant oils such as vegetable oil, sunflower, soya, corn and olive oil, nuts and seeds, and wheatgerm are the common sources of vitamin E |
| Vitamin K | Vitamin K is found mainly in green leafy vegetables such as broccoli and spinach, vegetable oils, and cereal grains |
Sources of Minerals
The list of important macrominerals that are needed for our good health and their important sources are given below in the table,
| Macromineral | Sources |
| Calcium | Milk, cheese, other dairy foods, soya drinks, fish, and green leafy vegetables such as curly kale, okra, etc |
| Chloride | A small amount of chloride is naturally found in meat and seafood, but the main sources in our diet are sodium chloride or table salt |
| Magnesium | Legumes, dark green leafy vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, fortified cereals, fish, poultry, and beef meat |
| Phosphorus | The richest sources of phosphorus are dairy, red meat, poultry, seafood, legumes, and nuts |
| Potassium | Leafy greens, beans, nuts, dairy foods, winter squash, raisins, apricots, potatoes, broccoli, avocado, chicken, salmon, dairy, yogurt, and plant milk (soy, almond) |
| Sodium | Low level of sodium is found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, meats, and dairy foods |
| Sulfur | Turkey, beef, eggs, fish, chicken, nuts, seeds, grains, legumes, allium vegetables, and cruciferous vegetables |
Sources of Trace Minerals
| Trace Minerals | Sources |
| Chromium | Whole grains, high-fiber bran cereals, broccoli, green beans, potatoes, apples, bananas, beef, poultry, egg yolks, fish, and coffee |
| Copper | Organ meats, shellfish, fish, nuts, sunflower seeds, chocolate, whole wheat pasta, potatoes, and spinach |
| Fluoride | Black tea and coffee, fluoridated water, canned shellfish, oatmeal, and potatoes |
| Iodine | Seaweed such as nori, kelp, kombu, wakame, fish, shellfish, iodized table salts, milk, cheese, yogurt, eggs, beef liver, and chicken |
| Iron | Oysters, clams, mussels, beef or chicken liver, organ meats, canned sardines, fortified breakfast cereals, beans, dark chocolate, nuts, seeds, etc |
| Manganese | Shellfish, nuts, brown rice, oatmeal, legumes, black tea, black pepper, spinach, and pineapple |
| Molybdenum | Legumes, beef liver, plain yogurt, milk, fortified whole-grain cereals, whole-wheat bread, and bananas |
| Selenium | Brazil nuts, fin fish and shellfish, beef, turkey, chicken, fortified cereals, whole-wheat bread, beans, and lentils |
| Zinc | Shellfish, beef, poultry, pork, legumes, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and fortified breakfast cereals |
Functions of Vitamins
Vitamins and minerals are also essential micronutrients that help to maintain our healthy life. There are thirteen essential vitamins that are found in various food sources and are useful for our healthy life. These thirteen vitamins may are classified into two categories,
- Fat-soluble vitamins
- Water-soluble vitamins
Functions of Fat Soluble Vitamins
Among these thirteen, four vitamins such as A, D, E, and K are fat soluble. The most important functions of such fat-soluble vitamins are,
Vitamin A
It is an important micronutrient for healthy vision, teeth, bones, soft tissue, mucous membranes, and skin. Vitamin A may also stimulate the production and activity of white blood cells and regulate cell growth and division in the human body that is needed for reproduction.
Vitamin D
It helps to regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body that is needed to maintain healthy bones, teeth, and muscles.
Vitamin E
It helps maintain healthy skin and eyes and strengthens the immune system or improves the body’s natural defense against illness and infection.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is an antioxidant that helps the body to form red blood cells. Some studies suggest that vitamin K is important for bone health.
Functions of Water Soluble Vitamins
The remaining nine vitamins such as vitamin C and eight B vitamins are water-soluble. The main biological functions of these nine vitamins are given below,
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Thiamine or vitamin B1 is an important micronutrient for our healthy hair, heart, and brain. It also helps the body cells to convert carbohydrates that we eat into energy.
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is an essential micronutrient that plays a key role in the growth of cells and the breakdown of fats, steroids, and medicines. Most riboflavin absorbed from different foods and supplements may not be stored in the body. Therefore, excess amounts are excreted in the urine.
Vitamin B3
Niacin (vitamin B3) helps your body release energy from food and keeps the nervous system and skin healthy.
Vitamin B5
It is an essential nutrient that metabolizes food that we eat into energy. It also helps in the production of hormones and cholesterol.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
Vitamin B6 helps in the formation of red blood cells and maintains brain function. It also plays an important function in protein metabolism.
Vitamin B7
A very small amount of biotin is needed to help the body make fatty acids. It plays a vital role in enzymes that break down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins in food to release energy. Biotin also helps to regulate signals sent by cells and the activity of genes (DNA and RNA).
Vitamin B9
Folate helps mainly to maintain healthy red blood cells and reduce the risk of birth defects. A lack of folate may cause folate deficiency anemia.
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Like the other B vitamins, it is important for our metabolism. Cobalamin may also help to form red blood cells (hemoglobin) and maintain the central nervous system.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that promotes healthy teeth and gums. It is also helpful for absorbing iron in your body and maintaining healthy tissue and wound healing.
Essential Minerals
Essential minerals are inorganic nutrients necessary to maintain the body’s health. A large number of inorganic elements are essential for all life processes and they are absorbed by plants or consumed by animals. A deficiency of vitamins and minerals leads to an abnormality in the metabolic functioning of animals.
Based on their quantitative requirements, minerals are further divided into two broad types:
Functions of Minerals
Macrominerals are minerals that require large amounts to maintain the biological function of our bodies. Our body needs and stores large amounts of macrominerals. Like trace minerals, they are no more important to your health and they are present in your body in greater amounts.
Calcium
It helps to build healthy bones and teeth, regulate muscle contractions, including your heartbeat, and help in your blood clotting. A lack of calcium may cause rickets in children and osteomalacia or osteoporosis in later life.
Chloride
Chloride helps to regulate the amount of fluid and types of nutrients going in and out of the cells and maintains proper pH levels. It also stimulates stomach acid needed for digestion, controlling the function of nerve and muscle cells, and facilitates the flow of oxygen and carbon dioxide within human cells
Magnesium
The mineral magnesium plays an important role in assisting more than 300 enzymes in controlling various biological functions. In our bodies, it helps to build proteins strengthen bones, and regulate blood sugar, high blood pressure, and muscle and nerve functions.
It also acts as an electrical conductor that contracts muscles and makes the heart beat steadily.
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a key component of our bones, teeth, and cell membranes. It helps to activate enzymes, keeps blood pH levels in a normal range, and regulates the normal function of nerves and muscles. It is also a building block of DNA, RNA, and ATP.
Potassium
Like sodium, it helps to maintain normal levels of fluid inside our cells. It also helps muscles to contract and maintain normal blood pressure in your body.
Sodium
A small amount of sodium is used by the human body to conduct nerve impulses, relax muscles, and maintain the proper balance of water and minerals.
Sulfur
Sulfur in the human body helps to build and fix your DNA and protect cells from damage that may cause cancers. It may also assist your body to metabolize food and contributes a significant role in the health of your skin, tendons, and ligaments. The two important amino acids that include sulfur are methionine and cysteine.
Functions of Trace Minerals
Chromium
Chromium helps to enhance the action of insulin. It is also involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Copper
Copper is a naturally occurring metal and an essential trace mineral that assists enzymes that produce energy for the body, break down and absorb iron, and build red blood cells, collagen, connective tissue, and brain neurotransmitters.
It supports our normal brain development and immune functions. It is a component of the enzyme superoxide dismutase that dismantles harmful free radicals.
Fluoride
Fluoride is a trace mineral used by your body in preventing and reversing dental caries and building strong teeth and bones. Children absorb fluoride more efficiently than adults because their teeth and bones are rapidly growing.
Iodine
The trace mineral iodine is not made by the human body so must be obtained from food or taking supplements. The important biological function of iodine is to make the thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These two hormones play an important role in the creation of proteins and enzymes that regulate normal metabolic function.
Iodine deficiency may inhibit the biological functions of these thyroid hormones and cause the medical conditions of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Iron
Iron is an important trace mineral that helps maintain healthy blood. It is an important component of hemoglobin, a type of protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body. A lack of iron may cause iron-deficiency anemia in many peoples of the world. It is also an important part of the protein myoglobin that carries and stores oxygen in our muscle tissues.
Iron plays a significant role in brain development and growth in children and in the normal production and function of various cells and hormones.
Manganese
A small amount of trace mineral manganese is essential for controlling various biological functions. It can not be produced in our bodies, therefore we need to intake manganese from food or supplements.
Manganese is a coenzyme that controls the activity of enzymes that are involved in breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and cholesterol. It also controls enzymes that help to build bones and keep the immune and reproductive systems healthy. It works with vitamin K in wound healing by clotting the blood.
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is an essential trace mineral that is an important component of four different enzymes in the body. These enzymes may help to break down proteins, alcohol, drugs, and toxins. Molybdenum-reached enzymes may also help to break down purines and sulfites.
Selenium
A small amount of trace mineral selenium is an essential component of various enzymes and selenoproteins that help to make DNA and protect against cell damage and infections. These selenium-containing proteins are also involved in reproduction and the metabolism of thyroid hormones.
Zinc
Product on sale