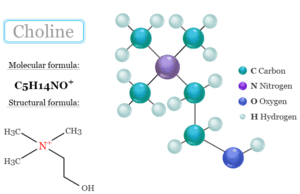
Vitamin List and Benefits
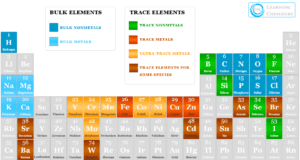
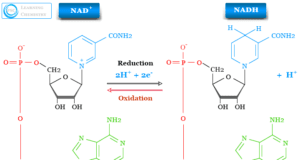
Vitamin is an organic compound or essential micronutrient found in various foods and necessary for the growth and good health of animals including humans. Most of a vitamin is not a single molecule but a list of related molecules called vitamers. In addition to oxygen, water, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and certain inorganic salts, all vitamins are also beneficial for humans and animals. Vitamins act as a catalyst in the generation of energy by utilizing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats properly and improving our immune system to save us from various diseases. Humans cannot live without vitamins. Except for vitamin D and B3, our body cannot synthesize a list of vitamins in our body. Therefore, we must obtain most of the vitamins through our diet or medicinal supplements.

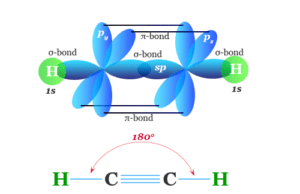
The word vitamin was derived from “vitamine”, a Latin word coined in 1912 by Polish-born biochemist Casimir Funk while working at the Lister Institute of Preventive Medicine. He created the name from the words vital and amine because these organic micronutrient food factors are vital for life and they were chemical amines. It is true for thiamine but vitamin C and other such list of micronutrients were not amines. The word vitamine was shortened to “vitamin” in English.
All Vitamins Names
| Vitamins | Vitamers | Solubility | |
| A | Retinol, Retinal, Retinic acid, beta-carotene, etc |
Fat | |
| B |
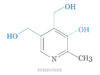
B1 | thiamine | Water |
| B2 | riboflavin | ||
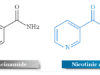
| B3 | niacin niacinamide |
||
| B5 | pantothenic acid | ||
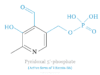
| B6 | pyridoxine, pyridoxamine, pyridoxal |
||
| B7 | biotin | ||
| B9 | folates, folic acid |
||
| B12 | cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin, methylcobalamin, adenosylcobalamin |
||
| C | ascorbic acid | Water | |
| D |
D1 | A mixture of molecular compounds of ergocalciferol and lumisterol with a 1:1 ratio | Fat |
| D2 | ergocalciferol | ||
| D3 | cholecalciferol | ||
| D4 | 22-dihydroergocalciferol | ||
| D5 | sitocalciferol | ||
| E | Tocopherols, Tocotrienols | Fat | |
| K |
K1 | Phylloquinone | Fat |
| K2 | Menaquinones | ||
Types of Vitamins
Thirteen vitamins that are useful for a healthy life have been arbitrarily classified into two types,
- Fat-soluble vitamins: Four vitamins such as A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble vitamins.
- Water-soluble vitamins: The remaining nine vitamins are water-soluble. Eight B complex and vitamin C are examples of water-soluble vitamins.
Sources of Vitamins
Most vitamins are obtained from various dietary food sources but some are synthesized in microorganisms. For example, microorganisms in the gut flora synthesize vitamin K and biotin.
A form of D3 (cholecalciferol) is synthesized from a derivative of the steroid cholesterol in the skin when exposed to a certain wavelength of ultraviolet light in sunlight
The human body can produce some vitamins from precursors which they consume from their dietary sources. For example, vitamin A is synthesized from beta-carotene, and niacin is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan.
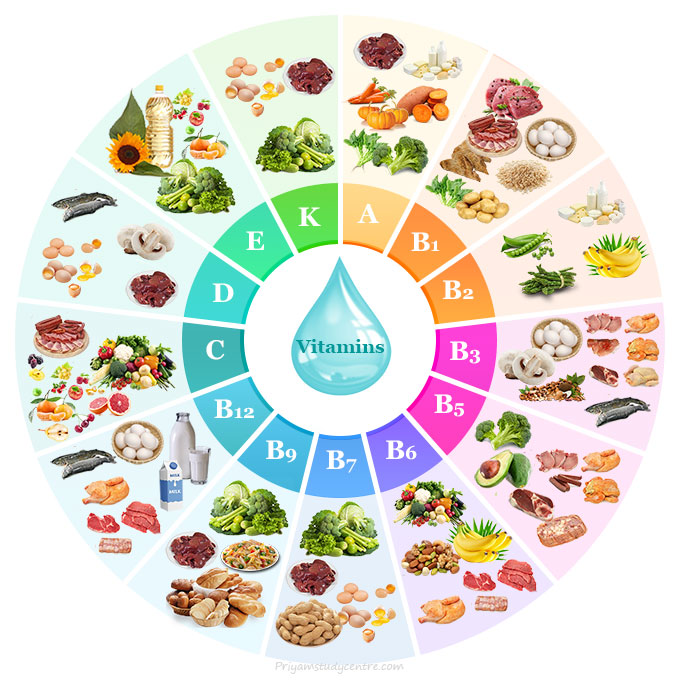
Vitamins in Foods
Vitamins are obtained generally from various plant and animal sources but B12 is the only micronutrient which obtains only from animal sources. The best sources of fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins with their deficiency diseases can be given in the table,
| Vitamins | Food sources | Deficiency disease(s) | |
| Fat-soluble | A | Fish, dairy products, oranges, ripe yellow fruits, leafy vegetables, carrots, pumpkin, squash, spinach | Night blindness, hyperkeratosis, and keratomalacia |
| D | Eggs, liver, fish-like sardines, mushroom-like shiitake | Rickets and osteomalacia | |
| E | Many fruits and vegetables, nuts and seeds, and seed oils | Deficiency is very rare but mild hemolytic anemia is found in newborn baby | |
| K | Leafy green vegetables such as spinach, egg yolks, liver | Bleeding diathesis | |
| Water soluble | C | Many fruits (mainly citrus fruits) and vegetables, liver | Scurvy and skin-related problems |
| B1 | Pork, wholemeal grains, brown rice, vegetables, potatoes, liver, eggs | Beriberi, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome | |
| B2 | Dairy products, bananas, green beans, asparagus | Ariboflavinosis, glossitis, angular stomatitis | |
| B3 | Meat, fish, eggs, many vegetables, mushrooms, tree nuts | Pellagra | |
| B5 | Meat, broccoli, avocados | Paresthesia | |
| B6 | Meat, vegetables, tree nuts, bananas | Anemia, Peripheral neuropathy | |
| B7 | Raw egg yolk, liver, peanuts, leafy green vegetables | Dermatitis, enteritis | |
| B9 | Leafy vegetables, pasta, bread, cereal, liver | Megaloblastic anemia and deficiency during pregnancy are associated with birth defects, such as neural tube defects | |
| B12 | Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk | Anemia or deficiency of hemoglobin | |
Vitamins Deficiency
They are essential nutrients that help our good health but deficiency may cause various health diseases. Deficiencies of vitamins are classified into two types primary and secondary.
- Primary deficiency: A primary deficiency occurs when an organism does not get enough of the vitamins in its food sources.
- Secondary deficiency: A secondary deficiency may occur due to an underlying disorder that prevents or limits the absorption or use of the vitamins due to lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive use of alcohol, or the use of medications.
Thiamine Deficiency
Thiamine deficiency can affect the cardiovascular, nervous, and immune systems of the human body. It commonly causes diseases like wet beriberi, dry beriberi, or Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.
Symptoms of thiamine deficiency can be hard to diagnose. The main signs and symptoms associated with thiamine deficiency might include:
- Weight loss
- Emotional disturbances
- Impaired sensory perception
- Weakness and pain in the limbs
- Irregular heartbeat
- Red blood cell status
- Abnormal urinary output
Riboflavin Deficiency
Riboflavin assists many enzymes in their various biological functions throughout the body. Therefore, a deficiency of riboflavin can cause various health problems. The common health problems caused due to riboflavin deficiency might include:
- Painful red tongue with a sore throat chapped and cracked lips
- Inflammation at the corners of our mouth
- Eyes can be itchy, watery, bloodshot, and sensitive to light
- Anemia
Niacin Deficiency
A deficiency of niacin causes pellagra, a reversible nutritional wasting disease characterized by four classic symptoms:
- Diarrhea
- Dermatitis
- Dementia
- Death
Vitamin B5 Deficiency
B5 (pantothenic acid) deficiency is rare because it can be found in a wide variety of food sources. The common symptoms of a B5 deficiency may include:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Depression
- Irritability
- Vomiting
- Stomach pains
- Burning feet
- Upper respiratory infections
Deficiency of Vitamin B6
A B6 deficiency commonly occurs when other B vitamins in the body are low, particularly B12 and folic acid. A mild deficiency may have no symptoms but a more prolonged deficiency may cause the following health problems:
- Microcytic anemia
- Electroencephalographic abnormalities
- Dermatitis
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis
- Neurologic symptoms (depression, somnolence, confusion, and neuropathy)
Vitamin B7 Deficiency
B7 (biotin) deficiency is rare in humans because biotin is widely available in various food sources and it can usually synthesize more than the body needs. It helps the body metabolize fats, carbohydrates, and protein in our body. The most common signs of biotin deficiency may include:
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Periorificial dermatitis
- Scaly, red rash around the orifices (eyes, nose, and mouth)
- Mild depression
- Generalized muscular pains (myalgia)
- Paresthesia
Deficiency of B9
Folate or B9 helps make DNA and produce red blood cells. Therefore, folate deficiency can lead to various health complications, especially in pregnant women. The most common sign and symptoms of a B9 deficiency may include:
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Weakness
- Sore tongue
- Headaches
- Pale skin
- shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Irritability
- Neurological issues
- Anemia (macrocytic, megaloblastic anemia)
Deficiency of B12
B12 deficiency anemia can cause a wide range of symptoms and health problems. It develops gradually but can worsen if the condition goes untreated. The most common signs and symptoms of B12 deficiency might include:
- Anemia
- Neurological and digestive disorders
- Feeling tired, weak, low-grade fevers and shakiness
- Lightheadedness and headaches
- Dizziness and breathlessness (rapid)
- A sore red tongue (glossitis)
- Feeling permanently cold, rapid heartbeat, cold hands, and feet
- Easy bruising and bleeding, lowering blood pressure and pale skin
- Nausea, stomach upset (dyspepsia), loss of appetite
- Weight loss, heartburn, constipation, diarrhea
- Severe joint pain, the paresthesia to the fingers and toes
- Angular cheilitis, mouth ulcers, bleeding gums
- Hair loss and thinning
- Dark circles around the eyes
Ascorbic Acid Deficiency
It is an essential nutrient and is consumed regularly to prevent deficiency. The deficiency is relatively rare in developed countries due to the availability of ascorbic acid in certain foods and supplements.
The most common risk factors for ascorbic acid deficiency in people are poor diet, alcoholism, anorexia, severe mental illness, smoking, and dialysis.
It is an important factor for our skin health. The most common sign and symptoms of ascorbic acid deficiency might include:
- Rough, dry, damaged, and bumpy skin
- Corkscrew-shaped body hair
- Bright red hair follicles
- Spoon-shaped fingernails with red spots or lines in fingernails
- Easy bruising
- Slowly healing wounds
- Weak bones with painful and swollen Joints
- Bleeding gums and tooth loss
- Poor immunity
- Persistent iron deficiency anemia
- Fatigue, poor mood, and unexplained weight gain
- Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress
Vitamin A Deficiency
The deficiency can result from a diet that contains a low level of vitamin A or an absorption or liver disorder. Retinol is necessary for the function of light-sensitive nerve cells (photoreceptors) in our eye’s retina. Therefore, it helps to maintain night vision.
It also helps with skin problems, the lining of the lungs, intestine, and urinary tract healthily, and protects against various infections. The most common list of signs of vitamin A deficiency may include:
- Inflamed skin
- Night blindness
- Childhood blindness
- Infertility
- Delayed growth
- Childhood infections
- Respiratory infections
Deficiency of Vitamin D
Lack of vitamin D in children causes rickets. The main signs and symptoms of rickets might include:
- Incorrect growth factors due to bowed or bent bones
- Muscle weakness
- Bone pain
- Deformities in joints
A deficiency commonly not observed in adults. The main signs and symptoms in adults might include:
- Fatigue
- Bone pain
- Muscle weakness, muscle aches, or muscle cramps.
- Mood changes, like depression
Deficiency of Vitamin E
The deficiency is extremely rare in humans but is sometimes by irregularities in dietary fat absorption or metabolism. The most common list of signs of vitamin E deficiency might include:
- Nerve and muscle damage
- Muscular pain or weakness
- Loss of body movement control.
- Visual challenges and deterioration
- Immunity problems
- Numbness and tingling
Vitamin K Deficiency
K deficiency is rare in adults because many of the foods we eat contain sufficient amounts of K1 and our bodies can make their own K2. Certain conditions and some medications can interfere with K vitamins absorption and creation.
The most common signs of deficiency might include the following:
- Vitamin K deficiency bleeding or VKDB in infants
- Sensitivity to bruising
- Bleeding gums
- Nosebleeds
- Heavy menstrual bleeding in women
VKDB is much more common in infants. The bleeding may occur anywhere in the body but when the bleeding occurs inside the body, it can be difficult to observe. It may occur when babies cannot stop bleeding because their blood does not have enough vitamin K to form a clot.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Vitamin?
Vitamin is an organic compound or essential micronutrient found in various foods and necessary for the growth and good health of animals including humans. A small amount of various types of vitamins are taken in our diet to perform specific biological functions for normal maintenance of optimum growth and health.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that resembles the structure of sterols and functions like a hormone. Ergocalciferol (D2) and cholecalciferol (D3) are the most common list of vitamin D found in plants and animals. It helps to regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in our body. It is also needed to keep our bones, teeth, and muscles healthy.
Why Vitamins are Important?
Vitamins are important for the generation of energy in our body by utilizing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats properly and improving our immune system to save us from various diseases. Except for vitamins D and B3, our body cannot synthesize vitamins in our body. Therefore, it is important to obtain most of the vitamins through our diet or medicinal supplements.
Is Vitamin C Good for Skin?
Yes, vitamin C is good for our skin because it plays the role of a coenzyme in the hydroxylation of proline and lysine when protocollagen is converted to collagen. Hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine are essential for collagen cross-linking and the strength of fiber in our body. Therefore, vitamin C is necessary for the maintenance of normal connective tissues and the wound healing process. It also plays a list of roles in maintaining good skin,
- As an antioxidant, it fights against harmful free radicals that damage our skin.
- Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, it may help to reduce acne in your skin.
- It may help regulate sebum production to make your skin oily.
- It also fights against dark circles, protects your skin from sun damage, lights your skin, etc.
What are Fat Soluble Vitamins?
The four vitamins namely A, D, E, and K are called fat or lipid-soluble vitamins because they are soluble in fats or lipids. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the liver and adipose tissue.
They are not readily extracted in urine. Therefore, excess consumption of these vitamins may cause toxic effects on your body.
What are Water Soluble Vitamins?
A list of eight B vitamins and vitamin C are called water-soluble vitamins because they are soluble in water. Water-soluble vitamins a heterogeneous group of compounds differ chemically from each other.
Most of these vitamins are readily extracted in urine. Therefore, excess consumption of these vitamins may not cause any toxic effects on your body.