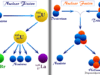
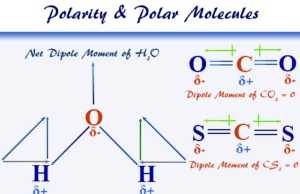
Meaning of Chemistry in Science
Chemistry is the study guide of pure science that deals with the physical or chemical properties, reactions, composition, structure, and formula of matter formed by atoms, ions, or molecules that interact with energy. Most of the chemistry articles we study are related to five basic branches such as physical, organic, inorganic, biochemistry, and analytical chemistry. The chemistry study guide also helps to describe the properties and structure of atoms of the periodic table elements. It is a branch of science that studies chemical compounds formed from atoms, molecules, and ions by various chemical reactions. In the branch of chemistry, we study various chemical and biological compounds such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), vitamins and minerals, and many other essential compounds that are important for living.
Learning chemistry suggests how new chemical compounds (inorganic or organic compounds) are formed from different types of atoms by chemical bonding like ionic bonding, covalent bonding, or metallic bonding. Apart from these chemistry also defines the behavior of matter found in our surroundings.
Branches of Chemistry
Physical, organic, inorganic, biochemistry, and analytical chemistry are the five basic branches of chemistry. Chemistry articles from these branches mostly help for systemic studying properties, composition, structure, and chemical reactions of various classes of compounds that exist in our universe.
Apart from these primary branches, chemistry has several specialized fields that deal with matters. These specialized branches may include:
- Medicinal Chemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that involves the identification, synthesis, and development of new chemical entities which is suitable for therapeutic use.
- Neurochemistry: It is a branch of chemistry that studies identities, structures, and functions of neurochemicals that control and influence the physiology of our nervous system.
- Materials Chemistry: It is the part of materials science and engineering that investigates the chemical nature such as structure, properties, processing, and performance of materials.
- Nuclear Chemistry: It is the sub-field of chemistry dealing with radioactivity, nuclear reactions such as nuclear fission and nuclear fusion, or reactions that happen inside nuclei of atoms.
- Environmental Chemistry: It is the sub-field of chemistry used for the scientific study of the chemical and biochemical phenomena that happen in natural places of our environment. It is used mostly for studying environmental pollution caused by various chemicals.
- Polymer chemistry: It is a sub-field of chemistry that focuses on studying structures, synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules.
- Thermochemistry: It is the sub-field of chemistry that studies heat and different types of energy changes or phase changes during any chemical reaction.
- Green Chemistry: It is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering that focuses on the design of products and processes to minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances.
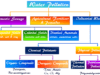
Matter Definition in Science
Matter in science can be defined as anything that has mass, volume, or occupies space and is felt by one or more sense organs. In our surroundings, we can see a large variety of objects with different shapes, sizes, and textures. These objects found in our earth and universe are called matter.
Everything that we see, taste, and smell is part of matter. Therefore, the oxygen we breathe, the food we eat, stones, clouds, stars, plants and animals, and even a particle in sand or a small drop of water−everything is a part of the matter.
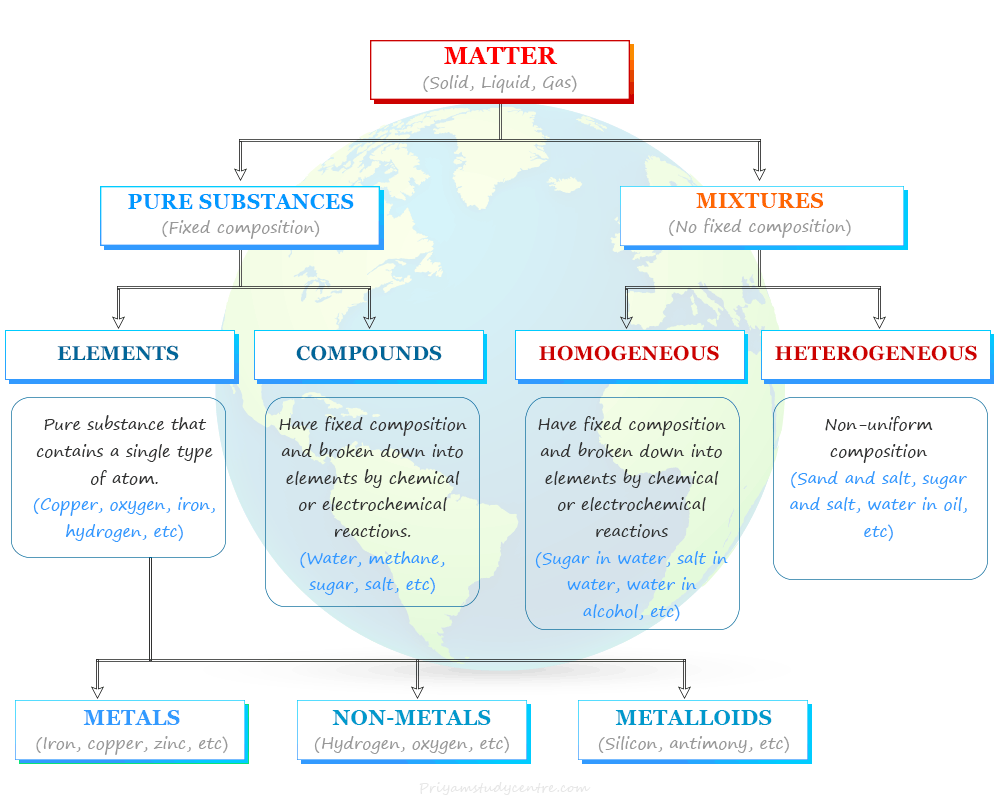
In chemistry, depending on the chemical composition, matter is classified into pure substances (elements, compounds) and mixtures. The substances found in our universe that contain only a single type of constituent particles are called pure substances. Based on the nature of constituent particles, a pure substance is of two types−elements and compounds.
List of Elements in Chemistry
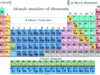
An element in chemistry is a pure substance that contains a single type of atom characterized by a particular atomic number. Till today, 118 periodic table elements are found in nature. Out of these 188 chemical elements, 92 are natural elements and 26 are artificial or man-made elements.
On the basis of chemistry and chemical properties, a list of 118 elements are classified into three categories:
- Metals: These are the chemical elements that are malleable, ductile, sonorous, and conductors of heat and electricity. Mercury is the only periodic table metal that is liquid at room temperature.
- Non-metals: Non-metals are chemical elements that are neither malleable nor ductile and do not conduct heat and electricity. Generally, they are solid or liquid but bromine is only a non-metallic element that exists in the liquid state at normal conditions of temperature and pressure.
- Metalloids: They are the elements having intermediate properties between those of metals and non-metals. Examples of metalloids found in the periodic table are boron, silicon, germanium, etc.
Formula of Compound in Chemistry
A compound in chemistry defines a substance that contains two or more chemical elements chemically combined with one another in a fixed proportion. The examples of compounds with their chemical formula that we use in our daily lives are water (H2O), methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), etc.
These chemical compounds are broadly classified into two groups−inorganic and organic compounds. Organic compounds are hydrocarbons and their related compounds and all the remaining compounds are called inorganic compounds.
Molecules of Compound
A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or compound which capable of independent existence and shows all the properties of that element or compound.
In general, molecules are formed by the bonding of two or more atoms of the same or different elements. However, molecules of many elements may also be formed by a single atom of that element. For example, noble gases such as helium, neon, argon, etc.
On the basis of atomicity (number of atoms present in a molecule), molecules are classified into various types−monoatomic, diatomic, triatomic, tetratomic, and polyatomic.
- Monoatomic molecules: They consist of only one atom in their molecules. Examples of monoatomic molecules are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), iron (Fe), aluminum (Al), etc.
- Diatomic molecules: They consist of two atoms in their molecules. Examples of diatomic molecules are hydrogen (H2), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), bromine (Br2), hydrochloric acid (HCl), carbon monoxide (CO), etc.
- Triatomic molecules: They consist of three atoms in their molecules. Examples of triatomic molecules are ozone (O3), carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), etc.
- Tetratomic molecules: They consist of four atoms in their molecules. Examples of such type of molecules are phosphorus (P4), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), etc.
- Polyatomic molecules: They consist of more than four atoms in their molecules. Examples of such types of molecules are pentatomic methane (CH4), octaatomic sulfur (S8), etc.
Molecule and Compound
In the study of chemistry, atoms of different elements are joined together in definite proportions to form molecules of compounds. For example, a water molecule is made up of hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of 1:8 by mass.
| Compound | Molecular formula | Combining elements | Ratio by mass |
| Water | H2O | Hydrogen and oxygen | 1:8 |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | Carbon and oxygen | 3:8 |
| Hydrogen sulfide | H2S | Hydrogen and sulfur | 1:16 |
| Ammonia | NH3 | Nitrogen and hydrogen | 14:3 |
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | Hydrogen sulfur and oxygen | 1:16:32 |
| Glucose | C6H12O6 | Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen | 6:1:8 |
| Baking Powder | NaHCO3 | Sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen | 23:1:12:48 |
| Common salt | NaCl | Sodium and chlorine | 23:35.5 |
| Limestone or calcium carbonate | CaCO3 | Calcium, carbon and oxygen | 10:3:12 |
| Caustic soda or sodium hydroxide | NaOH | Sodium, oxygen, and hydrogen | 23:16:1 |
| Caustic potash or potassium hydroxide | KOH | Potassium, oxygen, and hydrogen | 39:16:1 |
| Ethanol | C2H5OH | Carbon hydrogen and oxygen | 12:3:8 |
| Methanol | CH3OH | Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen | 3:1:4 |
| Ethyne or acetylene | C2H2 | Carbon and hydrogen | 12:1 |
Empirical Formula Determination
The empirical formula in chemistry defines the relative number of each class of atom in the general molecular formula that helps with the calculation of the percentage composition or chemical structure of the molecule or compound.
Question: If 0.202 g of an organic compound gave combustion 0.361 g of carbon dioxide and 0.147 g of water. How to find the empirical formula of the compound in chemistry?
Answer: Weight of carbon in the said compound,
= (12/44) × 0.361 g
= 0.0985 g
Weight of the hydrogen
= (2/18) × 0.147 g
= 0.0163 g
Weight of oxygen,
= 0.202 − (0.0985 + 0.0163)
= 0.0872 g
Therefore, the ratio of the molar mass of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atom,
C : H : O = (0.0985/12) : (0.0163/1) : (0.0872/16)
= 3 : 5.98 : 2
From the above solution, the empirical formula of said organic compound is C3H6O2.
Molecular Weight Measurement
The methods used for the measurement of molecular weight are,
- Vapour density
- Elevation of boiling point
- Depression of freezing point
These methods are described fully in the physical chemistry textbooks. But other physical methods include
- Graham’s law of diffusion
- Sedimentation
- The viscosity of liquid and gases
- Osmotic pressure
- X-ray radiation analysis
- Mass or atomic spectrum (used for substances that contain high molar mass)
Atoms in Chemistry
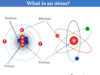
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element which may or may not have independent existence but take part in a chemical reaction for the formation of molecules. For Example, atoms of hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are not capable of carrying their independent existence whereas atoms of helium, neon, and argon exist independently.
An atom is the basic unit of chemistry and the building block of all matter. It consists of a dense core or positively charged nucleus surrounded by a space occupied by an electron cloud. The nucleus of an atom contains positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons while the electron cloud contains negatively charged electrons revolving in discrete orbits around the nucleus.
An electron of an atom carries the key to the chemical world. Therefore, electronic configuration explains most of the chemical properties of an element such as electronegativity, ionization energy, preferred oxidation number, coordination number, and preferred types of chemical bonding (metallic, ionic, covalent bonding).
Compound Mixtures and Elements
A mixture is a collection of compounds constituted by more than one kind of pure substance. Most of the matter around us exists as a mixture of two or more pure chemical components. The most common examples of mixtures found around us are seawater, minerals, soil, etc.
Physical Chemistry
Physical chemistry is a branch of chemistry that is used for studying macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics. It is the physical and fundamental basis of chemical systems and processes which is important for studying various laws and concepts.
Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics
Physical chemistry differs from other branches of science because it is employed for understanding chemical systems and reactions with the help of physics. The most common braches of physical chemistry may include:
- Spectroscopy: It is a sub-branch of physical chemistry which used to study the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation. Hydrogen spectrum and various multi-electronic spectrum is studied in this sub-branch of chemistry.
Quantum chemistry: It is a subfield of physical chemistry that studies the application of quantum mechanics to solve chemical problems, determine the strength and shape of chemical bonds, and how a specific wavelength or frequency of light can be absorbed or emitted by a chemical compound. - Chemical thermodynamics: It is used for studying the spontaneity of a chemical reaction and the properties of chemical mixtures in terms of thermodynamics. The conservation of energy principle, free energy, enthalpy, entropy, and activation energy are studied in this branch of chemistry.
Chemical kinetics: It deals with the feasibility and rate of chemical reactions, and the effect of the rate of reaction due to changes in temperature, pressure, concentration of reactants, and chemical catalyst.
Physical Chemistry Topics
In physical chemistry, we study general definitions, laws, principles, mathematical equations, units and dimensions, or formulas related to chemical systems. The most common articles or topics studied in physical chemistry may include:
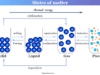
- States of matter: Solid, liquid, gaseous, and plasma state of matter
- Solid-state: Chemistry of crystalline solids and amorphous solids, etc.
- Gaseous state: Idea about ideal and real gas, critical temperature, pressure and volume, heat capacity of gases, Gas laws, Boyles Law, Charles Law, ideal gas law, Van der Waals equation, Graham’s law of diffusion and effusion, etc.
- Liquid state: Surface chemistry such as surface tension, density, surface energy, viscosity of liquids and gases, etc.
- Chemical equilibrium: Thermodynamics of chemical equilibrium, mass action law, Van’t Hoff equation, chemical catalyst, Le Chatelier Principle, etc.
- Chemical kinetics: Zero-order chemical kinetics, First-order chemical kinetics, etc.
- Spectroscopy: Electromagnetic spectrum, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, spectrophotometry, atomic absorption spectroscopy, atomic emission spectroscopy, microwave spectrum, electron spin resonance, etc.
- Quantum chemistry: Quantum mechanical concept of atoms and molecules.
The study of physical chemistry articles is incomplete if the student confines himself only to theoretical information. They must gain practical explanations of the theory, definition, problem, and solution.
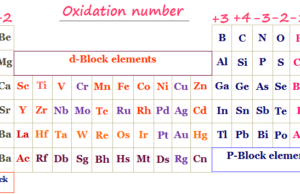
Inorganic Chemistry Study Guide
Inorganic chemistry is the study of the properties, composition, reactions, and formation of inorganic compounds by different types of atoms of chemical elements.
Study inorganic chemistry is a broad field of science and it has many sub-branches. The most common sub-branches of such field of chemistry may include:
- Coordination chemistry: It is a branch of science used for studying transition metal complexes.
- Bioinorganic chemistry: It is a specialized field of inorganic chemistry that focuses on the biochemistry of essential elements and compounds.
- Solid-state chemistry: This sub-discipline studies the synthesis and characteristics of solid materials.
In the inorganic chemistry study guide, we learn the properties of chemical elements or compounds that are closely related to their electronic configuration. Orbital hybridization, molecular orbital theory, and crystal field theory have given a clear understanding of modern inorganic compounds.
Inorganic Compound Meaning
Organic and inorganic compounds are two main classes of chemical compounds that are studied in chemistry. They can be differentiated by carbon−hydrogen bonds. The organic molecules contain carbon-hydrogen bonds in their structure while inorganic compounds do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds in their structure.
Inorganic compounds found in our earth are broadly categorized into four main categories, acids, bases, salts, and water.
- Acids: According to Arrhenius’s definition, in the presence of an aqueous solution all acids give H+ ion or H3O+ ion. In other definition, acids are electron acceptors and proton donors. Mineral acids such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4), hydrochloric acid (HCl), and nitric acid (HNO3) are common examples of inorganic acids used widely in various chemical processes.
- Bases: They are the chemicals that neutralize acids by donating their electrons, releasing the hydroxide ions, or accepting protons. Such substances contain metals bonded with a hydroxyl group. Bases like potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, and ammonia produce hydroxyl ions when dissolved in water.
- Salts: Salts are produced by the neutralization reaction between acid and base. They are neutral, acidic, or basic in nature. Therefore, the salts of strong acid and strong base are neutral but strong acid and weak base are acidic, and weak acid and strong base are basic in nature. They are characterized by their crystalline structure.
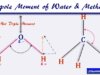
- Water: Dihydrogen oxide or water is the most abundant and important inorganic substance for living organisms. It is formed by combining one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms.
Inorganic Compounds Examples Everyday
In our everyday life, we use a wide number of inorganic compounds in various fields of science such as biology, chemical engineering, agriculture, medicine, electronics, etc. Examples of such common inorganic compounds are:
- Borax: Used widely in the field of biochemistry and medicine.
- Boric acid: Borate ions obtained mostly from boric acid are used in biochemical and chemical laboratories to make buffer solutions.
- Urea: Used as a fertilizer to increase nitrogen content in soil.
- Zinc sulfate: Used widely in the field of medicine and agriculture.
- Heavy water: Used in spectroscopy, biochemistry, and neutron moderator in nuclear power reactors.
- Chlorine dioxide: Used in the chemical industry for bleaching, food processing, and water treatment.
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is the study of properties, composition, and chemical reactions of organic compounds coming mainly from living organisms. Simply, it is the chemistry of carbon compounds.
The definition included compounds like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonates, carbon disulfide, etc. However, these compounds are usually studied in inorganic textbooks. Therefore, it is the study of hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon-related compounds.
Organic Chemicals
Organic compounds are substances that contain carbon and carbon atoms provide the key structural framework generating such a vast number of organic molecules.
These compounds are key components of living organisms and organic biopolymers such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates. Other materials useful for the comfort, and health of humans are the class of organic compounds. The common examples of such types of chemical compounds are:
- Vital substances such as hemoglobin, chlorophyll, enzymes, hormones, vitamins, etc.
- Clothing items made of cotton, wool, silk, and synthetic fibers.
- Common fossil fuels include wood, coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
- Components coatings such as varnishes, paints, lacquers, and enamels.
- Antibiotics, synthetic drugs, and pesticides.
- Natural and synthetic polymers such as rubber and plastics.
Organic Chemistry Topics
Biochemistry Study Guide
Biochemistry is the scientific study of chemical substances and processes that occur in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Various biochemical reactions help us to carry out every movement of life (from birth to death. No other science subject has as much application as biochemistry or biological chemistry. It applied many disciplines of science such as medicine, health, veterinary, agriculture bioengineering, and biotechnology.
Advanced biochemistry tremendous impact on human welfare and largely benefited their living styles. These include the application of such a branch of chemistry in laboratories for disease diagnosis and the production of various therapeutic agents by genetic engineering and recombinant DNA technology.
Biological Molecule
Life is composed of lifeless chemicals and biomolecules or biological molecules. A single cell of a bacterium has about 6,000 different types of biological molecules. It is believed that a man contains about 100,000 different types of biological molecules. Only a few of them are characterized and studied as a biochemistry subject.
Biochemistry is a sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology. It is used mainly to study four types of biological molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids.
- Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides are the monomeric units or building block carbohydrates.
- Proteins: Amino acids are the monomeric unit or basic building blocks of proteins.
- Fats or Lipids: It is the organic substances relatively insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents and potentially related to fatty acids utilized by living cells.
- Nucleic acids: Nucleotides are the monomeric units or basic building blocks of nucleic acids such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
Apart from these, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) are important biomolecules that participate in various metabolism processes. They act as electron carriers in various biological redox reactions.
Vitamins and Medicines
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A | B vitamins |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B1) | Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) |
| Niacin – Vitamin B3 | Pantothenic Acid – Vitamin B5 |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | Biotin – Vitamin B7 |
| Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) | Vitamin B12 |
| Vitamin C | Vitamin E |
| Vitamin K | Choline |
| Niacinamide | |
| Medicines | |
| Cyclophosphamide | Penicillin |
| Verapamil | Propranolol |
| Enalapril | Lisinopril |
| Ramipril | Losartan |
| Irbesartan | Valsartan |
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemistry is the study or analysis of the chemical formula, structure, or composition of the atom, molecule, or matter for chemical, forensic, medicinal, food science, or technology.
However, modern analytical chemistry helps to identify general substances by various analytical instruments. Electrophoresis, capillary electrophoresis, chromatography, atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), optical fiber technology, and polarimetry are the most common instrumental methods used by an analytical chemist for their analysis.
Analytical Chemistry Methods
Analytical technique or method used mainly to determine the chemical or physical properties of chemical substances, elements, or mixtures obtained from organic and inorganic matter. The most useful analytical instruments used widely in modern technology and biotechnology are:
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- Gas Chromatography (GC)
- Column Chromatography
- Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
- Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
- Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC)
- Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
- Ion exchange chromatography
There is a wide variety of classical and instrumental techniques used for the analysis of various substances in various fields of chemistry. The common techniques used for the analysis of various substances may include:
- Classical methods: It is a basic analytical method widely used in laboratories to determine the concentration of the analyte. The most common example of the classical method is the acid-base titration method.
- Spectrochemical analysis: It is a method of chemical analysis that depends upon the measurement of the wavelength and the intensity of the electromagnetic spectrum. Mass spectrometry (MS), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) are used commonly for the analysis of chemical and biological samples.
- Electroanalytical analysis: The three main sections of electroanalytical analysis that use the potential or current of an electrochemical cell are potentiometry, coulometry, and voltammetry.
- Chromatographic techniques: Chromatography in analytical chemistry is a laboratory technique used for the separation of chemicals or biochemicals mixture into its components. Ion exchange chromatography is a useful and common purification technique that allows for the separation of molecules by ion exchange resin. Another chromatographic technique such as paper chromatography is used as a teaching tool in chemical laboratories.
Analytical Chemistry Course
The most challenging task for an analytical chemist is to explain what is the nature of the analytical chemistry course. It is an interdisciplinary branch of science where a large number of research works have contributed to its development.
Most chromatographic studies were invented by biochemists or biological scientists. Physicists may also discover various methods related to electromagnetic spectrum and mass spectroscopy.
But if we look closely, different types of research topics are published in different sets of science journals by using analytical chemistry methods. About 60% of such materials are published by persons who are not analytical chemists in the true sense.
Frequently Asked Questions on Chemistry
What is the definition of chemistry?
Chemistry is the branch of science that scientifically studies the properties and behavior of matter.
How is chemistry used in daily life?
Chemistry is important to us and it is used for the production of several items that we use in our everyday life. It is used in everyday life for food processing and cooking, cleaning, medicine, solving environmental issues, and many more.
Why chemistry is important?
Chemistry is important because chemistry is the study of matter or chemicals from where our universe is made. All humans living on the earth are chemists because we fulfill most of our daily needs with many chemicals without thinking much of them.
Chemistry is important because our body and everything used in our daily life is made of chemicals. Biochemical reactions occur in our body when we breathe, eat, or even when we sit and sleep.
What are the main branches of chemistry?
Chemistry is the central science where we study the properties and composition of matter. There are 5 main branches of chemistry which include:
- Organic chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
How does chemistry affect our lives?
Chemistry can explain how food changes during cooking, how to preserve food, how medicine affects our body, and how pollutants pollute our environments and their solutions. Therefore, students wanting to become doctors, nurses, physicists, nutritionists, geologists, pharmacists, and chemists all study chemistry to achieve their goals.