Infrared Spectroscopy
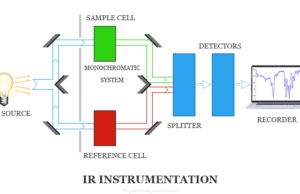
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy also called IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy is the analysis of infrared light that interacts with matter in the infrared...
Electron Spin Resonance
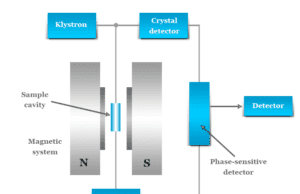
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Spectroscopy
Electron spin resonance (ESR) also called electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy is a method for studying paramagnetic substances that exhibit...
Inductively Coupled Plasma
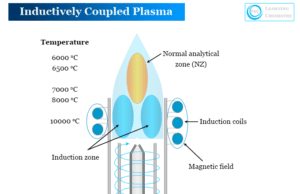
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Spectrometry
Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) work with atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) or mass spectrometry (ICP-AS) to give a powerful analysis technology...
Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
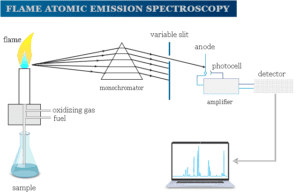
Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
Atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) is a method of chemical analysis of samples by the electronic transition of atoms by...
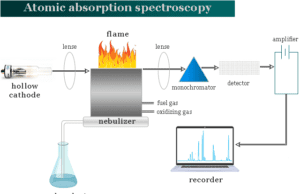
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy Principle
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) principle are based on the absorption and emission of light by atoms...
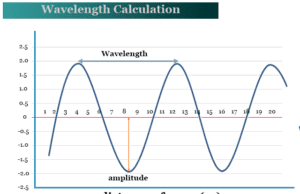
Wavelength
Wavelength Measurement
Wavelength can be measured by the distance between two successive maxima of a wave. It can be denoted by the symbol lambda (λ)...
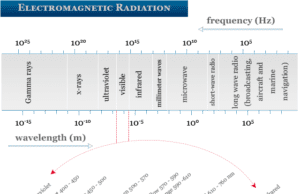
Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic Radiation and Waves
Electromagnetic radiation in physics or chemistry describes the form of energy that is transmitted through space at an enormous velocity. Each...
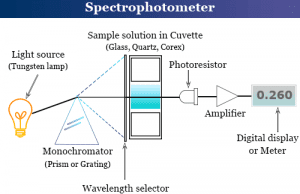
Spectrophotometry
Definition of Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is an instrument in the electromagnetic spectrum for the measurement of relative energy (emitted, transmitted, or reflected) as a function of...
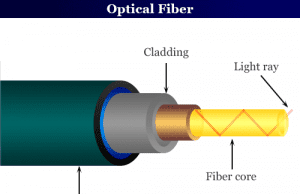
Optical Fiber
Optical Fiber Cable
Optical fiber cable or optical fiber cable is a new development in the field of communication technology that can transmit light along...
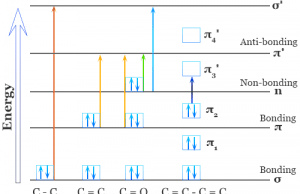
Ultraviolet Visible Spectroscopy
Ultraviolet Visible (uv vis) Spectroscopy
Ultraviolet visible spectroscopy or uv vis spectroscopy involves the measurement of absorption or transmittance of energy in the ultraviolet and...