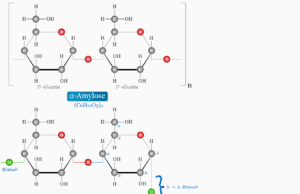
Glycogen
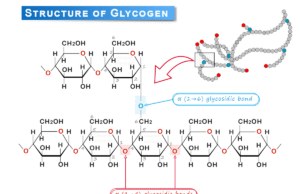
Glycogen Storage
Glycogen is a carbohydrate or an extensively branched polymer of glucose stored primarily in the cells of the liver, skeletal muscle, and brain....
Adenosine Triphosphate
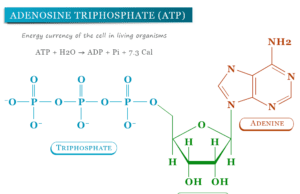
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in biology is a unique and most important high-energy biomolecule in living cells. The structure of adenosine triphosphate contains...
Peptides
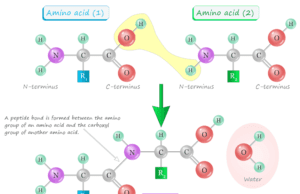
List of Peptides and What They Do?
Peptides are a continuous and unbranched list of amino acid biopolymers joined together by peptide bonds. A list...
Ecosystem
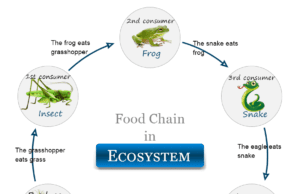
Definition of Ecosystem
An ecosystem or ecological system is a structural and functional unit of the biosphere where regular energy input and matter circulation occur....
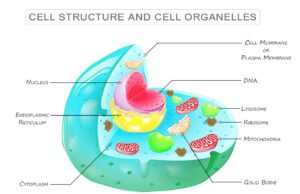
Cell in Biology
Cell and Molecular Biology
A Cell in biology is the structural and functional unit of life that contains fundamental molecules of living organisms. The main...
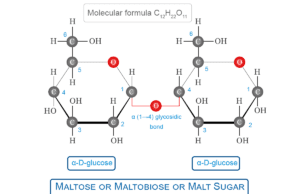
Maltose Sugar
Maltose Malt Sugar
Maltose Sugar also called maltobiose or malt is a carbohydrate or monosaccharide formed by two α-D-glucose units held together by α(1→4) glycosidic...
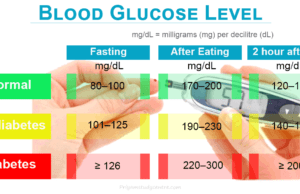
Glucose Molecule
Glucose Molecular Formula
Glucose is the simplest type of carbohydrate or sugar molecule that has the molecular formula C6H12O6. It is an odourless and sweet...
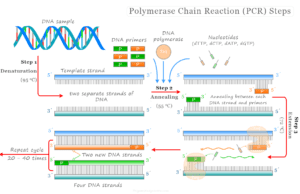
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in biology and chemistry is a laboratory method or technology uses for real-time genetic testing and amplification...
Biopolymers
Biopolymers in Body
Biopolymers are natural polymers or polymeric biomolecules produced by the cells of the living body. They are monomeric units that are covalently...
Starch
Healthy Starch Foods
Starch is a soft, white powder and tasteless carbohydrate reserved in plants. Various types of starches found in plants are the most...