Folic Acid and Folate
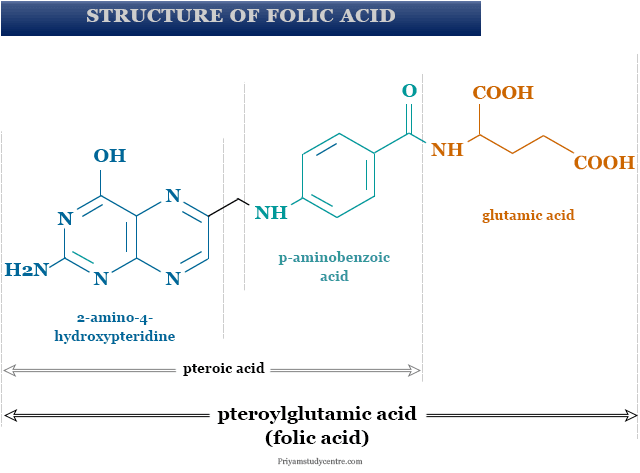
Folic acid and folate are the forms of vitamin B9 that we use for the treatment of certain types of iron deficiency anemia and pregnancy complications. Folate is an important supplement that makes DNA and RNA and metabolizes amino acids for cell division but humans cannot make it in their bodies. Therefore, we require folic acid in our diet. In chemistry, folate refers to the conjugate base of folic acid. In biochemistry, folates are the class of biologically active compounds related to folic acid. It is pteroylglutamic acid but the folic acid structure also contains three or seven glutamic acid residues. The structure of folic acid which contains 2-amino-4-hydroxypteridine-6-carboxylic acid, p-aminobenzoic acid, and glutamic acid is given below the picture,
Many foods such as leafy vegetables, okra, asparagus, certain fruits, beans, yeast, mushrooms, animal liver and kidney, orange juice, and tomato juice are the main sources of folate. Folate or folic acid supplements which we use widely in our daily life have very low side effects.
Animal tissue contains an enzyme that hydrolysis naturally occurring pteroylpolyglutamic acids to pteroylglutamic acid and free glutamic acid. It was discovered between 1931 and 1943 and most commonly prescribed medication for United States patients. According to the World Health Organization, folic acid or folate is an essential medicine for human health.
Structure of Folic Acid
The structure of folic acid was elucidated by Angier in 1946. The alkaline hydrolysis of the Lactobacillus casei factor (folic acid) in the absence of oxygen gives two molecules of D-glutamic acid.
On the other hand, alkaline hydrolysis of Lactobacillus casei factor in the presence of air or oxygen gives 2-amino-4-hydroxypteridine-6-carboxylic acid, p-aminobenzoic acid, and three molecules of glutamic acid residues.
The structure of 2-amino-4-hydroxypteridine-6-carboxylic acid, p-aminobenzoic acid has been identified by the ultraviolet-visible spectrum of such compounds. The presence of the amino group and hydroxyl group in 2-amino-4-hydroxypteridine-6-carboxylic acid can be identified by oxidation with chlorine water followed by hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid.
Folic Acid Deficiency
- Folate is an important supplement during cell division, fetal growth, and organ development. Therefore, folate or folic acid deficiency reduces DNA and RNA synthesis and cell division.
- Folate deficiency mostly impacts pregnant women during childbirth. Therefore, folate supplements are must intake during pregnancy to reduce the chance of birth defects.
- The other health problems caused by folic acid or folate deficiency are heart disease, stroke, deficiency of vitamin B12, cancer, brain defects, etc.
Uses of Folic Acid
Folate is found in several foods such as leafy vegetables, okra, asparagus, certain fruits, beans, yeast, mushrooms, animal liver or kidney, orange juice, and tomato juice but we also use folic acid supplements or tablets in our daily life.
The supplement or tablets may come in different forms such as L-methyl folate, levomefolate, and methyltetrahydrofolate. The supplements of folates are essential medicines according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- These supplements are used to increase folate levels in our bodies. Such types of low folate levels that caused by poor diet, alcoholism, pregnancy, and liver, and kidney disease that affect our health in several ways.
- It is very effective in the treatment of certain types of anemia.
- It helps to produce and maintain new cells in our body. It also reduces the change of DNA which causes cancer.
- It is also used with iron to prevent birth defects. We used folic acid supplements for pregnant women in their daily food or tablets prescribed by gynecologists.
- It is used to increase the brain health of adults. Low folate levels in the blood cause poor brain function which increases the risk of mental health disorders.
- It also improves heart health to reduce the risk of heart failure or attack.
- The supplement which contains folic acid is also beneficial for diabetes or kidney disease patients and helpful for fertility.
Dose
According to RDA recommendations, folic acid can intake 400 micrograms (mcg) of dietary folate equivalents (DFE) by adults, 600 mcg of DFE by pregnant women, and 500 mcg of DFE by breastfeeding women per day.
Side Effects
Folate in foods or supplements is beneficial for human health in several ways but it has also side effects. If you have any unusual effects after intake of folate supplement, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
The most common side effects after taking folate supplements include
- rash and itching
- nausea
- loss of appetite
- bloating
- gas and stomach pain
- bitter taste in your mouth
- confusion
- trouble concentrating and sleep problems
High folic acid intake may cause B12 deficiency, cancer, and negative effects during pregnancy. An overdose of folate or a folic acid supplement causes trouble bathing or may even die.