Valsartan Medication
Valsartan (brand name Diovan and others) is a class of medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. The dosage of valsartan may cause many common and serious side effects. Therefore, you can use valsartan tablets after consulting your doctor. It is a white fine crystalline powder soluble in ethanol and methanol but slightly soluble in water. The medicine valsartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). It works by blocking substances that tighten your blood vessel. Valsartan or Diovan is available online or in medical shops only after your doctor’s prescription. Using Valsartan Diovan tablet during pregnancy may harm your developing fetus. It is also not recommended for breastfeeding women.
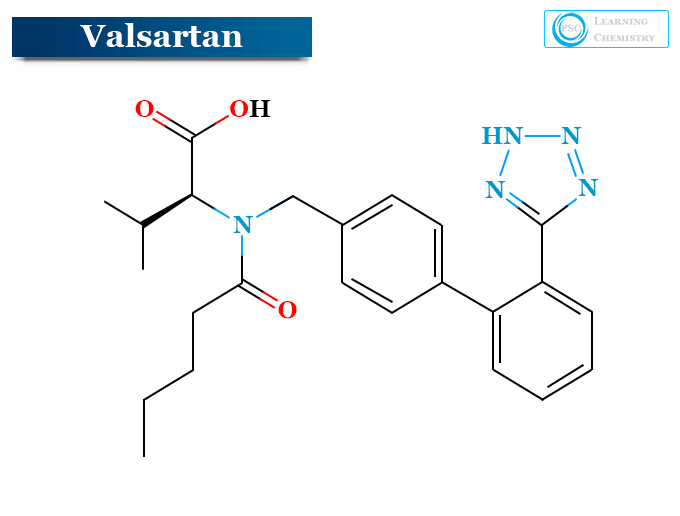
The structure of valsartan is given above the picture. It is chemically termed as N-(1-oxopentyl)-N-[[2′-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl) [1,1′-biphenyl]-4- yl]methyl]-L-valine with empirical formula is C24H29N5O3.
Valsartan is the most commonly prescribed medicine available as a generic medication. It was patented in 1990 and used since 1996. It is available in a combination of valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide, valsartan/amlodipine, valsartan/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide, or valsartan/sacubitril.
Uses of Valsartan
Valsartan medication is used alone or together with other medicines for the treatment of high blood pressure, heart failure, and kidney failure.
Valsartan for Blood Pressure
If you have high blood pressure for a long time, your heart and arteries may not function properly. It can damage the blood vessels of the brain, heart, and kidneys resulting in a stroke, heart failure, or kidney failure. Therefore, Diovan medication is used to lower your blood pressure and reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
Valsartan for Heart Failure
The medicine is an orally active nonpeptide angiotensin II (AII) receptor antagonist used to reduce rates of mortality and heart failure. It is used alone or combined with other beta-blockers. It has been recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with heart failure.
Mostly, valsartan is combined with sacubitril for the treatment of heart failure. This combination significantly reduced cardiovascular mortality and hospitalizations due to heart failure.
Valsartan for Diabetic Kidney Disease
In type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy, the low dose of Dioval can reduce urinary albumin excretion (UAE) without reducing systemic blood pressure. Therefore, it can be safely administered to patients who suffer from type 2 diabetes.
How does Valsartan Work?
It belongs to a class of medicine called angiotensin receptor blockers. Such medicine works by blocking a substance in your body that causes to tighten your blood vessels. It is used for relaxing your blood vessels. After relaxing, your blood and oxygen can flow more easily which lowers your blood pressure.
Lowering blood pressure can reduce the risk of various health problems such as strokes and heart attacks.
Valsartan Dosage
Valsartan or Diovan dosage is available as 40 mg, 80 mg, 160 mg, or 320 mg tablets for oral administration.
For High Blood Pressure
The recommended starting dose of Diovan for adults is 80 mg or 160 mg once per day. Your doctor may prescribe a higher dose or a diuretic for more significant reductions in blood pressure. The maximum dose may be increased up to 320 mg.
The addition of a diuretic shows a more significant effect than increasing the starting dose. The oral tablets can be taken at a fixed time in the day or after consulting your doctor. The impact of the dose may be seen within 2 weeks but the maximum reduction of blood pressure is generally attained after 4 weeks.
The starting dose for pediatric patients aged between 6 to 16 years is 1.3 mg/kg once per day with a maximum dose of 40 mg per day. Your doctor can maintain the dose up to 2.7 mg/kg per day according to patient response.
It is not recommended for pediatric patients under 6 years of age. If your child cannot swallow tablets or is not available in the prescribed strength, your doctor will make a liquid suspension for your child.
For Heart Failure
The starting adult dose is 40 mg orally twice per day. The maintenance dose is 80 to 160 mg twice per day. It may increase to the highest dose by your doctor if tolerated by you.
Post-Myocardial Infarction
Valsartan or Diovan medication may be initiated as early as 12 hours after myocardial infarction. It is also used to treat postmyocardial infarction like thrombolytics, aspirin, beta-blockers, and statins. The starting dose is 20 mg twice daily. It may be titrated upward within 7 days to 40 mg twice daily.
Valsartan or Diovan dose may increase up to 160 mg twice daily if tolerated by the patient. If symptomatic hypotension or renal dysfunction occurs, the dosage may be reduced by your doctor.
Side Effects of Valsartan Medication
Valsartan causes many common and serious side effects in your body. The side effects of this medicine depend on the reason for the medication, the age of the patient, and the reaction to the medicine in your body.
The most common side effects may include,
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Low blood pressure
- Tired feeling or fatigue
- Flu symptoms
- Upper respiratory infection
- Abdominal pain
- Cough
- Edema
- Diarrhea
- Back and joint pain
It also causes many serious side effects in your body. Therefore, you can always consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking valsartan medicine. The serious side effects may include
- Lightheadedness
- Swelling in the face or lips
- Rapid weight gaining
- Shortness of breath
- Urination problem
- Pounding heartbeats
- Fluttering in your chest
- Nausea
- Weakness feeling
- Tingly feeling
- Chest pain
- Irregular heartbeats
- Loss of movement
Although all of the above side effects may not occur for all patients who take such medicine. If occur any serious side effects, you may need medical attention.
Warning
- It can readily be discontinued when pregnancy is detected. Valsartan or Diovan acts directly on the renin-angiotensin system of the developing fetus. Therefore, it causes injury and death to your developing fetus.
- It increases the risk of low blood pressure or hypotension. Therefore, always monitor the signs and symptoms of hypotension during Diovan medication.
- It is also not recommended for breastfeeding women. Always consult your doctor before using it during the breastfeeding period.
- It may increase potassium levels in your body or cause hyperkalemia. It changes kidney function. Therefore, you need to monitor potassium levels throughout this medication. It causes adverse effects like weight gain and swelling in the hands or legs.
Valsartan Interactions
Valsartan may interact with various drugs and food supplements. It causes adverse effects on your body.
Taking it with lithium supplements can increase the risk of lithium toxicity. Therefore, lithium levels need to be monitored during such medication.
ACE inhibitors such as lisinopril, enalapril, captopril, and other angiotensin-receptor blockers such as losartan or candesartan cannot be taken with valsartan tablets. It can increase your risk of high potassium levels, kidney damage, and low blood pressure or hypotension.
It may not be used with drugs that contain potassium supplements or salt that contains high potassium levels. Taking these medications or salts with valsartan may increase your potassium levels even more.
Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) such as ibuprofen or naproxen with valsartan may increase the risk of kidney problems. Hence, ask your doctor when taking it with NSAID.
Valsartan Alternative
Your doctor may use various alternative medicines rather than valsartan to control your blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. All these are antihypertensive drugs.
Some common alternatives of valsartan or Diovan are given below the table,
| Class of medicines | Name of medicine |
| Thiazides (diuretics) | Chlorothiazide |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | |
| Cyclopentthiazide | |
| Loop diuretics | Frusemide |
| Ethacrynic acid | |
| Bumetanide | |
| Potassium-sparing diuretics | Triamterene |
| Spironolactone | |
| Beta-blockers | Propranolol |
| Atenolol | |
| Metoprolol | |
| Oxprenolol | |
| Acebutalol | |
| Timolol | |
| Nadolol | |
| Pindolol | |
| Alpha-blockers | Phentolamine |
| Phenoxybenzamine hydrochloride | |
| Tolazoline | |
| Prazosin | |
| Terazosin | |
| Doxazosin | |
| Mixed alpha- and beta-blockers | Labetalol |
| Carvedilol | |
| ACE inhibitors | Captopril |
| Enalapril | |
| Lisinopril | |
| Ramipril | |
| Quinapril | |
| Trandolapril | |
| Spirapril | |
| Moexipril | |
| Calcium channel blockers | Verapamil |
| Nifedipine | |
| Diltiazem | |
| Felodipine | |
| Amlodipine | |
| Nicardipine | |
| Angiotensin II receptor blockers | Losartan |
| Irbesartan | |
| Candesartan | |
| Telmisartan | |
| Vasodilators | Hydralazine |
| Minoxidil | |
| Diazoxide | |
| Sodium nitroprusside |
Valsartan vs Losartan
Valsartan and losartan are the same class of drugs called angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). Therefore, they work by blocking the actions of angiotensin II, a hormone that causes blood vessels to tighten.
They are sold under two brand names Diovan and Cozaar. Both the drugs are available in generic versions. Valsartan oral tablets are available in the strength of 40 mg, 80 mg, 160 mg, and 320 mg but losartan oral tablets are available in the strength of 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg.
According to the clinical study, 50 mg of losartan and 80 mg of valsartan are similarly effective for lowering your blood pressure. But 160 mg or 320 mg valsartan doses may be more effective for lowering your blood pressure than losartan 100 mg dose.
The average retail price of valsartan or Diovan medication is more than that of losartan medication.