Health Benefits of Vitamin E
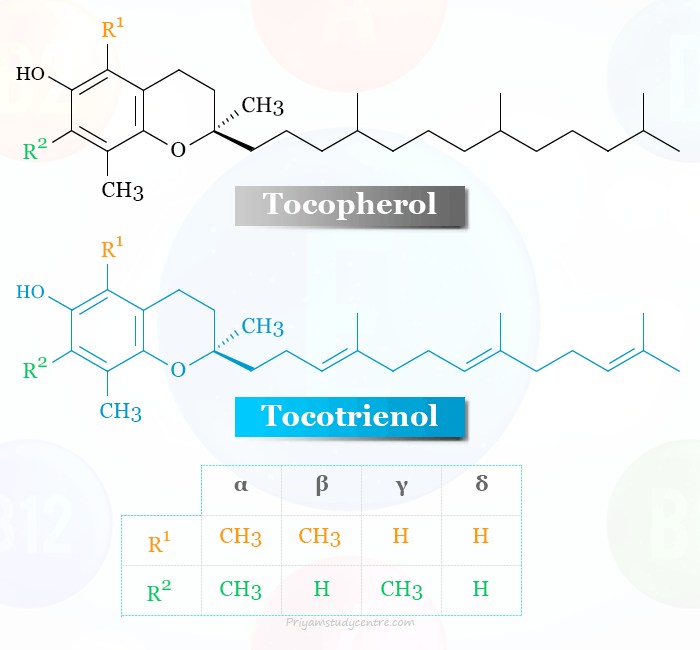
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin and a powerful antioxidant that is beneficial for immune health and cellular signaling in your body. The main health benefits of vitamin E observed due to its antioxidant properties that help to protect cells from free radicals which form when our bodies convert the food we eat into energy. It also formed due to various environmental pollution such as cigarette smoking, air pollution, and ultraviolet light from the sun. Vitamin E contains eight organic compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols but alpha-tocopherol is the only biologically active form used by the human body. A deficiency of vitamin E in the United States and other developed countries is rare because it is found in a variety of foods and supplements. The deficiency may be observed in people with certain genetic disorders and in premature infants.
Benefits of Vitamin E
Vitamin E is beneficial for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and eyes, and strengthens your immune health which benefits on illness and infection. It is also helpful in treating many other unhealthy conditions in humans but there is no good scientific evidence to support many of these uses.
Generally, people can get enough of this vitamin in their daily diet but it is also available in the form of supplements and skin care products. The main health benefits of vitamin E reached foods and supplements may include:
- Protect the body from free radicals
- Improving your immune system
- Improving your skin health
- Control your hair fall
- Help to improve vision
- Balancing cholesterol
- Balances hormones
- Decreasing the risk of cancer
- Help in cognitive decline/Alzheimer’s Disease
Protect the body from free radicals
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble micronutrient that has antioxidant properties. The powerful antioxidant abilities of various isomers of vitamin E can reduce the damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals may break down healthy cells in your body and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, oxidative stress, and age-related macular degeneration.
Free radicals are highly energetic molecules that are produced naturally during many biological processes such as the conversion of food into energy. They also enter your body due to environmental stress such as pollution, UV radiation, or smoke.
Vitamin E for the immune system
Vitamin E is found in higher concentrations in immune cells compared to other cells in your blood. It supports your immune system by the production of T cells which is essential for effective immune response.
Vitamin E is one of the most effective antioxidants that defend against oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that damage the lipid membranes and DNA of your cells.
If your body does not have enough antioxidants, the toxic free radicals can not be neutralized. Therefore, the lipid layers of cells can be damaged which can disrupt cell integrity. The deficiency may also cause DNA damage and protein oxidation which causes aging. Therefore, as an antioxidant, vitamin E supports your immune system and reduces oxidative stress.
Vitamin E benefits for skin
Vitamin E is found in various creams and oils for topical use. It is added to many cosmetic products such as anti-aging creams, eye serums, sunscreens, and makeup products. The most common health benefits of vitamin E for your skin may include:
- The antiinflammation properties of this vitamin may protect your skin from UV radiation. Taking vitamin E with vitamin C may be useful in decreasing signs of acne and eczema.
- Various research indicated that topical use of vitamin E reduced acute and chronic skin damage caused by ultraviolet rays from sunlight. It can remove scars, acne, and wrinkles because it speeds up cell regeneration. Therefore, it makes your skin look healthier and younger.
- Many researchers have shown that skin care products containing vitamin E can moisturize your skin. It works as a humectant that absorbs water into the skin and an emollient that traps water in the skin.
- Vitamin E oil is distinct from vitamin supplements because it is an excellent moisturizer for dry, patchy areas of the skin.
Benefits in menopause
Vitamin E is a proven remedy for hot flashes and night sweats during menopause. Naturally occurring mixture of tocopherols and tocotrienols is beneficial in the prevention of hot flashes, night heat, sleep disruption, bladder urgency and leaking, and other menopausal symptoms.
It is a useful remedy for early menopause when a woman may have occasional periods and her body is still capable of making some estrogen. This vitamin helps to stabilize or balance estrogen levels in women’s bodies. The hormone-balancing effect may be effective in improving mental clarity, mood changes, and better sleep.
It also helps to relieve vaginal dryness that faces many women during the menopausal period. Dryness or tightness of vaginal opening, post-coital bleeding, vaginal discharge, and bladder leakage occurs due to declining estrogen levels during the menopausal period.
It impacts women’s social lives, confidence, sex lives, and their partner relationships. Vitamin E reached foods and supplements may help to reduce such health conditions.
Vitamin E for hair fall
Earlier research suggests that it may improve scalp circulation and prevent hair fall in many people. However, more research is needed to understand the possible benefits of this vitamin for healthy hair.
he supplementation may improve hair growth in people who suffer from hair fall problems. It helps to reduce oxidative stress on the scalp which is linked to hair fall problems.
It may increase blood flow which encourages the growth of your hair. The oil reached with vitamin E helps seal out moisture, reduce breakage, and protect your hair from damage.
Help to improve vision
Vitamin E may protect eye cells from free radicals that break down your healthy eye tissue. It helps to decrease the age-related macular degeneration that is a common cause of blindness.
The National Eye Institute performs an Age-Related Eye Disease study and shows that a high dose of vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, and zinc is effective for vision and reduces 25 percent of age-related macular degeneration.
It also found that daily intake of high doses of vitamin E and vitamin A seems to improve healing and vision in people undergoing laser eye surgery.
Balancing cholesterol
The forms of this vitamin called tocotrienols may fight against cholesterol oxidation because they protect against free radicals that cause cholesterol oxidation. Oxidation of LDL-cholesterol promotes blockages in coronary arteries that lead to atherosclerosis and heart attacks. Therefore, vitamin E functions as an antioxidant that reduces the oxidation of cholesterol and lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Tocotrienols positively impact cardiovascular health due to their ability to reduce the activity of an enzyme (HMG-CoA reductase) that controls the production and synthesis of cholesterol.
Some research suggests that tocotrienols may improve arterial health, control high blood pressure, and reduce the risk of other heart-related conditions. However, much of this research has been done on animals rather than humans. Therefore, more studies on humans are needed in order to confirm these effects.
Decreasing the risk of cancer
The cancer-preventive activity of various isomers of vitamin E has been suggested by many researchers. However, several recent large-scale human trials with α-tocopherol failed to show a cancer-preventive effect.
Some scientific evidence suggests that the consumption of vitamin E may reduce the risk of certain forms of cancer.
A large, randomized SELECT trial of selenium and vitamin E with 400 IU daily supplementation may not reduce the risk for prostate cancer in healthy men aged 50 and older. However, men who had taken this vitamin had a higher risk of prostate cancer compared to men who did not take this.
Alzheimer’s Disease
An older review suggests that higher consumption of this vitamin from foods lowers the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of cognitive decline.
Researchers hypothesize that free radicals may damage the neurons over time and contribute to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. Therefore, sufficient supplementation might reduce the risk of such diseases.
Most clinical trials may not support these hypotheses and show that there are no beneficial results of vitamin E supplements for healthy or mildly impaired people to maintain good cognitive performance. Therefore, more research is needed to identify the health benefits of vitamin E in Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of cognitive decline.
Sources of Vitamin E
Vitamin E is found naturally in various plant and animal-based food sources. Gamma-tocopherol (γ-tocopherol) is the most common form in the North American diet. However, alpha-tocopherol (α-tocopherol) is the most biologically active form of this vitamin.
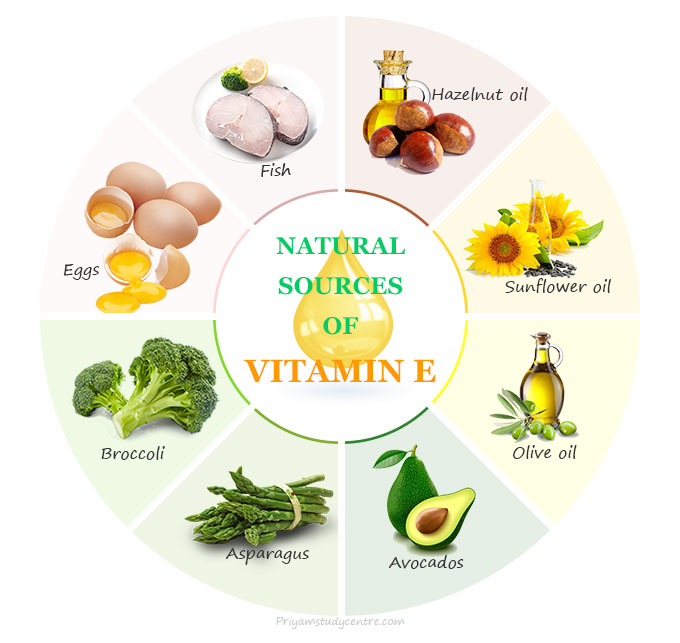
The daily recommended amounts of this vitamin may be fulfilled by eating the following foods given below the table,
| Plant-based source | Amount (mg / 100 g) |
Animal-based source | Amount (mg / 100 g) |
| Wheat germ oil | 150 | Fish | 1.0-2.8 |
| Hazelnut oil | 47 | Oysters | 1.7 |
| Sunflower oil | 41.1 | Butter | 1.6 |
| Almond oil | 39.2 | Cheese | 0.6-07 |
| Almonds | 25.6 | Eggs | 1.1 |
| Corn oil, olive oil | 14-15 | Chicken | 0.3 |
| Peanuts, Peanut butter | 9-9.3 | Pork | 0.1 |
| Avocados | 2.6 | Beef | 0.1 |
| Spinach, raw | 2.0 | Milk, whole | 0.1 |
| Asparagus | 1.5 | Milk, skim | 0.01 |
Dietary recommendations
The United States National Academy of Medicine suggests average requirements (EARs) and recommended dietary allowances (RDAs) for vitamin E. The EARs and RDAs recommended values vary by age and gender. The EAR value for women and men ages 14 and up is 12 mg/day and the RDA value is 15 mg/day.
The RDAs values for alpha-tocopherol in milligrams (mg) are given below in the table,
| Age | Daily recommended value (mg) | |
| children | ages 1–3 years | 6 |
| ages 4–8 years | 7 | |
| ages 9–13 years | 11 | |
| ages 14–18 years | 15 | |
| adults aged above 18 | 15 | |
| during pregnancy | 15 | |
| during lactation | 19 | |
Adequate intakes (AIs) are set when there is not sufficient information obtained from EARs and RDAs.
AIs were developed for healthy breastfed babies because insufficient data were obtained from RDAs. AI value for children ages 0–6 months is 4 mg/day and AI for children ages 7–12 months is 5 mg/day.
Vitamin E Deficiency
The deficiency is rare in the United States and other developing countries because it is found in a variety of foods and supplements.
The deficiency may also cause due to diseases where fat is not properly digested or absorbed. Therefore, digestive disorders such as pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and celiac disease may cause this vitamin deficiency.
Genetic abnormality is one of the most common reasons that cause alpha-tocopherol transfer protein (α-TTP) deficiency. Large amounts of dietary supplements of alpha-tocopherol are needed to overcome the lack of α-TTP.
The most common signs and symptoms of this vitamin deficiency may include:
- Vision problems (damage to the retina of the eyes or retinopathy)
- Peripheral neuropathy (nerve and muscle damage that results in loss of feeling in the arms and legs)
- Ataxia (loss of body movement control, muscle weakness)
- Weakened immune system
Vitamin E Supplement
It is a fat-soluble micronutrient and its dietary form is commonly esterified with acetic acid to generate tocopheryl acetate. It is also dissolved in vegetable oil to obtain a softgel capsule. The supplements typically contain alpha-tocopherol, although mixed products of other tocopherols and tocotrienols are also available in the market.
Most vitamin E supplements contain less than or equal to 67 mg (100 IU) of the nutrient which is substantially higher than the RDA recommended values. Smaller amounts are observed in various multivitamins or multimineral tablets.
Best vitamin E supplement
The supplements are available in a variety of forms such as capsules, softgels, liquid, and chewable tablets. The best brands of vitamin E supplements and their comparison to others are given below in the table,
| Brand | Cost around | Quantity | Format | Dosage (mg) |
| Nordic Naturals | $35 | 30 | softgel | 22.5 |
| Ancient Nutrition | $28 | 60 | capsule | 95 |
| Nature Made | $11 | 100 | softgel | 180 |
| Naturelo | $30 | 90 | capsule | 180 |
| Natures Plus | $36 | 90 | chewable tablet | 268 |
| Solgar | $15 | 2 fl oz | liquid | 100 |
| Kirkland Signature | $15 | 500 | softgel | 180 |
| Garden of Life | $29 | 60 | capsule | 125 |
| CVS Health | $15 | 100 | 180 |
Alpha-tocopherol is an ideal form of this vitamin because it is biologically active and most well-absorbed by your body.
The deficiency of vitamin E is rare for healthy people and supplements are generally not necessary unless your doctor instructs you to take them. Therefore, you can take supplements if your doctor confirms that you need or deficiency in vitamin E.