Water Molecule
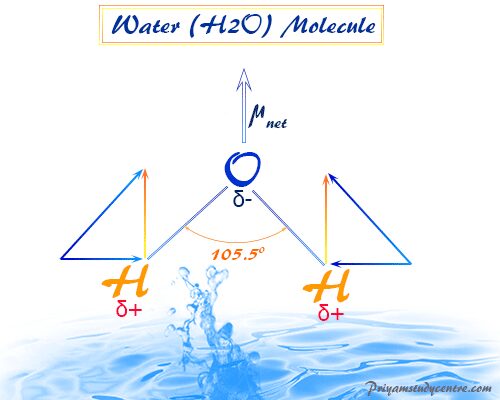
Water molecule, chemical formula H2O, made by oxygen and hydrogen atoms, exists in our earth’s environment as a crystalline solid, liquid, or gaseous form. Due to the presence of electron pairs on the oxygen atom, a water molecule forms a V-shape molecular structure with an H-O-H bond angle of 105.5°. Generally, pure water is a tasteless, colorless liquid that plays an important role in human body and living organisms. Natural water is an essential liquid that has the ability to dissolve many inorganic and organic compounds or chemical elements and according to dissolved minerals, it can be categorized into two types hard and soft water. Liquid and solid states of water arise due to the existence of hydrogen bonding. The amphiprotic substance water has the properties to act as an acid or base solution.
The molecular weight of H2O is 18 g mol−1 with melting and boiling points of 0 °C and 100 °C respectively. The pH of pure water at 25°C = 7. It suggests that the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the pure H2O solution is inversely proportional to each other.
Water is one of the most essential natural resources for the existence of human life on our earth. About 75% of the total water content covers the earth’s surface in the form of snow over mountains and in the form of liquid in springs, rivers, lakes, oceans, etc. Out of these 75%, only 1% is present in freshwater which is available for human use.
Importance of Water in Human Body
Water is essential for living beings and humans because all organisms need to maintain the level of water within their bodies in order to survive. The main biological importance of water in human life are:
- It provides the aqueous medium for all the cellular processes that take place in the human body.
- It is the solvent of life and necessary for the transportation of biomolecules from one part of the body to another in dissolved form.
- All the biochemical reactions that take place in our body and within the cells occur between the biological substances that dissolve in the aqueous medium.
- Every part of our body uses water to regulate body temperature and also makes our the majority of body weight.
- It helps to flush out waste from our bodies and control human brain function.
- H2O molecule is also required to maintain the balance of salts within the human body.
Water Pollution
The availability of hygienically safe and pure drinking water for home use is a big problem all over the world. Freshwater is found as frozen ice caps at poles and on the snow-covered mountains. The underground and water from rivers, lakes, and ponds is also fresh. However, it getting polluted day by day due to various human activities such as agriculture, industrial, mining, etc. It changes the physical, chemical, and biological quality of H2O.
We used many techniques to purify H2O from different sources before its utilization in various processes. For example, the reverse osmosis system can be used for the purification of drinking water.
Sewage disposal, industrial waste, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, fertilizer, insecticides, and detergents are the major pollutant that causes water pollution in our environment. It provides a home to pathogens that cause infections in humans. These pathogens include viruses, bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and protozoans. They cause various human diseases such as typhoid, cholera, jaundice, etc.
Thermal pollution sudden changes in the temperature of waterbody can be dangerous for aquatic organisms.
Structure of Water Molecule
The valance shell electronic configuration of the central oxygen atom in the water molecule is 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1. All these four atomic orbitals hybridize to form four equivalent sp3 tetrahedral hybrid orbitals.
Two of these four hybridized orbitals contain singly occupied electrons. These two orbitals overlap with two 1s-orbital of the hydrogen atom to form two covalent bond. The remaining two orbitals contain two electron pairs.
Due to the presence of electron pairs on the central atom, H2O is a v-shape molecule with an H-O-H bond angle of 105.5°.
Properties
H2O molecules are polar. It is a universal solvent that dissove most of the polar and ionic substances. It is the solvent of life and more important than any other single compound of life. The heat capacity of water is very high. Therefore, it takes a large amount of energy to raise one degree of temperature.
Liquid H2O molecules are denser than ice because ice crystals contain huge empty spaces. It has cohesive and adhesive properties. Cohesive properties of H2O responsible for surface tension. The contaminated water may show some acidic or basic behavior.
- The acidic behavior of contaminated water generally shows due to dissolved weak organic acids such as tannic acid or acetic acid and strong mineral acids like hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, etc. However, dissolved carbon dioxide is the main source of acidity in natural H2O.
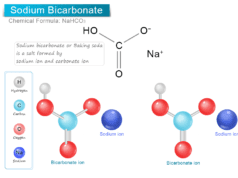
- The primary reason for the alkalinity of contaminated water is the salts of weak acids or strong bases. Therefore, the major portion of the alkalinity of surface water is caused by hydroxides, bicarbonates, and carbonates.
Physical Properties
A small quantity of H2O appears colorless but a large quantity of molecules is a blue color liquid due to the atomic absorption of red light.
It appears in two forms, hard and soft. Present-day, the hardness or softness and pH scale level of water change due to the formation of acid rain and dissolving materials. It has harmful effects on the biological systems of plants and animals.
| Properties of Water | ||
| Molecular formula | H2O | |
| Molar mass | 18 g mol−1 | |
| Melting point | 0°C or 32°F or 273.15K | |
| Boiling point | 99.98°C or 211.96°F or 373.13K | |
| Density (g/ml) | Liquid | Solid |
| 0°C: 0.9998396 25°C: 0.9970474 |
0°C: 0.9167 | |
| Conjugate acid base pair | Acid | Base |
| hydronium ion (H3O+) | hydroxide ion (OH−) | |
| Heat capacity | 75.385 ± 0.05 J mol−1 K−1 | |
| Crystal structure | hexagonal | |
| Dipole moment | 1.8546 D | |
Polarity of H2O
The electronegativity and electron affinity of oxygen is much greater than that of hydrogen. Therefore, electric polarization arises due to gaining a partial positive charge on hydrogen and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom.
The polarity of the H2O molecule comes from two facts,
- Dipole moment due to oxygen-hydrogen electronegativity differences.
- Presence of two-electron pairs in the central oxygen atom with v-shaped structure.
Conductivity of H2O
The pure solution is not a good conductor of electricity. It slightly dissociates and behaves like a weak electrolyte. The specific conductance of pure water at 25 °C has been found to be 0.58 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1.
Structure of Ice
The crystal structure of ice represented the different types of complex structures in chemistry. The ice molecule formed nine complex crystal lattices established according to the different ranges of temperature and pressure.
In ordinary forms, it freezes at 0°C and 1 atm pressure with a puckered hexagonal structure. In this structure, each H2O unit is surrounded tetrahedrally by the oxygen atoms of four other H2O molecules through hydrogen bonding extended over the entire structure.
What Happens When Ice Melts into Water?
In ice crystals, there are huge empty spaces. Each oxygen atom has two near and two distant neighbors.
- At a very low density and very low temperature of about −120 °C, the cubic crystal lattice of ice is observed. The experimental zero-point entropy of ice is 3.4 joule mol−1.
- When the number of H2O molecules is brought together, the positive end of one dipole attacks the negative end of the other dipole. Therefore, H2O molecules are associated together to form the cluster (H2O)n,
- In the gas phase of the water molecule, no such hydrogen bonding or association is found.
pH for Pure Water
The protons unite with a water molecule to produce H3O+ or hydronium ions. The acid-base neutralization process in H2O involves the diffusion of the proton to the base.
Pure H2O molecule gives equal concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions at equilibrium. Therefore, the chemical equilibrium reaction of H2O,
H2O → H+ + OH−
From the law of mass action, it can be observed that for pure water at 25 °C,
kw = k [H2O] = [H+] [OH−] = 10−14
Sorensen defined the pH of a solution as the negative logarithm of H+ ion concentration,
∴ pH = −log [H+]
The ionic product is constantly equal to 10−14. Therefore, the pH of pure water at 25°C = 7. It suggests that the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the H2O solution is inversely proportional to each other.
Pure H2O functions as an acid in the presence of a base stronger than itself. For example, when H2O reacts with ammonia, it functions as an acid.
NH3 (base) + H2O (acid) → NH4+ + OH−
In the presence of acids, it behaves like a base by accepting a proton. For example, pure H2O can accept a proton from an acidic hydrogen sulfate ion to form an H3O+ ion.
HSO4− + H2O → H3O+ + SO4−2
The hydrogen ion concentration in the H2O solution can be measured by pH meter via a glass electrode or a saturated calomel reference electrode. Generally, the pH of the H2O solution can be measured in order to calculate dissolved carbonate, bicarbonate, carbon dioxide concentration, corrosion, etc.
Hard and Soft Water
The universal solvent water is categorized into two types, hard and soft, according to dissolved minerals. Some of these minerals are beneficial for our health.
Hard Water
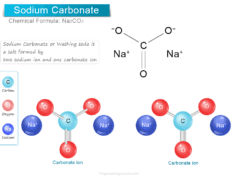
It contains common calcium and magnesium salt. These ions produce insoluble precipitates with shop material. Such types of solutions are termed hard water. Calcium and sodium bicarbonate make the solution temporarily hard.
When the solutions contain soluble sulfates of calcium or magnesium which are not precipitated by boiling are called permanent hard water.
Soft Water
On boiling, the temporary hardness of the water can be removed but the permanent hardness can not be removed by the easy process.
- Hard solutions are made soft by passing them through beds of insoluble aluminum sodium silicates or ion exchange resin (zeolites).
- A useful regent like EDTA or ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid or Calgon (sodium hexametaphosphate) is used in removing the hardness of water to make a soft solution.
Pure Water
Pure or purified water can be obtained after the removal of all kinds of impurities such as minerals and organic matter. Such purification is generally performed in microporous filtration, carbon filtration, and ultraviolet oxidation.
The most commonly used pure water for laboratory work is of two types, distilled and deionized form. Compared to distillation, deionization is a less expensive and cheaper way to purify H2O. However, deionization is not capable of producing H2O with the same purity and consistency. Therefore, distilled water may be used in replacement of deionization but the reverse is not always possible.
Distilled Water
Distilled water can be obtained in a distillation system where H2O can be heated to its boiling point. When producing steam obtained during heating is condensed the impurities are left behind and we can give distilled water.
Distillation generally removes all inorganic and organic contaminants including microorganisms. Therefore, such type of water molecule is very useful for laboratory work.
Deionized Water
A deionized type of pure H2O molecule can be obtained by the ion exchange method. Deionization is a physical process that uses ion exchange resins for exchanging H+ ions and OH− ions for dissolved contaminated ions.
In the ion exchange method, all mineral ions such as calcium, sodium, iron, copper, chloride, and sulfate are removed from water. However, the ion exchange method is not so efficient in eliminating unchanged organic molecules and microorganisms from water.