Chemistry and Environmental Science
Environmental chemistry is the branch of science where we study abiotic, biotic, energy components, and chemical elements of the ecosystem of our environment which are responsible for the origin and conservation of our life. Therefore, for learning chemistry of our environment, we need to know about the major components like air, water, soil, and sunlight in our ecosystem. The earth’s environment and air become heated or polluted due to the trapping of electromagnetic spectrum radiation (IR-radiation) by the greenhouse effect. The soil component is also polluted by acid rain or excess uses of the wrong acid fertilizer produced mainly from nitric acid and sulfuric acid. Therefore, the main aim of environmental science or chemistry is to study water pollution, air pollution, and soil pollution of our environment, and the remedial measures necessary to free it from this pollution.
Components of Environment
The environmental chemistry components are classified into three main types
- Abiotic components
- Biotic components
- Energy components
Abiotic Components
Any non-living environmental chemistry component used in our ecosystem is known as an abiotic component. These are present mostly in the lithosphere. The non-living environmental chemistry factors present in our environment may include,
Biotic Components of Ecosystem
The study of living components of our environment in environmental chemistry is known as biotic factors. The biotic factors present in our environment may include,
- Plants
- Animals including human
Energy Components of Environment
Energy components in environmental chemistry are globally leading end-to-end hydrocarbon for production and transport to sales for revenue generation. These may include
- Renewable energy (solar energy, wind energy, geochemical heat, hydroelectric power)
- Chemical energy
- Nuclear power
Origin of Life in Environmental Chemistry
The origin of life on earth timeline 3 billion years ago after changes in our environment. In 1953 Miller and Urey showed that lighting discharges through a mixture of methane gas, water, ammonia, and hydrogen produce significant amino acids for our earth. Therefore, it produces a significant amount of amino acids which is the essential product of the life cycle.
Abelson also showed that solar photon particle acts on carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and a small amount of hydrogen cyanide. But glycine, adenine, and other biological chemistry significant products formed by the chemical bonding of hydrogen cyanide and other biological environmental factors. Therefore these chemistry compounds undergo a series of chemical complex evaluations over millions of years to produce environmental living organisms.
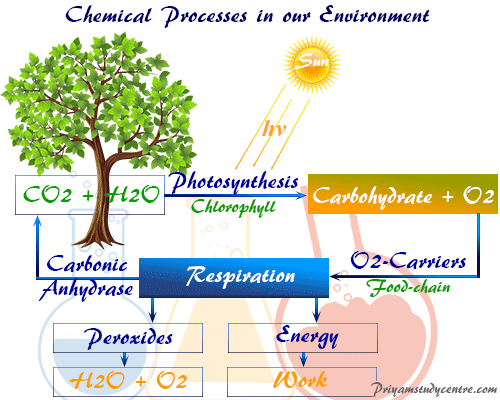
Photosynthesis in environmental chemistry generally appeared approximately 2.5 billion years ago in the Earth’s atmosphere. Therefore, our earth gradually reaches dioxygen and sustains the aerobic of life. These diverse biological processes of today have largely developed with this form of life.
Ecosystem Meaning
Major factors of our ecosystem may include,
- Animals, plants, microorganisms
- Biotic components
- Living organisms
- Abiotic or non-living material may include inorganic carbon dioxide, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus
- Organic substances like protein, and carbohydrate molecules
- Climate factors like specific heat and humidity
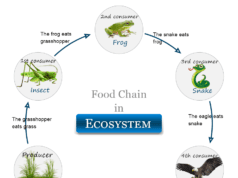
The ecosystem is the coexistence of the population of all species of living, and nonliving that live together in a particular area or an ecosystem is the living organism’s presence in its physical environment.
In other words, ecosystems are different types and dimensions of the community namely marine, aquatic, or terrestrial.
Marine life in the ecosystem is present in the sea and ocean. This marine life mostly balances the living organisms in the sea and non-living organisms in a seawater environment. The law of energy conservation follows in every ecosystem during the conservation of matter into free energy.
Importance of Environmental Chemistry
The substances present in the air, water, and soil and their adverse effects on animals and plants are called pollutants. Therefore, to save our environment from this pollution we need to recycle household products. These include waste, sewage, garbage, and much toxic industrial waste.
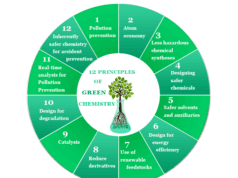
The study of green chemistry was introduced in 1990 to protect our environment from toxic environmental elements used in our daily lives.
Production of some substances produced from the oxidation of daily uses chemical reactions is toxic. Hence we need to decrease the release of toxic chemicals into the atmosphere. The effort has been made during use of chemicals from various oxidation reactions.
According to environmental chemistry, the presence of the ultraviolet emission spectrum, sound waves, microwaves, and chemical catalysts (enzymes) are harmful to our enviorment.