Durg Verapamil
Verapamil drug is a class of calcium channel blockers medicine uses widely to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), angina, supraventricular tachycardia, migraines, and cluster headaches. The tablet and injection of verapamil are sold in the market under various trade names. Verapamil poisoning can cause serious types of cardiac side effects such as heart block, conduction abnormalities, hypotension, and even death. Therefore, it is not recommended for people who suffer from slow heart rate or heart problems. It is also not taken during pregnancy because verapamil causes fetus problems during pregnancy.
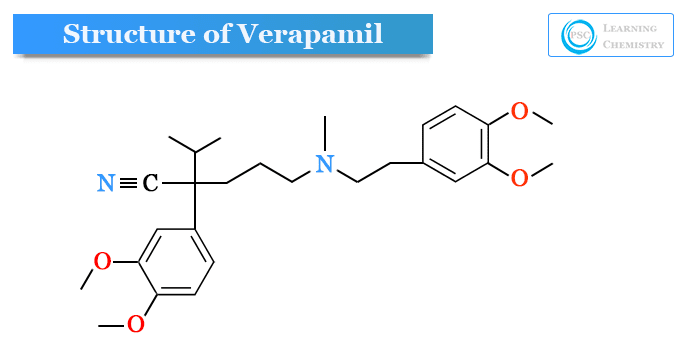
Verapamil or 5-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenethyl)methylamino]-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)isopropylvaleronitrile is synthesized by alkylating 3,4-dimethoxyphenylacetonitrile with isopropyl chloride in the presence of sodium amide. The subsequent condensation of intermediate with 3,4-N-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethyl]-N-3-(chloropropyl)-N-methylamine to form dl-verapamil.
Verapamil Uses
Verapamil is a list of essential medicines approved by the United States and the World Health Organization. It is used for the treatment and prevention of high blood pressure, angina, supraventricular tachycardia, migraines, cluster headaches, etc.
For High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
Verapamil is used commonly to treat high blood pressure or hypertension and angina or chest pain caused by not enough blood flow to the heart. It should be worked by affecting the movement of calcium into the heart cells and blood vessels. Verapamil can relax the blood vessels of our body. Relaxing blood vessels can improve blood and oxygen flow from the vessel to the heart.
Controlling high blood pressure in our bodies can help to prevent several health problems such as strokes, heart attacks, and kidney diseases.
Verapamil for Migraine
Several people in the world experience chronic migraine and cluster headaches but verapamil is not a primary option to treat migraine or cluster headache problems. There are various effective medications are available for the treatment or prevention of migraine and cluster headaches. It is worked by relaxing blood vessels and allowing to flow of blood more freely from the vessel to the heart.
In the past, doctors thought increasing blood pressure in vessels might cause migraine attacks. Therefore, doctors can prescribe verapamil for the treatment and prevention of migraine attacks.
It is not an FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved medicine for treating migraine or cluster headaches. Verapamil is an off-label medicine for the treatment of migraine or cluster headaches.
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Verapamil is the most widely used calcium antagonist or drug to treat cardiac arrhythmias. It is a class of medicine which extremely effective for the acute treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. It works through the atrioventricular node, reducing ventricular response to atrial flutter and fibrillation.
Verapamil Dosage
Verapamil is sold under different brands or trade names,
- Isoptin SR: 240 mg (light green), 180 mg (light pink), and 120 mg (light violet).
- Calan SR: 120 mg, 180 mg and 240 mg.
- Covera HS: 180 mg and 240 mg tablets.
- Isoptin IV: Verapamil Hydrochloride Injection, USP 2.5 mg/mL.
- Calan: 40 mg, 80 mg and 120 mg tablets.
- Verap: 40 mg tablet
- Verelan: 120 mg to 360 mg gelatin capsules.
The injectable solution is available in the market at 2.5 mg/mL. Most of the tablets, capsules, and extended release dosages of verapamil are available in the market at 40 mg, 80 mg, 100 mg, 120 mg, 180 mg, 240 mg, and 360 mg.
Possible Dosages
The dosage of verapamil should depend mainly on,
- Age of the patient
- Treating conditions of the patient
- Other medical conditions
- Response to the first dose
Therefore, we should advise medical professionals before taking verapamil. Possible dosages for angina and high blood pressure (hypertension) used by several doctors are given in the table,
| For treatment |
Verapamil dosage | ||
| Immediate release | Extended-release | ||
| Angina |
For adult | 80 mg orally every 8 hours initially. The usual range is 80 to 120 mg orally every 8 hours but does not exceed 480 mg per day | 180 mg/day orally at bedtime initially and maintenance 180 to 540 mg/day orally at bedtime |
| For geriatric | 80 mg orally every 8 hours initially. The usual range is 80 to 120 mg orally every 8 hours but does not exceed 480 mg per day | 180 mg/day orally at bedtime initially and maintenance 180 to 540 mg/day orally at bedtime | |
| Hypertension | For adult | 80 mg orally every 8 hours initially and maintenance 80 to 320 mg orally for every 12 hours | 120 to 180 mg/day orally given in the morning and increases up to 360 mg/day. |
| For geriatric | 40 mg orally every 8 hours initially and maintenance 80 to 320 mg orally for every 12 hours | Calan SR, Isoptin SR, Verelan 120 mg per day orally given in the morning | |
Supraventricular Arrhythmia and Atrial Fibrillation or Flutter
- 5 to 10 mg dose may be repeated after 15-30 minutes.
- Alternatively, 0.075-0.15 mg/kg over 2 minutes, and the dose may be repeated once after 30 minutes of the first dose.
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
For prevention or immediate release of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia 240 to 480 mg/day orally divided every 6 to 8 hours.
Supraventricular Tachycardia for Pediatric
For Children Less than 1 Year
- Initially 0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg IV bolus over at least 2 minutes. The usual single dose range is 0.75 to 1 mg.
- 0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg IV repeated after 30 minutes if the initial dose response is inadequate.
For Children from 1 to 15 Years
- 0.1 to 0.3 mg/kg IV bolus over at least 2 minutes is given initially. The usual single dose range is between 2 to 5 mg.
- 0.1 to 0.3 mg/kg IV is given after 30 minutes if the initial dose-response is inadequate. The usual single dose range is between 2 to 5 mg.
Migraine (Off-Label)
160 to 320 mg orally every 6 to 8 hours. It is not a primary option to treat migraine or cluster headache problems. There are several effective medication options available to treat migraine or cluster headaches.
Overdose
Acute overdose may cause nausea, weakness, slow heart rate, dizziness, low blood pressure, and abnormal heart rhythms. Serious symptoms of overdose or verapamil poisoning are very low blood pressure, heart rhythm problems, kidney problems, convulsions, slow heart rate, etc.
Therefore, you can always take the exact dose of verapamil prescribed by your doctor. You cannot be taking a dose by your own decision.
Verapamil Side Effects
The side effects of verapamil are varied from person to person.
- The side effects for most people who use verapamil daily are mild.
- Serious side effects of verapamil can be observed in many people.
If you experience a serious or life-threatening reaction call the emergency medical center or doctors immediately. Your doctor or pharmacist can provide more information about all the side effects.
- Constipation, cough, headache, low blood pressure, and drowsiness are the most common side effects of verapamil medicine.
- Serious side effects after taking verapamil are difficulty breathing, dizziness, fainting, changes in heart rhythm, palpitations, chest pain, skin rash, swelling of your legs or ankles, etc.
Health Problems Person
The person who suffers from below health problems can not take verapamil without consulting their doctor,
- It may raise the enzyme levels for some people. Therefore, they cannot take such medicine without a proper prescription. Fatigue, fever, and pain in the right upper area of your belly are common symptoms for such people after taking verapamil.
- If you have certain heart rhythm problems, it is not the right choice for you.
- If you drink alcohol, it is not the right choice for you. Drinking alcohol can increase the side effects of verapamil.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women may not be taking verapamil because it is not safe to use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.