Atomic Structure and Theory
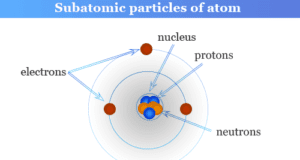
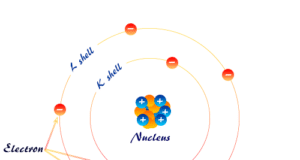
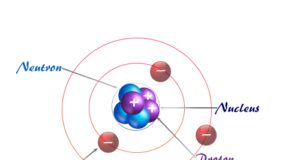
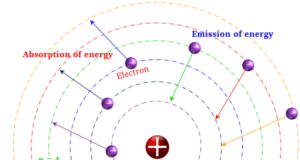
Atomic structure and atomic theory describe the smallest unit of matter or element which contains subatomic particles of atoms such as electrons, protons, and neutrons. Every state of matter contains neutral or ionized atoms. An atom is considered to be made up of a tiny nucleus carrying neutrons and protons where the tiny nucleus is surrounded by a certain number of negatively charged electrons in a definite order. To know the arrangement of electrons and protons within an atom, many scientists proposed various atomic models or structures. According to an earlier atomic model, the extranuclear electrons rotate around the nucleus in some definite energy level or orbit.
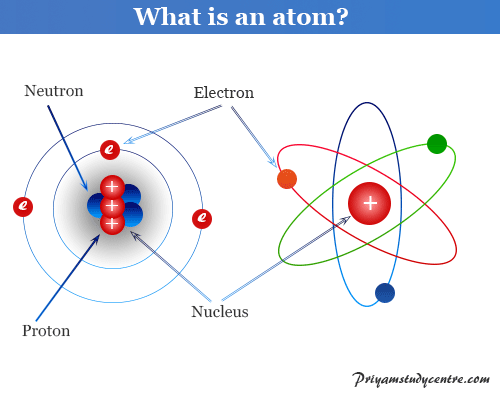
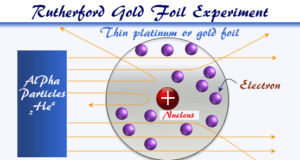
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, the atom was an indivisible and indestructible part of elements. However, after the discovery of two fundamental particles (electrons and protons) inside the atom, led to the failure of the aspect of Dalton’s theory.
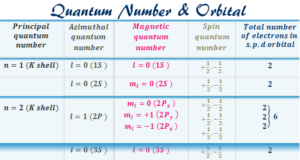
Today the electrons are considered to be standing waves. The probability of finding a particular electron in a certain region of space around the nucleus is called orbitals. The electronic structure of an atom holds the key to understanding the chemical properties, chemical bonding, and chemical reactions of the elements. However, the Journey from the Daltonian model to the modern atomic structure is a long and arduous one.
In learning chemistry or biology, every chemical or biological molecule contains neutral or ionized atoms with a definite order arrangement.
Atoms and Atomic Structure
In learning chemistry or physics, atoms are the smallest particles of an element which may or may not have independent existence but take part in a chemical reaction. The atoms of hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are not capable of independent existence. However, atoms of helium, neon, argon, and metal are capable of existing independently.
Atoms are the basic building blocks of all 118 periodic table elements and matter. They are very small in size and their radios can be measured in nanometers.
1/109 m = 1 nm
∴ 1 m = 10−9 nm
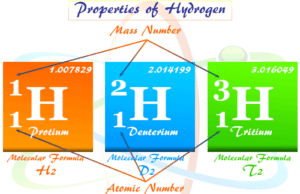
For example, hydrogen is the smallest atom among the periodic table elements. The radius of the hydrogen atom = 0.0529 nm.