Four States of Matter
States of matter or all four states of matter in science define one of the distant forms in which the aggregation of atoms, ions, and molecules occurs in nature. In learning chemistry or physics, the various types of substances that made up matter can be divided mainly into four states or phases such as solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. The states or phases of matter can change their states depending on the conditions like pressure and temperature.
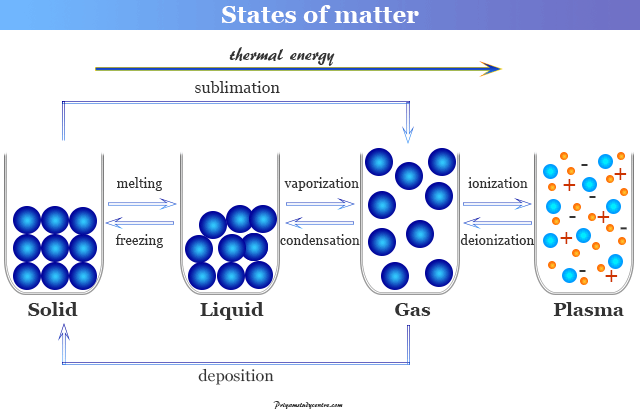
We observed all states of matter through daily human experience. For example, a solid changes to a liquid, gaseous, or plasma state by increasing temperature. Therefore, heat is added to the substances to change the states of matter from solid to liquid to gas to plasma.
Particles of Matter
When we study the state of matter, we find particles that constitute a certain matter. Some important properties of such particles of matter are:
- Matter is made up of particles that differ in shape, size, and nature from one matter to another.
- The particles of matter are very small or tiny and we cannot see them individually with our naked eye.
- In a state of matter, particles are continuously moving. It suggests that they process some energy, called kinetic energy. Therefore, when the temperature rises, the kinetic energy of the particles increases and they move faster.
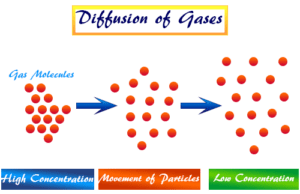
- The particles of matter have a tendency to diffuse or intermix with each other. Diffusion is the process in which particles of matter move from higher concentration to lower concentration and go until a uniform mixture is formed.
- Particles of various states of matter attract each other by intermolecular force of attraction. It keeps the particles together and varies from one state of matter to another.
Solid, Liquid, and Gases
Solid is changing to liquid at its melting point. Similarly, liquid changes to a gas at its boiling point. If heat is high enough, the state is entered into plasma. Two types of opposing molecular forces derive the states of matter.
- One is molecular forces of attraction which tend to hold the molecules together.
- Another is disruptive forces due to the thermal energy of the molecules.
Solid State of Matter
The solid-state of matter has a definite volume and shape. Therefore, component particles like atoms, ions, or molecules are closed together and arranged in a fixed place.
Properties of Solid State of Matter
Sugar, sand, rocks, stones, and metals like iron, copper, aluminum, gold, silver, and lead are common examples of matter that exist in the solid state. Some important properties of the solid state of matter are:
- In the solid state of matter, the forces of attraction between the atoms, ions, or molecules are much greater than the thermal energy.
- Solids have definite shapes, distinct boundaries, and fixed volume. Therefore, the compressibility of solid matter is negligible.
- The molecules in the solid state do not possess any translational energy.
- They have only vibrational energy. Therefore, they can vibrate about their mean position.
- The rigidity of most solids is very high because they may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape.
- Solids differ from liquids and gases in respect of size, shape, and volume.
- It changes to liquid with the addition of heat energy.
- Generally, solids have higher densities compared to their liquid or gaseous forms.
Liquid State of Matter
Matter in the liquid state has a fixed volume but it contains variable shapes. Therefore, liquid can adapt to the shape of the container where it can be placed. Water, milk, juice, oil, kerosene, petrol, alcohol, glycerol, and benzene are common examples of matter that exist in the liquid state.
In a liquid state, the forces of attraction are greater than the thermal energy. The liquid molecule has kinetic energy but it cannot go very far due to larger forces of attraction amongst them. Due to this fact, liquid has a definite volume, but that does not have a definite shape. They take the shape of the vessel in which they are placed.
Properties of Liquid State of Matter
In general, the liquid state is more denser and less compressible than gases. On cooling a gas changes into the liquid state and further cooling, the liquid freezes into the solid state. Therefore, the liquid state is the intermediate between the gaseous and solid states of matter.
In fact, a liquid has some of the properties of solid and gas. Some important properties of the liquid state of matter are:
- Liquids are one of the four states of matter in which they do not contain a definite shape. Therefore, they take up the shape in which they are kept.
- Liquids are not rigid because they change their shape easily and flow on a solid surface.
- The three states such as solids, liquids, and gases can diffuse into liquids. The atmospheric gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse and dissove in water. Such processes are essential for the survival of aquatic animals and plants. For example, aquatic animals can breathe in water due to the presence of dissove oxygen in the water.
- The rate of diffusion in the liquid state is higher than that of the solid state. This is due to the fact that in a liquid state, particles have greater space between each other compared to the particles in the solid state.
- The attraction force between the particles in the liquid state is greater than that of the gaseous state but less than that of the solid state.
- The density of a liquid is generally less than that of its solid form because particles in liquid form are less denser than that of its solid form. For exception, the density of solid water (ice) is less than that of the liquid form of water and ice floats on water.
Gaseous States of Matter
The gaseous state of matter is characterized by a lack of definite volume and shape. In gaseous states, the matter has the property of filling any available space to a uniform density. Low density and high compressibility are also the characteristics of gases.
If the thermal energy is much greater than the forces of attraction, then we find the gaseous state of matter. Molecules in a gaseous state move at very high speeds. Air is an example of a gaseous state of matter where it contains a mixture of gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, inert gases, etc. Other examples of gaseous matter are hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen dioxide, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, etc.
The forces of attraction amongst them are not sufficient to bind the molecules in one place. All the gases are found to expand to the same extent when heated to the same interval of temperature.
Properties of Gaseous State of Matter
In the gaseous state of matter, the thermal expansion is also the same. Gases have properties to obey some simple common pressure, volume, temperature, and mole number relation. These are called gas laws such as Charles law, Boyles Law, Ideal gas law, Van der Waals equation, etc.
- The common and most important properties of the liquid state of matter are:
- Gases are called fluids because they have a tendency to flow as liquids do.
- The diffusing property of gases is high because particles in the gases move very fast and there is a large space between them.
- Gases are highly compressible in nature and they can compressed in a small cylinder. This fact is useful for transporting a large amount of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), for our home uses, Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicle fuel, and oxygen supplied to hospitals in a small cylinder.
- In a gaseous state, the particles move randomly at high speed and exert pressure on the wall of the container in which they are kept.
- The density of gases is minimum and a gas is much lighter compared to the same volume of a solid or a liquid form.
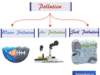
Plasma States of Matter
Plasma is one of four fundamental states of matter that contains a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. Like gases, the plasma state has no fixed shape and volume and is less dense than the liquid or solid state. In modern science or technology, the plasma state of matter can be used for making television or many electronic devices.
Properties of Plasma State of Matter
This state of matter is mostly found in the sun and stars of our universe. Artificially, plasma can be generated by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to strong electromagnetic radiation or a strong magnetic field.
The most common and important properties of the plasma state of matter are:
- The plasma state is electrically conductive because it contains charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons.
- Plasma may respond to electromagnetic fields. This technology can be used for making many modern devices such as plasma televisions.
- Depending on temperature and density, plasma may contain a certain number of neutral particles which make plasma partially ionized. Examples of partially ionized plasmas are neon signs and lightning
- Unlike the phase transitions between the other three states (solid, liquid, and gas), the transition to plasma is not well defined.
Change of States of Matter
In our daily lives, we come across various substances that exist in solid, liquid, and gaseous states of matter. Water is the most common example of matter that exists in solid (ice), liquid (water), and gaseous (water vapor) states.
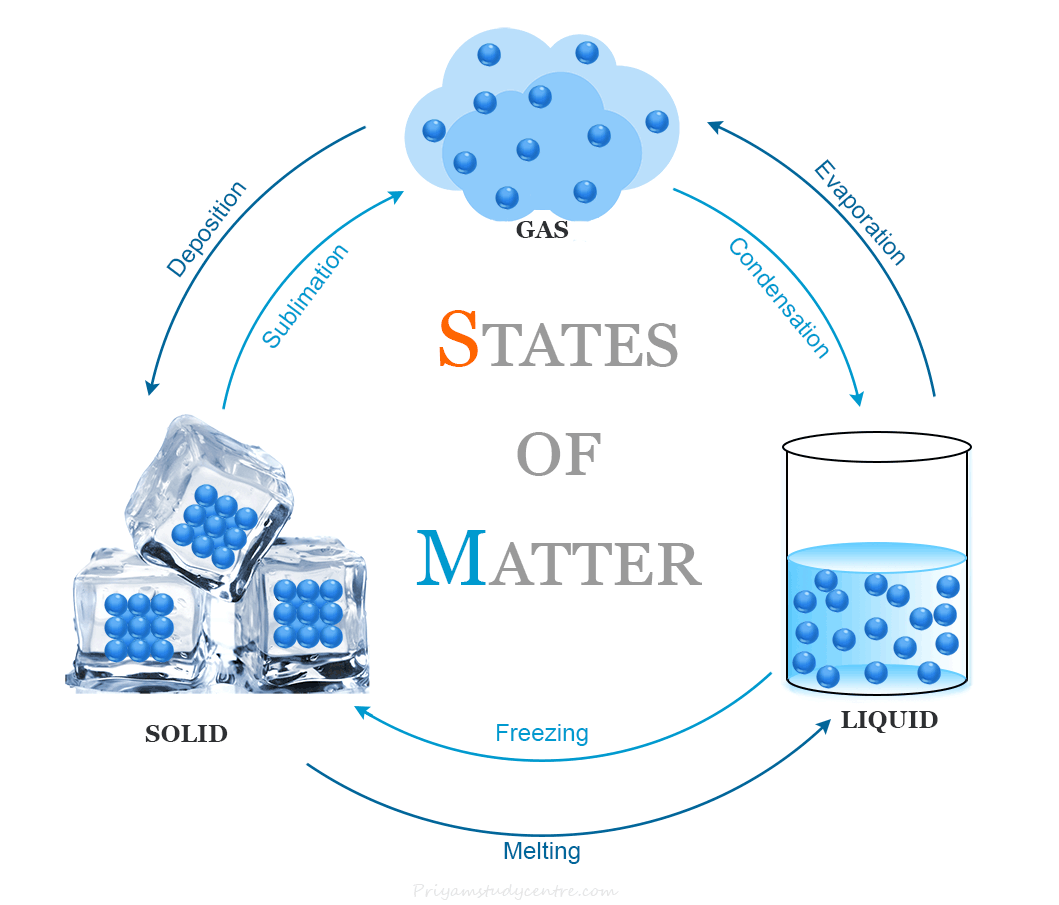
The states of matter are interconvertible and they can interchange by changing their temperature and pressure. The phenomenon of change of matte from one state to another and back to the original by altering the conditions of temperature and pressure is called the interconversion of states of matter.
The following six terms are involved in the change of states of matter,
- Fusion or Melting
- Boiling
- Sublimation
- Vapourization
- Freezing
- Condensation
Fusion or Melting
The fusion or melting is the process of conversion of matter from its solid state to its liquid state at specific conditions of temperature and pressure. The definite temperature at which a solid form of matter starts melting is called the melting point.
The melting point can indicate the strength of attraction between the particles of a solid. Therefore, a high melting substance has a greater force of attraction between its constituent particles. For example, iron has a higher force of attraction between its constituent particles than ice because iron has a higher melting point than ice.
Boiling
Boiling is the process of conversion of matter from its liquid state to its gaseous state at specific conditions of temperature and pressure.
The temperature at which a liquid form of matter starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is called its boiling point. At boiling point, particles from the bulk of the liquid gain enough energy to change into vapour state.
Sublimation
The process of changing of solid state directly into a gaseous state by heating or a gaseous state changes directly into a solid state by cooling without passing through the liquid state is called sublimation.
Dry ice (frozen form of carbon dioxide) is the best example of sublimation. When dry ice gets exposed to air, it directly changes its state from solid to gas which appears as fog. Other examples of chemical compounds which undergo sublimation are naphthalene, camphor, iodine, ammonium chloride, etc.
Vapourization
Vaporization is the process of conversion of matter from its liquid or solid state to its gaseous state at specific conditions of temperature and pressure.
When conditions allow the formation of vapour bubbles within a liquid, the vaporization process is called boiling and direct conversion from solid state to vapour state without appearing liquid state is called sublimation. Heat can be supplied to a solid or liquid to perform the vaporization process.
Freezing
Freezing is a process of conversion of matter from its liquid state to solid state when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. It is the reverse process of fusion or melting.
The definite temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid by giving out heat energy at one atm pressure is called the freezing point of such liquid. Freezing is a common state of matter that is used widely for food preservation. It slows down the decay of preserved food items and also slows the growth of microorganisms that may damage our foods.
Condensation
Condensation is the process of conversion of matter from its gaseous state to its liquid state at specific conditions of temperature and pressure. It is the reverse process of vaporization of a liquid.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What state of matter is fire?
In a candle flame or small fire, most of the matter found in a flame contains hot gases. A very hot fire releases enough energy to ionize the gaseous atoms found in fire and form plasma states of matter.
The distance between particles and their electrical charge can differentiate the plasma state from the gaseous state of matter. The charged particles (ions) in the plasma state of matter are much more widely spaced than the particles (molecules, atoms, and ions) present in the gaseous state of matter.
Who discovered the plasma state of matter?
Plasma was first identified by Sir William Crookes in his laboratory but systematic studies of plasma started with the research of Irving Langmuir and his colleagues in the 1920s.
Which state of matter has the highest kinetic energy?
The plasma state of matter has the highest kinetic energy among the four fundamental states. This is because the particles (ions) in a plasma state move randomly at a higher speed than the particles in a solid, liquid, or gas of the same substance. If we consider three states of matter then solid has the lowest kinetic energy and gas has the highest kinetic energy.
Which state of matter has the highest density?
Generally, the solid state of matter has the highest density as compared to its liquid and gaseous forms but ice has a lower density than water. Hence solid ice is lighter than water and it floats easily on water.
Which state of matter has the lowest density?
When we consider three states of matter solid, liquid, and gaseous, the density of the gaseous state is lower because a gas is much lighter than the same volume of a solid or a liquid.
If we consider four states of matter, the density of the plasma state is lower because it is much lighter than other phases. The plasma state of the matter is an electrically quasineutral medium of unbound positive and negative particles.
How many states of matter are there in the universe?
There are seven states of matter found in our universe but four states such as solid, liquid, gas, and plasma exist on our earth.
The seven states or phases of matter present in our universe are solids, liquids, gases, plasma, Bose-Einstein condensates, quark-gluon plasma, and degenerate matter.