Gel Electrophoresis System
Electrophoresis in analytical chemistry is a system of analysis or separation process of dispersed particles relative to a fluid or gel under the influence of the electric field due to different rates of migration. Capillary and gel electrophoresis are the most common types of electrophoresis that we use for the separation of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) or proteins based on their size and electrical charge. In analytical chemistry, gel and capillary electrophoresis machines or apparatus are widely used to test biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, nucleotides, colloids, proteins, and enzymes in the human body. The choice of gel largely depends upon the molecular size and chemical properties of the substances to be separated. The following process is used in the gel electrophoresis machine,
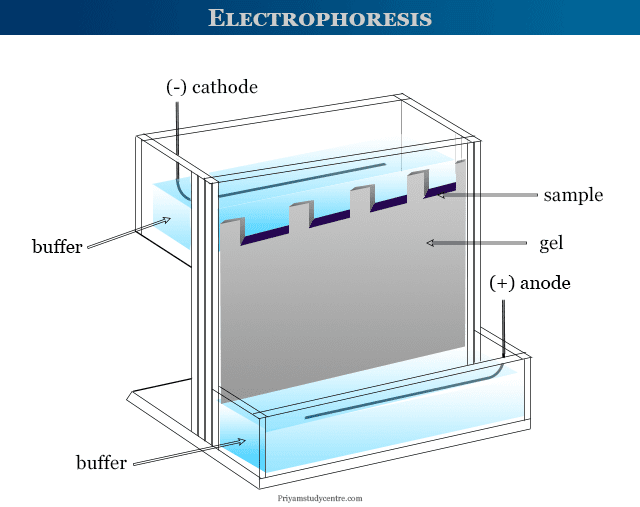
In recent years exciting discoveries have been made in the field of gel and capillary electrophoresis. An electrophoresis system in analytical chemistry is used widely in biochemistry and medicine to analyze or separate biomolecules and pharmaceuticals.
In electrophoresis, an electric current is used to move the biomolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, etc) through a gel or other matrix. The pores present in the gel or matrix work by allowing smaller molecules to move faster than larger molecules.
Electrophoresis Machine
An electrophoresis machine contains several key components, each with a specific function for separating charged molecules. The main components of an electrophoresis machine are:
- Buffer
- Wicks
- Support medium
- Cover
- Power supply
- Densitometer
Buffer in Electrophoresis
Buffer in electrophoresis machine used for carrying current and maintaining the pH of the analyzed medium. Therefore, optimum ionic strength of the buffer is necessary for good test results.
A higher ionic strength may increase the share of current carried by buffer ions and generate heat. Therefore, it slows down the sample migration and increases the diffusion of separation bands. Similarly, the low ionic strength of the buffer may also reduce resolution due to low current passing through the medium.
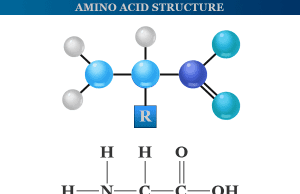
The ionization of biomolecules (proteins and amino acids) depends on the pH of the buffer. Alteration in the pH of the can alter the direction and velocity of migration of biomolecules. Therefore, Used for carrying current and maintaining the pH of the medium.
Wicks
Supporting medium with buffer solution to complete the circuit of capillary or gel electrophoresis system. It is used for connecting buffer solution with gel or other supporting medium.
Supporting Media Used in Electrophoresis
Supporting media is the matrix or gel in which separation takes place. Different types of supporting mediums are used for the separation of different biomolecules. The most common supporting mediums are:
Whatman Filter Paper
Whatman filter paper is a poor supporting medium because the resolution of separated analytes is very poor due to the higher diffusion.
Cellulose Acetate
Cellulose acetate is expensive supporting media in a gel electrophoresis system but the resolution of separated bands is far sharper than paper electrophoresis. Therefore, it is used widely for separating lipoproteins, proteins, enzyme isoforms, and hemoglobin.
Agarose Gel in Electrophoresis
Agarose gel in electrophoresis forms a viscous solution when dissolved in a hot buffered solution but solidifies after cooling. Therefore, agarose gel supporting medium is used for the separation of serum proteins, hemoglobin, and nucleic acids, as well as products obtained from polymerase chain reaction or PCR test.
Polyacrylamide Gel in Electrophoresis
Polyacrylamide gel is formed when a polymerization reaction occurs between acrylamide and bis-acrylamide in the presence of ammonium persulfate, N,N,N’N’-tetramethylethylenediamine, and riboflavin under ultraviolet rays.
The pore size of such gel can be controlled by adjusting the concentration of monomers. Due to its excellent resolution and minimum interaction, polyacrylamide gel can be used for various analysis processes to analyze biomolecules such as proteins, peptides, nucleic acid (DNA and RNA), and nucleotides.
Cover
A cover is used to reduce the evaporation of the buffer and prevent contamination during the electrophoresis. The gel chamber must have a lid or cover for safety operation to prevent accidental contact with energized electrodes or buffer solutions.
Power supply
Electricity for the movement of charged particles in the electrophoretic medium. The mobility of the analyzed particle is proportional to the potential gradient or voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
Particles with a negative charge always go in the direction of the positive pole but a particle with a positive charge moves in the direction of the negative pole. In gel electrophoresis system, the positive pole refers to the anode and the negative pole refers to the cathode.
Densitometer
A device that is used to measure the degree of darkness or optical density. The densitometer represents the bands as peaks of the electrophoresis test.
Such bands or peaks are used for making a graph or electrophoregram. The electrophoregrams are printed on a recorder chart or computer display.
Gel Electrophoresis Process
Gel electrophoresis is a technique that works for fractionating substances such as proteins, enzymes, DNA, and RNA according to their molecular sizes.
It has a stationary phase consisting of a heterogeneous cross-linked polymer gel. Agar, agarose, and polyacrylamide are the most common types of gel which we use in electrophoresis instruments.
They are available in the market under the trade names,
- BioGel
- Sephadex
- Styragel
- Agarose
The mechanism is based on the different permission rates of each solute molecule in the interior gels.
Using an electric field, proteins, enzymes, DNA, and RNA can move through a gel made of agar, agarose, polyacrylamide, etc. The electric field contains a negative electrode at one end which pushes the molecules through the gel and a positive electrode at the other end which pulls the molecules through the gel.
When the electric field is applied, the larger molecules move more slowly through the gel while the smaller molecules move faster through the gel. By the flow of liquid, molecules diffused all the parts of the gel. Only those molecules having larger sizes remain behind the gel.
Buffers in gel carry current and are used to maintain the pH value. It contains plenty of ions that carry a passage of electricity. For analysis of nucleic acids such as DNA or RNA, we used Tris/Acetate/EDTA (TAE) or Tris/Borate/EDTA (TBE) as a buffer.
Principle of Electrophoresis
If a charged foreign phase is subjected to a potential gradient, the foreign phase migrates through a continuous medium to the electrode according to the sign of the charge on the particle.
- Electrophoresis of positively charged particles or cations is called cataphoresis.
- Electrophoresis of negatively charged particles or anions is called anaphoresis.
It establishes the basic concentration gradient across the system. Colloids, proteins, DNA, RNA, and enzymes show particular electrophoretic mobilities and isoelectric points. These properties can be used for the identification of substances.
Generally, the term electrophoresis is used for the transport of charged solutes through paper or gels under the influence of potential gradients.
The migration of charged particles through the instrument depends on the surface, changes, applied voltage, electrolytic concentration, ionic strength, pH scale, viscosity, and other properties of the migration medium. Ions migrating in one direction are affected by the ionic mobility of other ions moving in the opposite direction.
It is used to compare two types of proteins in the human body albumin and globulins with similar molecular weights. The mobility of compact globular proteins is faster than that of fibrous proteins.
The mobility of the analyzed molecule is inversely proportional to the size and directly proportional to the net charge of such molecule.
Applications of Electrophoresis
- Large biological molecules can be separated and purified by electrophoretic instruments.
- Gel or capillary electrophoresis is widely used in forensics, genetics, microbiology, and biological chemistry for the analysis and separation of samples.
- It is applied for the separation of proteins, enzymes, DNA, RNA, and biopolymers.
- Electrophoresis instruments are also used widely in the separation of inorganic ions and clinical diagnosis.
- Inorganic separations are most readily achieved in the presence of complexing agents like EDTA.
Some important applications of gel or capillary electrophoresis machine or apparatus are given below,
Application of DNA Fragments Analysis
One of the most important applications of electrophoresis is the analysis of DNA and the study of DNA fragments. On the application of an electric field, DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid breaks down into large and small fragments.
It occurs because different parts of DNA fragments are affected by different scales of electric current. Now gel electrophoresis system is used to separate and analysis of different fragments of DNA samples.
Application of Electrophoresis on Proteins
Proteins are important building blocks of our body because they form the structural part of most organs and make various enzymes and hormones that regulate various biological activities in our body. Protein electrophoresis is a laboratory technique for analyzing or separating proteins in an analytical sample based on their size and electrical charge. It is commonly performed on serum (the fluid portion of blood), urine samples, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Protein electrophoresis is a biochemical test used to know which proteins are present, absent, or decreased in body fluids such as serum, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, it helps to diagnose or monitor various health diseases and conditions caused by the abnormality of proteins in body fluids.
Such proteins may participate in many biological activities in the human body such as transporting nutrients, removing toxins, and controlling body functions.
Immunoelectrophoresis is a common type that we use to analyze the unusual behavior of proteins. Irregular proteins are formed due to different types of medical conditions such as kidney failure, multiple sclerosis, and certain types of cancers. These irregular proteins can be detected with the help of immunoelectrophoresis of blood and urine samples.
Application on Testing Antibiotics
To detect the purity of antibiotics, we used the electrophoresis principle. Capillary and paper electrophoresis instruments are used to test the purity of antibiotics. It is also used for the determination of strength and exact dose of antibiotics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Electrophoresis?
Electrophoresis in analytical chemistry is the technique or process of analysis or separation of dispersed particles relative to a fluid or gel under the influence of the electric field due to different rates of migration. Therefore, electrophoresis is the migration of electrically charged molecules under the influence of the electrical field.
Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) or proteins based on their size and electrical charge.
What is Protein Electrophoresis?
Protein electrophoresis is a laboratory technique for analyzing or separating proteins in an analytical sample based on their size and electrical charge.
Serum protein electrophoresis is the most common biomedical test used to analyze and separate proteins in the blood based on their size and electrical charge. It measures the types of proteins in the serum part of a blood sample.
Why is Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Important?
Argose gel electrophoresis system is important because it forms a viscous solution when dissolved in a hot buffered solution but solidifies after cooling. Therefore, an agarose gel supporting medium is effective for the separation or analysis of serum proteins. It also useful for analysis of hemoglobin, nucleic acids, and products obtained from polymerase chain reaction or PCR test.
What is the Serum Protein Electrophoresis Test?
Protein serum electrophoresis is a biochemical test used to know which proteins are present, absent, or decreased in the serum of your blood. Therefore, it helps to diagnose or monitor various health diseases and conditions caused by the abnormality of proteins in blood serum.
Serum protein gel electrophoresis machine or system commonly helps to test health diseases such as lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, kidney disease, liver disease, and immune system problems.