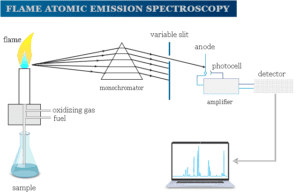
Units and Dimensions Formulas
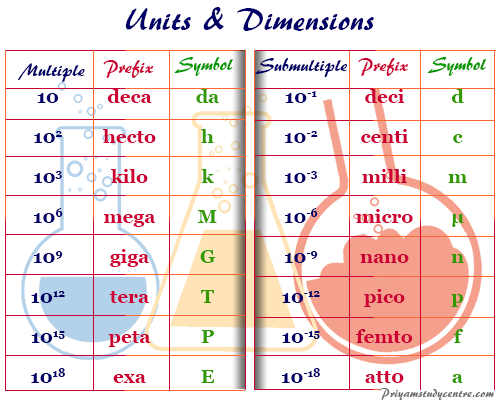
Units and dimensions formulas and measurements in SI or CGS systems in science are recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). In the standard unit system or SI measurement system, we used the seven base units of physical quantities for analysis, measurement, and conversion. We generally use units and dimensions of mass, length, and time for measurement and conversion of force, density, energy, work, heat capacity, pressure, surface tension, etc. Therefore, these physical quantities can be derived from base units or dimensions data. The SI unit of luminous intensity or candela is not needed in physics or chemistry learning but it is included only for the sake of completeness.