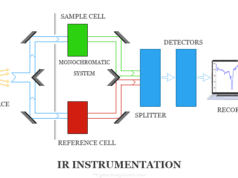
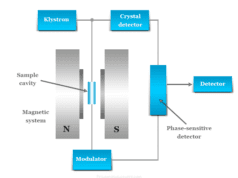
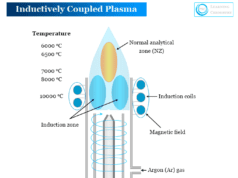
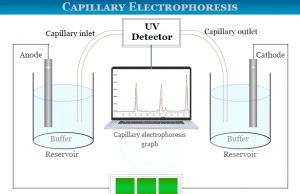
Wavelength Measurement
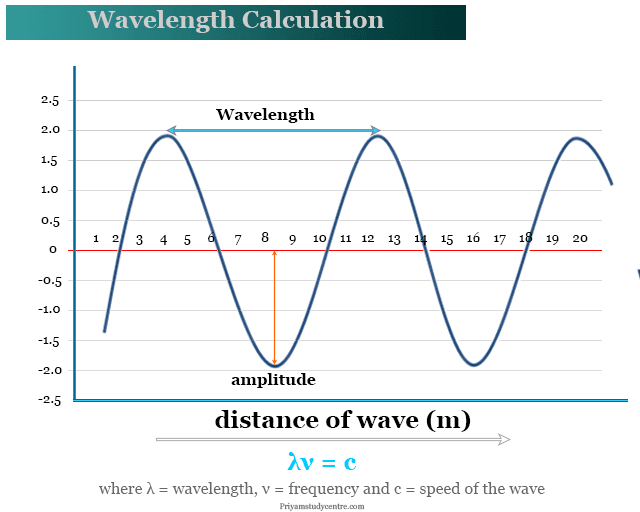
Wavelength can be measured by the distance between two successive maxima of a wave. It can be denoted by the symbol lambda (λ) and calculated by the formula λν = c, where ν = frequency and c = speed of the wave. Sound, light, water, and electromagnetic waves are the most common examples of waves whose wavelength measurement depends on the medium where they are traveled. A sound wave depends on the air pressure whereas electromagnetic radiation depends on the strength of the electric and magnetic fields. Generally, we use a photometer for the measurement of energy, wavelength, and frequency of light waves. The range of waves over which electromagnetic radiation exists is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
Some commonly employed units such as meter (m), centimeter (cm), millimeter (mm), micrometer (μm), nanometer (nm), and angstrom (Å) are used for the measurement of the wavelength of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Frequency
The number of complete wavelengths passing through a given point in unit time is called the frequency of radiation. It is denoted by the Greek letter ν and measured by the unit reciprocal to time.
Frequency is generally expressed in cycles per second or Hertz. The other units of frequency are kilocycle per second or kHz and megacycle per second or MHz.
Velocity Wavelength Frequency Formula
At constant frequency, the velocity depends upon the medium through which the wave is passing. It is the unit of cm s−1 or m s−1.
The product of wavelength and frequency is measured by the velocity of the wave in the medium.
Wavelength (λ) × frequency (ν) = velocity (v)
When the density of the medium through which the wave is passing decreases, the wavelength and velocity of radiation increase. It reaches a constant or maximum value in a vacuum. Therefore, the velocity of light in a vacuum is denoted by the formula, c = λν, where, c = 3 × 108 m/s.
Sound Waves
In physics, sound is an acoustic wave that propagates through a medium such as a gas, liquid, or solid. The velocity of sound waves in air is 343 m/s at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
The wavelength of sound that is audible to the human ear is between 17 m to 17 mm. Some higher wavelength of a sound wave is used by bats to identify their targets.
The speed and wavelength of sound waves depend on the medium where sound travels and the temperature of the medium. The speed of sound in a different medium is given below the table,
| Medium | Speed of sound (m/s) |
| Gases at 0°C and 1 atm pressure | |
| air | 343 |
| carbon dioxide | 258 |
| carbon monoxide | 337 |
| oxygen | 326 |
| hydrogen | 1270 |
| Nitrogen | 349 |
| Liquids at 20 °C, 1 Atm pressure | |
| ethanol | 1160 |
| mercury | 1450 |
| freshwater | 1480 |
| seawater | 1540 |
| Solid | |
| Glass | 5640 |
| Lead | 1960 |
| Aluminum | 5120 |
| Steel | 5960 |
Wavelength of Light
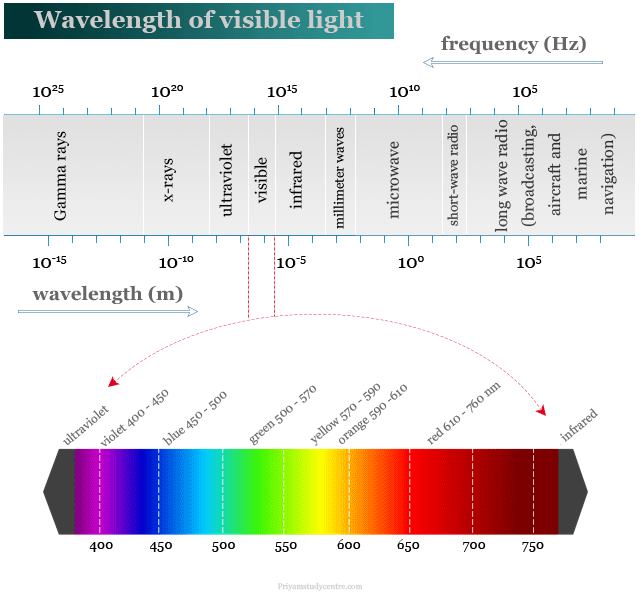
Radiation which we call light is the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. It lies between the wavelength 400 nm (violet) to 750 nm (red).
Within the visible region, a person with normal color vision can be able to correlate the wavelength of light striking the eye. The color of light corresponds to different wavelengths is given below the table,
| Colour | Wavelength (nm) |
| Violet | 400 – 450 |
| Blue | 450 – 500 |
| Green | 500 – 570 |
| Yellow | 570 – 590 |
| Orange | 590 – 610 |
| Red | 610 – 750 |
We see that sunlight can be separated by passing through a prism into the light of many colors (red to violet). A light that contains a continuous sequence of colors varying from red to violet is called a continuous spectrum.
Similarly, some light sources have a few colored lines separated by dark spaces is called line spectrum. Most of the line spectra are produced by atoms. Therefore, it is often called the atomic spectrum. For the hydrogen atoms, it is called the hydrogen spectrum.
Calculating Wavelength of Light
The dual nature of light or electron was first proposed by the de Broglie equation in 1924. A light wave must have energy, wavelength, frequency, velocity, and amplitude. Experimentally, the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation is found to be the same 3 × 108 m/s in a vacuum.
The bundle of energy emitted by light is called a photon. The wavelength and frequency of light can be measured by the following equation,
- The velocity of light (c) = νλ
- The energy of light (E) = hν
Where, ν = frequency of light
λ = wavelength of light
h = Planck constant = 6.62607004 × 10-34 joule second.
The measurement or conversion of wavelength to frequency and energy of photons was suggested by Planck. According to Planck’s quantum theory, if a photon energy E is emitted or absorbed with frequency = ν and wavelength = λ.
Therefore, energy (E) = hν = hc/λ.
The Planck calculation suggests that a photon of a long wavelength has low energy and a photon of a short wave has high energy. We use a photometer for calculating the energy of light, it can be converted to frequency or wavelength by the above formula.