Vitamin C
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in many fruits mainly citrus fruit and vegetable sources. Many...
Vitamin A
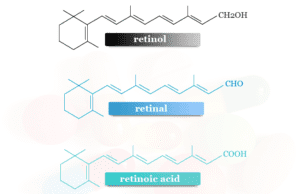
Retinol in Vitamin A
Vitamin A referred to a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal, retinoic acid, and several provitamins A carotenoids like...
Vitamin B6
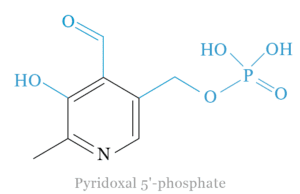
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxal 5 Phosphate)
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin or essential nutrient found naturally in various foods and added to foods and supplements....
Vitamin B12
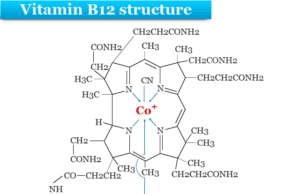
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water soluble vitamin containing cobalt in its structure. Therefore, it is a coordination complex of...
Thiamine
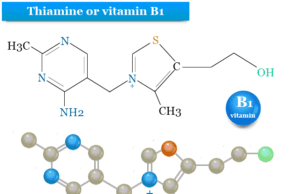
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
Thiamine or vitamin B1 is one member of the water soluble vitamin B complex found naturally in some foods or sold as...
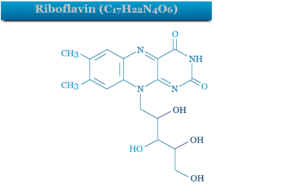
Riboflavin
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2 is a water soluble vitamin that occurs widely in nature and is necessary for growth and...
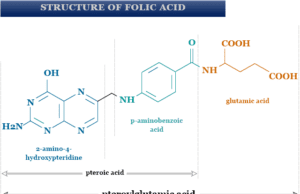
Folic acid (Folate)
Folic Acid and Folate
Folic acid and folate are the forms of vitamin B9 that we use for the treatment of certain types of iron...