Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2 is a water soluble vitamin that occurs widely in nature and is necessary for growth and health. Riboflavin occurs free or phosphate or joined to specific proteins to form enzymes. Therefore, it is also called lactoflavin. The common sources of riboflavin are vegetables, meat, and dairy products. It was first isolated from milk which is closely related to yellow water soluble crystalline powder like flavins. It involved energy metabolism, cellular respiration, antibody production, and activation of iron, folic acid, and vitamins B1, B3, and B6. Riboflavin deficiency is very rare because we consume several foods which contain a huge amount of riboflavin. The preliminary test shows that the structure of riboflavin contains an aromatic diamino group. Riboflavin is 6,7-diethyl-9-(D-1′-ribityl)-isoalloxazine with chemical formula C17H20N4O6.

Vitamin B2 is a bright yellow powder that shows green fluorescence. It is soluble in water and ethanol but insoluble in chloroform and other organic solvents. The aqueous yellow solution of riboflavin shows a yellowish-green fluorescence with λmax = 565 nm. It is used for determining riboflavin quantitatively.
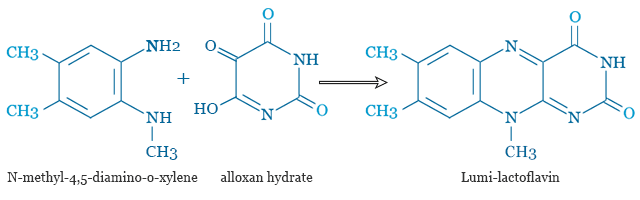
When exposed to light in the presence of sodium hydroxide, it forms mainly Lumi-lactoflavin. The structure of Lumi-lactoflavin has been identified by its synthesis. It can be synthesized by condensation of N-methyl-4,5-diamino-o-xylene with alloxan hydrate in an aqueous solution at 50 to 60 °C.
Riboflavin Structure
The structure of riboflavin shows that it contains lumichrome with a side chain attached to the N-9 atom. Lumichome is Lumi-lactoflavin where a hydrogen atom present at 9 positions is replaced by a methyl group.
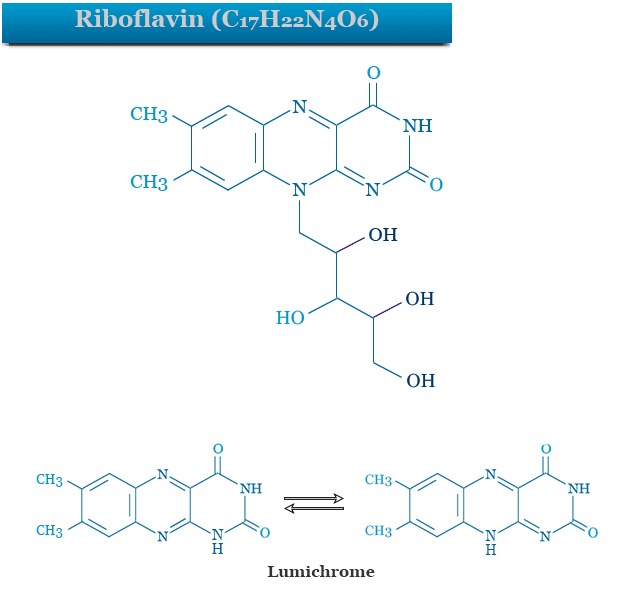
- It contains five active hydrogen atoms in its structure. Therefore, the riboflavin molecule has four hydroxyl groups with four active hydrogen atoms and one NH group with one active hydrogen atom.
- The side chain of riboflavin is a tetrahydroxy derivative. Oxidation with lead tetraacetate produces formaldehyde. It suggests that the sidechain contains a terminal CH2OH group.
- The side chain contains three chiral centers. So there are eight optically active forms possible. Russian-born Swiss chemist Paul Karrer in 1935 showed that the configuration of riboflavin is that of D(−) ribose.
- Therefore, it is 6,7-diethyl-9-(D-1′-ribityl)-isoalloxazine with the chemical formula C17H20N4O6.
Synthesis
Riboflavin can be synthesis riboflavin by the following methods,
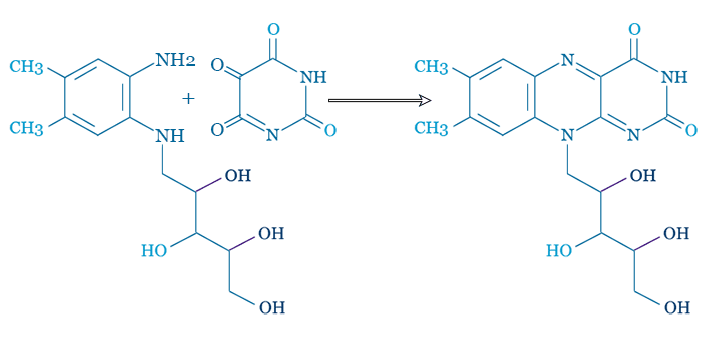
Many other procedures for the synthesis of riboflavin have been developed recently. In 1947, Tishler synthesized it from the azo compound which was prepared by Karrer synthesis. The azo compound synthesis from Karrer can be combined directly with barbituric acid in the presence of an acetic acid solution. The product obtained by this method is good and very pure.
Sources of Riboflavin
Like other B vitamins, riboflavin or vitamin B2 is found widely in foods but we also sold it as a dietary supplement. Vegetables, meat, and dairy products are the main sources of riboflavin.
- Beef, beef liver, chicken liver, salmon, turkey, pork, chicken, and eggs are the main animal sources of riboflavin.
- Mushrooms, nuts, parsley, pumpkins, rosehips, sage, sweet potatoes, and cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, brussels sprouts, spinach, dandelion greens, and watercress are the main sources of vitamin B2. Whole-grain bread, enriched bread, and wheat bran also contain a huge amount of vitamin B2.
- Dairy products such as cow’s milk, cheese, and yogurt contain a huge amount of riboflavin.
It is a water-soluble vitamin. Therefore, cooking food by boiling can cause it to be lost.
Functions of Riboflavin
Like other vitamins and minerals, it is very important for the growth and health of the human body. It is essential to the formation of two important coenzymes flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). These two coenzymes are very important for breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates to release energy.
It also controls cell respiration, antibody production, growth, and the health of the human body.
It helps to convert carbohydrates into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The ATP produced by this process provides the energy that the body requires. ATP also plays a vital role in storing muscle energy.
Many redox reactions in human bodies are controlled by flavin coenzymes. Riboflavin deficiency causes a reduction in red blood cell production. Therefore, it causes iron deficiency anemia.
Deficiency of Riboflavin
Riboflavin deficiency is very rare in developed countries like the United States, Canada, Australia, the United Kingdom, etc. People who live in these countries consume a significant amount of vitamin B2 in their dietary supplements. A deficiency of riboflavin can be primary or secondary.
- A primary deficiency happens because of poor vitamin sources in their regular diet.
- Secondary deficiency happens when the human body cannot use it or an increased rate of excretion of vitamin B2. The deficiency causes different types of health diseases like cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
Riboflavin deficiency is known as ariboflavinosis. It causes mouth ulcers, hair loss, and itchy, watery, bloodshot eyes. It also causes anemia and degeneration of the liver or nervous system. The deficiency of riboflavin during pregnancy can cause fetal birth defects.
How Much Do We Need Vitamin B2?
Riboflavin or vitamin B2 deficiency is very rare for developed countries because they can consume a sufficient amount of B2 in their dietary supplement.
According to the RDA recommendation, vitamin B2 for men aged over 19 or more is 1.3 milligrams per day, and for women, it is 1.1 milligrams per day. Pregnant women can need 1.3-milligram vitamin B2 per day and during breastfeeding, the value can rise up to 1.6 milligrams per day.
Developed countries like the United States, Canada, United Kingdom can consume excessive amounts of vitamin B2 in foods. It is excess from RDA recommendation. The very low population of these counties can consume less than that of estimated values.
Uses of Riboflavin
We used riboflavin supplements for the treatment of corneal thinning, migraine, and food coloring. High-dose riboflavin (400 mg) is very effective in the treatment of migraine.
It is a yellow-orange crystalline powder. Therefore, it can be used for food coloring. Riboflavin is very useful for absorbing and activating iron, folic acid, and vitamins B1 (thiamine), vitamin B3 (niacin), and vitamin B6 (pyridoxine).