Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
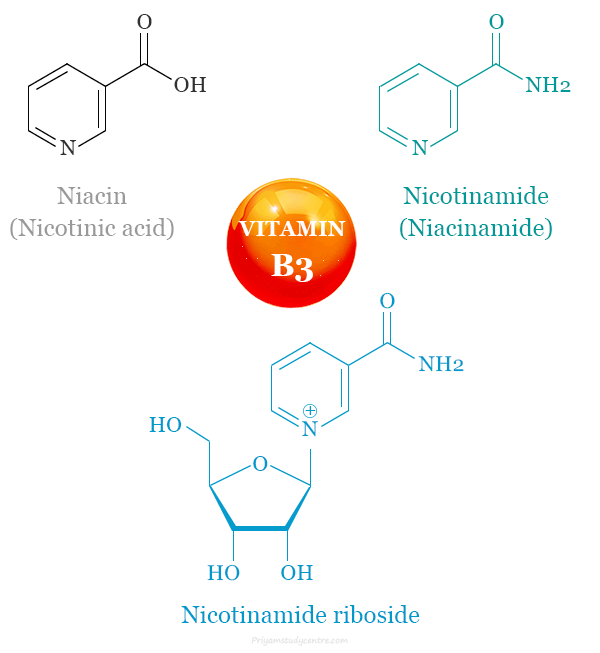
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) is a water-soluble B vitamin found naturally in some foods and sold as a supplement. Nicotinamide (niacinamide), niacin (nicotinic acid), and nicotinamide riboside are three forms or vitamers of vitamin B3. Vitamin B3 (Niacin) is a precursor for coenzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). Plants and animals can produce vitamin B3 or niacin from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin works in our body as a coenzyme and helps more than 400 enzymes dependent biological reactions. The antioxidant niacin helps to convert nutrients into energy, create cholesterol and fats, and repair DNA. A dietary supplement of vitamin B3 is beneficial for the treatment of pellagra, a disease caused by niacin deficiency.
Vitamin B3 deficiency is rare because it is reached with various animal and plant foods. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variety of food sources such as fortified packaged foods, meat, poultry, redfish, nuts, legumes, and seeds.
Nicotinic Acid and Nicotinamide
Nicotinic acid and nicotinamide are two vitamers that have the human pellagra-preventing factor. Nicotinamide is a part of coenzyme codehydrogenase I and II which helps in many biological oxidation reactions.
Nicotinic acid (Niacin) was first prepared commercially by the oxidation of nicotine. Another commercial method is the vapour phase oxidation of 3-methyl-pyridine (β-picoline) in presence of a vanadium and iron catalyst.
Nicotinamide is manufactured by the action of ammonia on nicotinyl chloride or by heating nicotinic acid with urea in presence of a molybdenum catalyst. Another commercial method is the action of hydrogen peroxide on 3-cynopyridine in an alkaline solution.
Sources of Vitamin B3
Vitamin B3 is found naturally in a wide variety of both animal and plant-based foods products. Animal-sourced foods contain high level of niacin but dairy products and eggs contain very little.
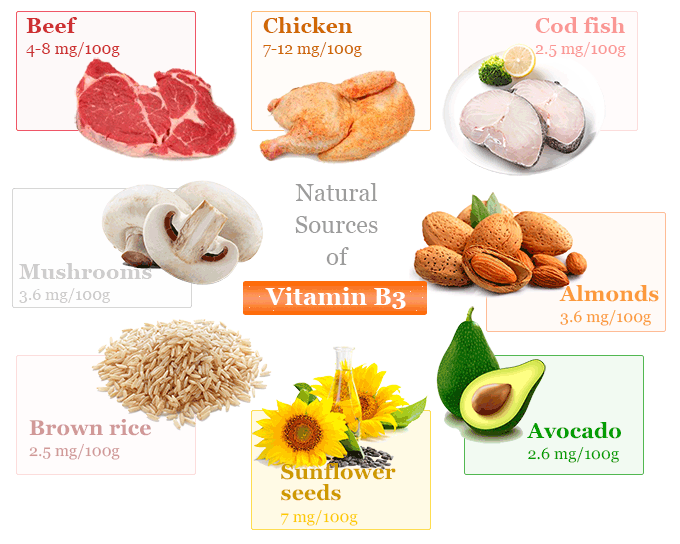
It is a water-soluble vitamin. Therefore, it may be lost during high-heat cooking with water or in the presence of acidic foods and sauces. The main food sources with the highest niacin content per 100 grams are given below the table:
| Animal source | Amount (mg / 100g) |
Plant source | Amount (mg / 100g) |
| Tuna, yellowfin | 22.1 | Peanuts 14.3 | 14.3 |
| Salmon | 10.0 | Sunflower seeds | 7.0 |
| Turkey | 7-12 | Almonds 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Chicken | 7-12 | Mushrooms, white | 3.6 |
| Beef | 4-8 | Brown rice | 2.5 |
| Pork | 4-8 | Avocado | 2.6 |
| Tuna, white, canned | 5.8 | Potato, baked, with skin | 1.4 |
| Cod-fish | 2.5 | Corn (maize) | 1.0 |
| Eggs | 0.1 | White rice | 0.5 |
| Milk | 0.1 | Kale | 0.4 |
Dietary Allowance
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of niacin can be measured in milligrams (mg) of niacin equivalents (NE). 1 mg of NE = 1 mg niacin or 60 mg of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level of niacin for all adults 19+ years is 35 milligrams.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for adults 19+ years are:
- 16 mg NE for men
- 14 mg NE for women
- 18 mg NE for pregnant women
- 17 mg NE for breastfeeding women
Niacin Supplement
Vitamin B3 (niacin) supplement is available in the form of nicotinic acid or nicotinamide. The supplements are also available as a prescribed medicine that supports a healthy blood lipid profile. When supplementation is far beyond the RDA recommendation, it causes unpleasant side effects of flushing.
The American Heart Association (AHA) is strongly against using non-prescription dietary niacin supplements rather than prescribed niacin because it causes unpleasant side effects of flushing. Therefore, niacin supplemental only is used under the supervision of a medical professional.
Toxicity of Vitamin B3
Toxicity is rare when eating niacin-reached foods but can occur from long-term use of high-dose supplements. A reddened skin flush with itching or tingling on the face, arms, and chest is a common sign of high-dose supplementation. Flushing occurs mainly when taking high-dosage nicotinic acid supplements rather than nicotinamide.
Vitamin B3 supplements typically come in an extended-release form of nicotinic acid with slower absorption. Therefore, it does not cause flushing.
Niacin Flush
Niacin flush is a common side effect of taking high doses of supplementals which can be supporting a healthy blood lipid profile. It is uncomfortable but harmless for humans.
Niacin flush can affect the face and upper part of our body. It can cause reddening of the skin, uncomfortable or even painful burning, or itching, and skin may feel warm or hot to the touch.
Health Benefits of Vitamin B3
Niacinamide or nicotinamide is a hydrophilic amide of vitamin B3 that is an important component in various medicines and cosmetics products.
Vitamin B3 is a component of the coenzymes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). They are utilized in electron transfer reactions within DNA repair and the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and alcohol.
NADH is the reduced form of NAD formed by donating electrons. It plays a critical role in every cell of our body. NADH is the primary carrier of electrons for mitochondrial ATP synthesis. ATP produced in mitochondria is the main source of cellular energy. Therefore, we need niacin for the production of NADH which converts foods that we eat into energy that our body can use.
Niacinamide for skin
A form of vitamin B3 (Niacinamide) is helpful to build cells in the skin and protect the skin from environmental stresses, such as sunlight, pollution, and toxins.
- Improve hydration: The topical application of niacinamide may boost the skin-hydrating ability of moisturizers if struggle with dry skin. It may work brilliantly with common moisturizing ingredients like glycerin, non-fragrant plant oils, cholesterol, sodium PCA, and sodium hyaluronate.
- Treatment for acne: Niacinamide-containing cream is used for the treatment of acne. The anti-inflammatory actions are beneficial for inflammatory skin conditions.
- Reduce environmental damage: Air pollution is a major environmental hazard for humans due to the excessive use of fossil fuels. Environmental pollution and UV rays from the sun can create free radicals (unstable molecules) that damage our healthy skin cells. The antioxidant properties of niacinamide can protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals.
- Minimize signs of aging: Collagen is an important anti-aging protein that keeps the skin looking youthful. Niacinamide has the ability to improve skin collagen production. Therefore, niacinamide-containing skincare help to manage signs of aging by reducing skin lines and wrinkles.
- Manage hyperpigmentation: Topical niacinamide may relieve a stripped moisture barrier in the skin, reducing irritation, an increase of collagen production, and lessening hyperpigmentation in the skin.
- Skin cancer: A dose that contains 500 to 1000 mg of niacinamide daily decreases the risk of skin cancer.
Treatment for high cholesterol
Niacin (vitamin B3) obtained from various foods and supplements can boost HDL cholesterol levels but decrease the levels of triglycerides, a type of fat that increases the risk of heart disease. It works by blocking the enzyme responsible for producing cholesterol in the liver.
Generally, a high dose of supplementation is required to maintain our cholesterol levels. These high doses of niacin may cause undesirable side effects of flushing. Therefore, always talk to your doctor before beginning to take high doses of vitamin B3 or niacin.
Niacin for high blood pressure
Nicotinic acid (niacin) may play a role in the prevention or treatment of dyslipidemia and high blood pressure, an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). It helps your blood vessels widen to improve blood flow and reduce blood pressure.
A form of vitamin B3 niacin boosts the production of nitric oxide which relaxes and widens the inner muscles of the blood vessels and increases blood circulation in your body and brain.
Niacin and weight loss
Niacin can increases adiponectin, a weight-loss hormone secreted by fat cells. Clinical trials show that niacin-bound chromium supplements helped to reduce our body weight.
Improving brain function
Vitamin B3 can improve cognitive function by stimulating the production of neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. These three neurotransmitters are improving the normal brain function of humans. It is also an antioxidant that helps to eliminate free radicals that can damage our brain cells.
Serotonin and noradrenaline strongly influence mental behavior patterns while dopamine acts as a chemical messenger that communicates messages between nerve cells in your brain and your brain and the rest of your body. Low levels of vitamin B3 result in brain fog, slow mental processing, and cognitive decline.
Niacin can help you to protect against Alzheimer’s and dementia. Niacin supplementation may also decrease the risk of age-related cognitive decline, memory loss, migraines, depression, motion sickness, insomnia, and alcohol addiction.
Vitamin B3 Deficiency
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) deficiency is rarely seen in the United States and other developed countries but mild niacin deficiency can have a negative impact on our health and cognition. It is well-absorbed from most food sources except for some cereal grains in which niacin is bound to its fibers and decreases the absorption. It is also added to many foods and multivitamins.
A severe vitamin B3 or niacin deficiency in our diet causes the disease pellagra. Pellagra is a condition that causes:
- Diarrhea
- Sun-sensitive dermatitis involves hyperpigmentation and thickening of the skin
- Inflammation of the mouth and tongue
- Delirium
- Dementia
- If untreated pellagra causes death
The common psychiatric signs and symptoms of niacin deficiency may include:
- Irritability
- Poor concentration
- Anxiety
- Fatigue
- Loss of memory
- Restlessness
- Apathy
- Depression
The deficiency may occur due to poverty, excessive alcohol consumption, use of birth control pills, anorexia, and a vegan diet.
For treating vitamin B3 deficiency, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends using niacinamide or nicotinamide instead of niacin to avoid the side effect of flushing.