Cell in Biology
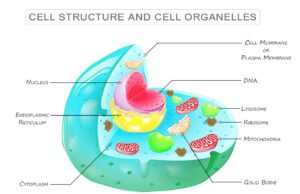
Cell and Molecular Biology
A Cell in biology is the structural and functional unit of life that contains fundamental molecules of living organisms. The main...
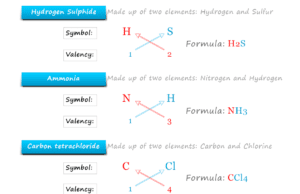
Chemical Formula
Chemical Formula Drawing
A chemical formula is the shortest way to represent a compound or molecule with the help of symbols and chemical proportions of...
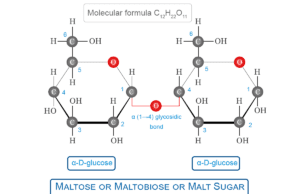
Maltose Sugar
Maltose Malt Sugar
Maltose Sugar also called maltobiose or malt is a carbohydrate or monosaccharide formed by two α-D-glucose units held together by α(1→4) glycosidic...
Glucose Molecule
Glucose Molecular Formula
Glucose is the simplest type of carbohydrate or sugar molecule that has the molecular formula C6H12O6. It is an odourless and sweet...
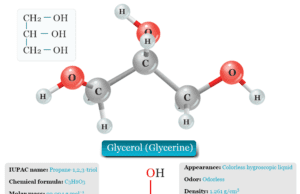
Glycerol
Glycerol (Glycerine)
Glycerol, also called glycerine or glycerin is a naturally occurring organic trihydric alcohol that has a variety of benefits and uses in the production...
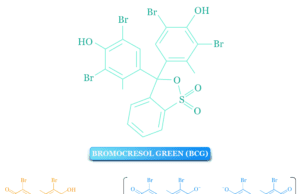
Bromocresol Green pH Indicator
Bromocresol Green Indicator
Bromocresol green (BCG) is a dye that is used in chemistry as a pH indicator in acid-base titration and in thin-layer chromatography...
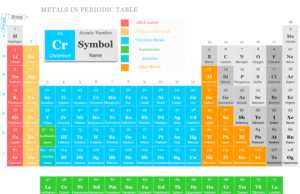
Metals
Metals in Periodic Table of Elements
Metals in chemistry are chemical elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity and form positive ions by...
Water Electrolysis
Water Electrolysis Equipment
Water electrolysis is the process where water can split into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) through the requirement of electricity or electrical energy...
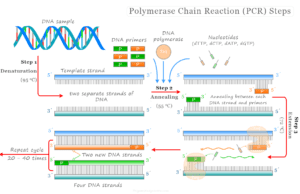
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in biology and chemistry is a laboratory method or technology uses for real-time genetic testing and amplification...
Biopolymers
Biopolymers in Body
Biopolymers are natural polymers or polymeric biomolecules produced by the cells of the living body. They are monomeric units that are covalently...