Planck’s Quantum Theory
Planck's Quantum Theory of Black Body Radiation
Planck's quantum theory was presented by Max Planck on December 14, 1900. According to Planck's quantum theory, an...
Electron
Electron Definition in Chemistry
Electron in chemistry, the lightest subatomic or elementary particle of an atom carries a negative charge, −1.602176634 × 10−19 coulomb or...
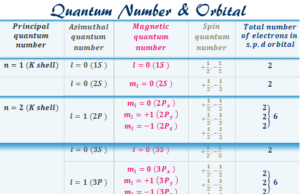
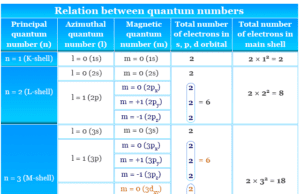
Quantum Number
Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals
Quantum numbers such as principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum number are the identification number of an electron present in...
Atomic Theory Questions
Atomic Theory Multiple Choice Questions
Atomic theory multiple choice questions or quizzes set in online learning chemistry for school college students provide 9 practice problems...
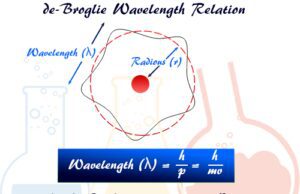
de Broglie Relation
de Broglie Wavelength Formula
de Broglie wavelength formula proposed by French physicist Louis de Broglie in 1924 derived the relation between Einstein's mass-energy equation and...
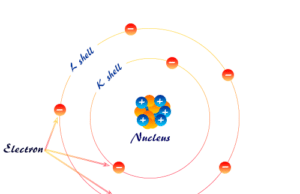
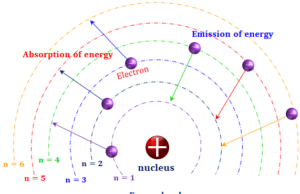
Bohr Model
Bohr Model of Hydrogen Atom
Bohr Model of hydrogen atom was adopted by Neils Bohr in 1913 for the explanation of the Rutherford model and the...
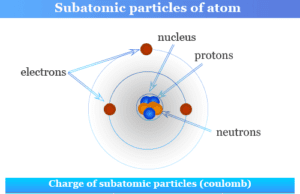
Elementary Particles
Elementary Subatomic Particles
Elementary particles or subatomic particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons in physics or chemistry were discovered by Scientists Thomson, Golstine, and Chanweak....
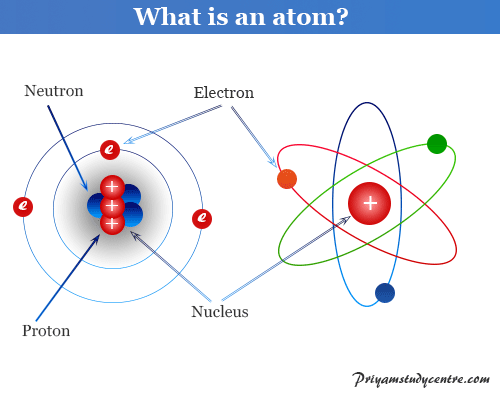
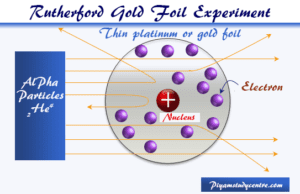
Rutherford Model
Rutherford Model of an Atom
Rutherford model or nuclear planetary model of an atom in chemistry or physics describes by New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford...
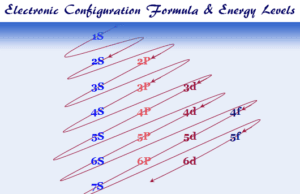
Electron Configuration
Electron Configuration of Elements in Periodic Table
Electron configuration or electronic configuration or electronic structure of atoms or ions of s, p, d, and f...