Electrical Energy
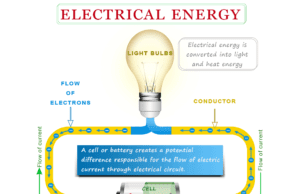
Electrical Energy and Power
Electrical energy is the energy obtained from the electric potential or kinetic energy of the charged particles (electrons) while electric power...
Water Electrolysis
Water Electrolysis Equipment
Water electrolysis is the process where water can split into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) through the requirement of electricity or electrical energy...
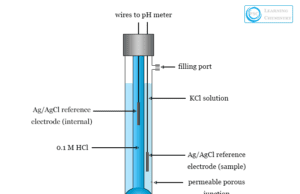
Glass Electrode
Glass Electrode for pH Measurement
Glass electrode is a type of ion selective electrode used mainly for the measurement of the pH of a solution....
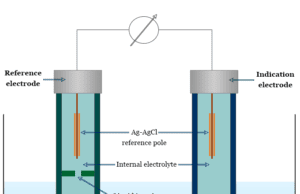
Ion Selective Electrode
Ion Selective Electrode (ISE)
Ion selective electrode (ISE) is an electrochemical sensor that works based on the principle of a galvanic cell. It converts the...
Semiconductor
Material Used in Semiconductor
Semiconductor material is a substance which has electrical conductivity between conductors and a non-conductor or insulator. It is pure elements such...
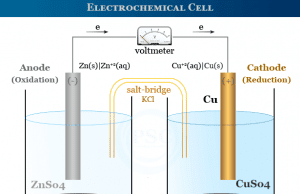
Electrochemical Cell
Electrochemical Cell Types
An electrochemical cell or simply a chemical cell is a device that produces electrical energy due to oxidation reduction or redox reactions....
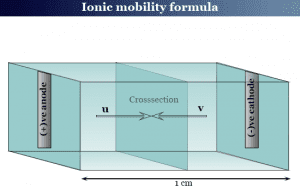
Ionic Mobility
Ionic mobility in electrochemistry
Ionic mobility in chemistry is the velocity of an ion under a unit potential gradient or field strength. Therefore, ionic mobility...
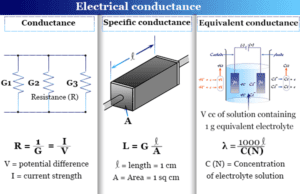
Conductance
Electrical Resistance and Conductance
Conductance or electrical conductance is the reciprocal of resistance and describes the property of an electrolyte solution that helps to conduct...
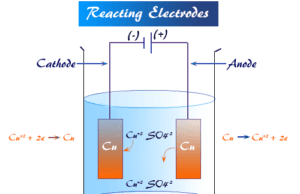
Electrode
What is Electrode in Chemistry?
Electrode is the type of electronic conductor, usually metals partly immersed in an electrolytic solution, and imparts or receives electrons...
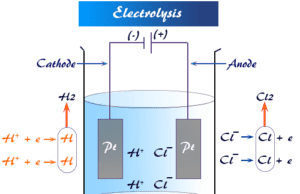
Electrolysis
Electrolysis Definition in Chemistry
Electrolysis in chemistry is defined as a process where chemical changes occur at the electrodes (cathode or anode) due to the...