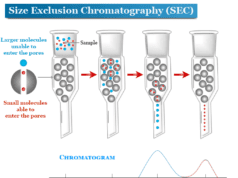
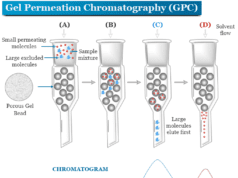
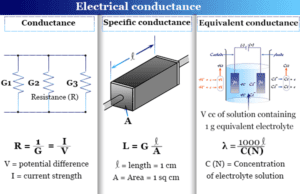
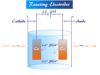
Capillary Electrophoresis Instrument
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) or capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) is a system that separates small quantities of substances in a short time with very high resolution. By this technique, we can easily separate 18 amino acids in 16 minutes. Large biological molecules like proteins, peptides, DNA, RNA, and bio-polymers are also sequenced and separated by the capillary electrophoresis instrument. One can analyze 10−9 nanolevel materials with a detector sensitivity of 10−18 nanolevel by a capillary electrophoresis instrumentation. It is an instrument in which charged species are separated based on ionic mobility or differences in migration rate under the influence of the electric field. The electrophoretic mobility of the analyzed molecule is dependent upon the charge of the molecule, the viscosity, and the atomic radius. Inorganic cations like lithium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium ions are also separated by CZE.
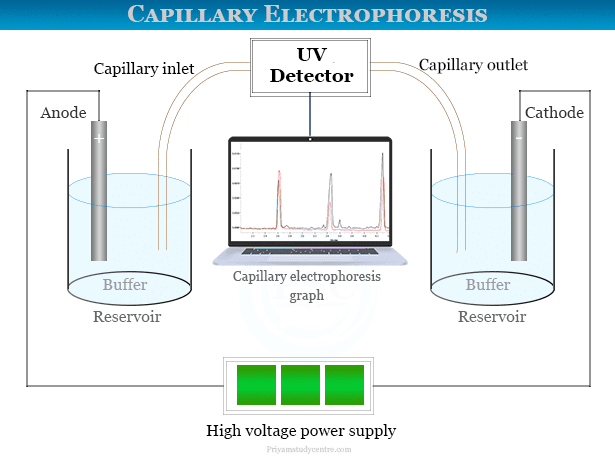
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Instrumentation
A capillary electrophoresis system contains commonly a high-voltage power supply, a sample introduction system, a capillary tube, a detector, and an output device. It is used most effectively because it gives faster results and provides high-resolution separation.
There are six types of capillary electro-separation instruments available for the separation of molecules in analytical chemistry. These may include:
- Capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE)
- Capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE)
- Micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography (MEKC)
- Capillary electrochromatography (CEC)
- Capillary isoelectric focusing (CIEF)
- Capillary isotachophoresis (CITP)
A capillary zone electrophoresis instrument (CZE) is more or less similar to that of an electrophoresis instrumentation with the addition of a detector. The separation medium is a fused silica capillary tube (10 to 100 μm) containing a suitable electrolyte.
The volume of the sample introduced one end of the capillary and the other end immersed in buffer solution. A high voltage current with the potential of 1000 to 30,000 volts is supplied to the zone electrophoresis system.
Detector
Normally, the detector used to perform the process is an ultraviolet-visible absorption type. A focused laser beam is passed through the optical fiber coupled to a photomultiplier tube. Sensitive detection is possible due to the very low path length of 10 to 100 μm. The detector can send the data to an output device such as an integrator or computer.
The data sent from the detector can be displayed as an electropherogram given above the picture. Fluorescence detection can also be used in CZE instrumentation for the samples which naturally fluoresce. For example, in DNA sequencing, we used fluorescent detection.
Fused Silica Capillaries
Fused silica capillaries are used with an ionizable silanol group. At a pH scale of 2.0, SiOH produces a negative charge on the capillary surface. It is called zeta potential. It creates a double layer for cation accumulation with a high-voltage electric current.
During electrophoresis, positive charges migrate toward the electrode or cathode. The buffer facilitates the flow of such cations. It results in a unidirectional flow of all ions from the analytic sample.
The velocity of migration of samples in fused silica capillary depends on the rate of electroosmotic flow of buffer solution.
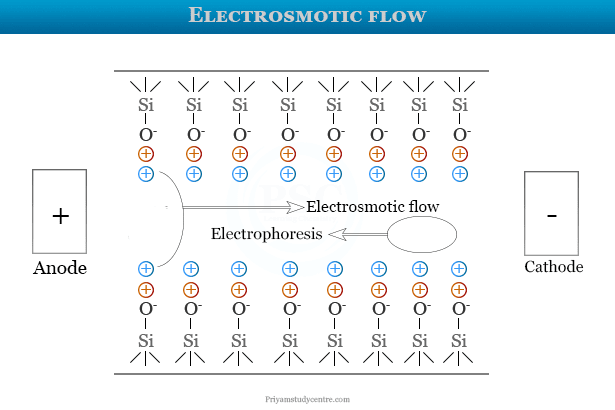
The first layer given above picture is a fixed layer. It is bound tightly to the silanol group. The outer layer is called the mobile layer which further forms a silanol group. When an electric field is applied, the cations on the mobile layer flow to the negatively charged cathode. It causes the electroosmotic flow of the buffer solution. Initially, most positive ions are detected while negative ions are detected later.
By this technique, we can easily separate and analyze DNA, RNA, and a mixture of 18 amino acids. It does not involve chromatographic distribution. Therefore, it is used for macromolecule separation.
Applications of Capillary Electrophoresis
- Large biological molecules such as DNA, mRNA, protein, peptide, and biopolymers can be separated and analyzed by the CZE system.
- It may be used for the simultaneous determination and separation of inorganic ions like ammonium (NH4+), sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+), and calcium (Ca2+) ions. This type of separation can be done very accurately within a small time interval.
- In forensic science, an electrophoresis system is used for the detection or analysis of DNA fragments. Therefore, a capillary electrophoresis instrument is important and cost-effective for DNA sequencing. It provides high accuracy in sequencing information.
- A major use of capillary electrophoresis instrumentation by forensic biologists is to detect or analysis of mRNA for identifying biological fluid or tissue origin on forensic samples.
- The modified form of CE is the affinity capillary electrophoresis (ACE) system. Pharmaceutical companies use an ACE instrument for the detection and analysis of drugs due to their low price and high resolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Capillary Electrophoresis?
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is an analytical technique that separates small quantities of substances in a short time with very high resolution. In a CE instrument, analytes can migrate through an electrolyte solution under the influence of an electric field and be separated according to their ionic mobility.
CE instruments can used in forensic science to detect genetic variation. It is also used in biochemistry for protein analysis and DNA sequencing. Inorganic cations like lithium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium ions are also separated by CZE.
What is Capillary Gel Electrophoresis?
Capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE) is an analytical technique where physical gels, such as diluted polymer solutions used to separate molecules by their size. CGE is a powerful analytical method for the analysis of biopolymers such as DNA, RNA, and proteins.
How Does Capillary Electrophoresis Work?
In a capillary zone electrophoresis instrument, charged species are separated based on ionic mobility or difference in migration rate under the influence of the electric field. Therefore, it separates molecules due to their electrophoretic mobilities. Such analytical technique is performed in a thin diameter glass tube
The working process of a zone electrophoresis instrument is more or less similar to that of an electrophoresis instrument with the addition of a detector.
What is Capillary Electrophoresis Used for?
Capillary electrophoresis is used for the separation of biomolecules such as DNA, mRNA, protein, peptide, and biopolymers. Inorganic cations like lithium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium ions are also separated by this system.
In forensic science, it can used for the detection or analysis of DNA found in crime spots. Pharmaceutical companies use an affinity capillary electrophoresis instrument or system for the detection and analysis of drugs due to their low price and high resolution.