Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) in analytical chemistry is a chromatography principle or technique which we use to separate or identify non-volatile mixtures on a small scale. The working method of thin layer chromatography is similar to column chromatography. In the TLC technique, the adsorbent is coated on a glass plate which acts as a stationary phase. Usually, we used alumina or silica gel with little calcium sulfate for the production of thin layer chromatography plates. The solvent or mobile phase which we used in thin layer chromatography is a very important step. Compared to paper chromatography, it uses a very small amount of samples for quantitative analysis with a lower detection limit. The TLC technique is very useful for the analysis of a large number of compounds. Therefore, compounds that are not volatile or too labile for liquid or gas chromatography can be analyzed by the TCL technique.
Thin layer chromatography is an extremely useful, easy to use, faster, and cost effective separation technique. It is also highly sensitive and produces more accurate results by using the least number of equipment. However, TLC in analytical chemistry is used for qualitative analysis but it is not suitable for quantitative application.
In 1938, two Russian scientists, NA Lzmailov and MS Schreiber investigated the plant extracts by using a thin layer of slurried adsorption medium for the first time. Then in 1941, MO’L Crowe repeated the same experiment by using a thin layer in a petri dish. After that, in 1949, JE Meinhard and NF Hall improved the technique by introducing binders. The thin layer chromatography instrument used in present-day developed by Dr Justus G Kirchner by introducing thin layer plates.
Thin Layer Chromatography Principle
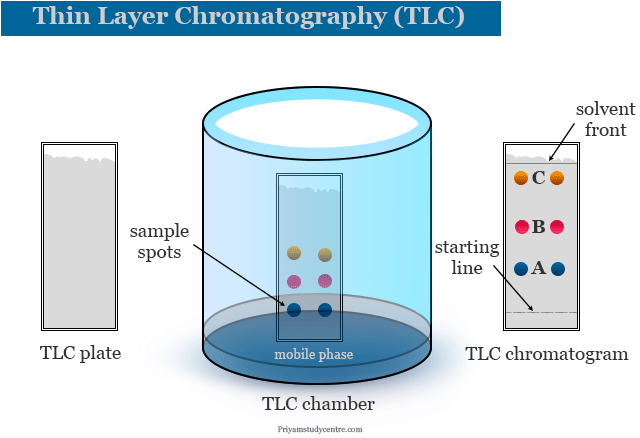
The thin layer chromatography can be performed on the TLC plate. A TLC plate is a sheet of aluminum foil, plastics, or glass that supports the stationary phase or a thin layer of solid absorbent. Silica or alumina are used commonly for making solid absorbents. The mobile phase in the TLC technique is a solvent or a mixture of solvents.
After sporting the TLC plate, it is kept in a closed jar or beaker (TLC chamber) containing the eluent or mobile phase. The solvent rises up the TLC plate by capillary action. The solvent also drags the sample mixture along with it.
The component of the sample is attracted by the polar sites of the absorbent surface by the electrostatic force of attraction. The solvent also interacts with the components of absorbents. Depending on the polarity and interaction of solute, solvent, and absorbent, different components of the mixture move at different rates. When the solvent almost reaches 90 percent of the length of the TLC plate, it is taken out from the TLC chamber.
The TLC plate is allowed to dry by evaporating the solvent and the components of the mixture are marked under the ultraviolet (UV) light. Therefore, the individual components are identified by calculating the retardation factor (Rf) and comparing it with the standard substances.
Solvent Used in Thin Layer Chromatography
The compounds in the spot will move up on the TLC plate depending on the solvent used in the mobile phase. Polar solvents will drug polar substances while nonpolar solvents can help to move nonpolar compounds with them.
- Very polar solvents: Methanol > ethanol > isopropanol
- Moderately polar solvents: Acetonitrile > ethyl acetate > chloroform > dichloro methane > diethyl ether > toluene
- Nonpolar solvents: Cyclohenane, petroleum ether, hexane, pentane
The choice of solvent system and composition of thin layer plate determined the principle of TLC. The solvent used in the TCL technique should be nonpolar and volatile. The eluting powers of the common solvents are,
Pentane < hexane < carbon tetrachloride < chloroform < diethyl ether < ethyl acetate < acetone < ethanol < methanol < water.
Thin Layer Chromatography Method
The method or procedure of thin layer chromatography instrumentation is carried out by the following four main steps,
- Preparation of TLC plate
- Application of sample
- Chromatogram
- Identification of components
Thin Layer Chromatography Plates
Thin layer chromatography or TLC plate is a glass plate that has three different sizes 25 × 75 mm, 5 × 20 cm, and 20 × 20 cm. We used alumina or silica gel with little calcium sulfate for the coating of TLC plates. Cellulose powder and diatomaceous earth can also be used for coating TCL plates.
Photodensitometry plates are also used for quantitative analysis. Such analysis can be carried out by UV, visible, and IR, or fluorescence spectrophotometry. Two methods are generally used for the preparation of TCL plates.
- A uniform slurry of absorbent neither too thick nor too thin is prepared by water. It is speared on the glass plate by a commercial spreading device. The glass plate is dried at 1200 °C for the production of TLC plates.
- A uniform 1:1 slurry of adsorbent can be prepared by mixing the adsorbent with chloroform and methanol and stored in a well-stopped bottle. Two microscope slides can be coated by dipping them in the slurry. The solvent is evaporated. Two TLC plates are separated and activated by drying in an oven.
Sample
For solid samples, a small quantity is dissolved in a suitable solvent to make a solution that can be directly used for spotting on a TLC plate. A capillary tube or a micropipate is used to make spots about o.5 cm in diameter. A minimum quantity of solution should be used to avoid diffusion.
Generally, 1 to 2% solutions are applied by a capillary tube or a microsyringe at about 1.5 to 2 cm from the edge. The spots must be 1 cm apart from each other. When analysis of the reaction mixture, the starting materials can be spotted along with the reaction mixture.
Chromatogram
When the spot becomes dry, the plate is put into the chamber which contains a suitable solvent with its saturated vapour. The absorbent layer must be under the solvent and spots must be above the solvent. When the solvent front travels at least three fourth of the length of the plate, a chromatogram is developed.
Identification of Components
Components of colour compounds mixture are directly identified by colour spots in the chromatogram. Components of colorless compounds can be identified by UV light on the dried plate to obtain fluorescence or by placing it into an iodine chamber or spring with a suitable reagent to give coloured spots. After making the spot, the Rf values are calculated.
Thin Layer Chromatography Experiment
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is useful for the analysis or identification of amino acids, dyes, and ink. A new technique like high-pressure thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) is applied for pharmaceutical analysis.
Thin Layer Chromatography of Amino Acids
Identification and analysis of an individual amino acid from a mixture of amino acids can also be done by thin layer chromatography experiment.
- 10 mg of each known amino acid are dissolved in 10 ml of 95% ethanol. Solution of unknown amino acids mixture also prepared by the same method.
- The spotted thin chromatography plate is put into the solvent chamber.
- The thin layer chromatography or TCL plate is taken out from the solvent chamber and the solvent front is marked quickly. The plate is dried in an air oven.
- Detection of spots can be done by spraying ninhydrin solution and drying again. The purple colour spots appear for amino acids at different distances corresponding to their respective Rf values.
Thin Layer Chromatography Applications
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is widely used all over the world due to its various applications. The TLC technique is used in chemistry to examine the reaction mixture, separation, isolation, and characterization of organic and inorganic compounds. TLC is also used for testing sample purity, identification of components in natural products, and analysis of pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics products.
- TLC technique is mostly used for analysis of the reaction mixture to examine the advancement of the chemical reaction. Therefore, the TLC technique can tell us whether the reaction is complete or not. It is also used to separate the components of the reaction products.
- The TLC technique is applied in chemistry for the separation, isolation, and characterization of inorganic and organic compounds. In biochemistry, it is also useful for separation and characterization of vitamins.
- The TLC can provide information about the purity of substances. Therefore, any impurity present in the test samples can show an extra spot on the chromatogram.
- Thin layer chromatography can identify and separate different components of natural products such as essential or volatile oils, glycosides, waxes, alkaloids, fixed oil, terpenes, steroids, etc. It is also applicable for the analysis of amino acids, plasticizers, antioxidants, ink, dye, etc.
- In the pharmaceutical industry, thin layer chromatography is used for checking the purity of medicines such as analgesics, anesthetics, hypnotics, anticonvulsants, sedatives, tranquilizers, etc. A new method like high pressure thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) is used widely in pharmaceutical analysis.
- In the food and cosmetics industry, the TLC method is used for the detection of impurities in food and cosmetics products.
- Forensic chemists used the thin layer chromatography (TLC) technique for the separation of samples found in criminal spots.