Sources of Methane Gas
Methane gas (chemical formula CH4) also called marsh gas is the simplest hydrocarbon compound of the alkanes or paraffin with a regular tetrahedral chemical structure. Natural gas is the main source of methane molecules. Methane gas is uses as a liquid fuel in our everyday life and an important chemical product of the organic decay of swamps and marshes. The organic compound, methane is produced by the action of bacteria on swamps and marshes in our environment. The fermentation of sewage sludge by bacteria yields methane gas of about 70 percent. It also forms 40 percent of the volume of coal gas. Methane gas is one of the greenhouse gases that cause global warming by trapping heat.
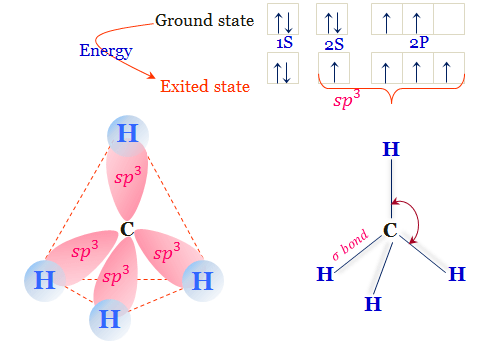
Structural Formula of Methane
The quadrivalent carbon atom in the methane molecule shows the tetrahedral structural formula. The carbon atom in CH4 has 2s1 2px1 2py1 2pz1 electronic configuration.
Mixing these four atomic orbitals gives four equivalent sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybridized orbitals are directed towards the corner of the regular tetrahedron.
Each of these half-filled hybrid orbitals of the carbon atom chemical bonding with half-filled atomic orbitals of the hydrogen atom. Therefore, the methane molecule has a tetrahedral shape with an H-C-H bond angle of 109.5°.
Four hydrogen atoms in the CH4 molecule are equivalent with no dipole moment. Therefore, the bond angle, bond energy, and bond length of all carbon hydrogen bonding are equivalent in the CH4 molecule.
How to Produce Methane Gas?
Methane is the main part of natural marsh gas synthesized by striking electricity between carbon electrodes in atmospheric hydrogen or by the heating mixture of carbon and nickel at 475 °C in the presence of hydrogen.
Sabatier and Senderens in 1897 invented the equation for methane production by passing a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide or carbon dioxide over finely divided elements like nickel at about 300 °C.
CO + 3H2 → CH4 + H2O
CO2 + 4H2 → CH4 + 2H2O
Laboratory Preparation of CH4
In the laboratory, it is generally prepared by heating a 1:3 chemical composition of sodium acetate and soda-lime.
It is also prepared by the reduction of methyl iodide with dissolving metals or by strong base lithium aluminum hydride.
CH3COONa + (NaOH + CaO) → CH4 + Na2CO3.
CH4 is prepared by hydrolysis of inorganic compounds like aluminum carbide or Grignard reagent (methyl magnesium iodide) by water molecules.
Al4C3 + 12 H2O → 3 CH4 + 4 Al(OH)3
Properties of Methane Gas
Marsh gas having the common name methane is the simplest natural unsaturated hydrocarbon compound in an alkenes series with the molecular formula CH4.
At normal temperature, CH4 is a colorless, odorless, non-poisonous gaseous, flammable substance.
| Properties of methane gas | |
| Chemical formula | CH4 |
| Molar mass | 16.043 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless flammable gas |
| Density | 0.657 kg m−3 at 25 °C, 1 atm |
| Melting point | −182.456 °C or −296.421 °F |
| Boiling point | −161.5 °C or −258.7 °F |
| Critical temperature | 190.56 K |
| Conjugate acid base pair | methanium and methyl anion |
Chemical Properties
This gas is less soluble in water but more soluble in organic solvents (alcohol and ether). Therefore, 100 ml of water is used to dissolve about 5 ml of CH4 gas at 20°C.
In chemistry, the thermodynamics combustion of methane gives non-luminous flame in air or oxygen by forming carbon dioxide and water.
Chemical Reactions
- The natural gas explodes violently when mixed with air which causes the explosion in coal mines, where methane is known as fire-damp.
- In the presence of a suitable chemical catalyst, it produces methanol and formaldehyde.
- But when a mixture of methane and oxygen passed through the copper tube at 100 atm pressure and 200°C temperature produced the chemical compound methanol.
Uses of Methane Gas
- Methane on heating to 1000 °C or by incomplete combustion of the gas produces carbon or a very finely divided state of carbon black. It is used in paint, printer ink, and the rubber industry for making motor tires.
- It is also used as an organic fuel in our everyday life.
- It is used for the preparation of organic compounds like methyl chloride, acetylene, formaldehyde, and methanol. These chemicals are generally used in chemical plants.
- The synthesis gas is produced when a mixture of methane and steam passes over the heated nickel supported on alumina. Synthesis gas is used in the chemical industry for the preparation of different chemicals.
- It is mostly used as a natural source of hydrogen gas in the chemical industry.
Methane as a Greenhouse Gas
Now a serious concern about the increase in the use of methane, carbon dioxide, CFC, ozone gas, and nitrous oxide. They raise the global temperature of our environment. It is known as the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse is generally used in winter counties for artificial heating.
The contribution to global warming of CH4 gas is about 16 to 20 percent. Therefore, CH4 heats the earth’s atmosphere by trapping electromagnetic spectrum radiation (IR) from sunlight or heat reflected from the earth’s surface.
Effects of Methane on the Environment
Recently due to many global activities like the Industrial Revolution and the use of natural gas, the concentration of greenhouse gases (CFC, carbon dioxide. methane, etc) has increased.
The average temperature of the earth’s atmosphere rises about 2.5 °C in the next 30 years which results in a major climate change in the world.
The polar ice caps will melt indirectly by greenhouse gases. These consequently increase the sea level. Many seaside localities including some big Iceland completely submerged.
Therefore, to save our civilization, we use non-fossil fuel or renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, and nuclear power instead of natural gas like methane.