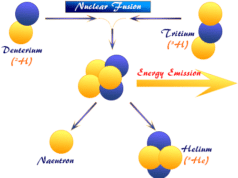
Definition of Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction where a heavy nucleus of an atom is split spontaneously to produce two or more smaller fragments by the release of energy. The process of nuclear fission releases a large amount of energy which we use to create electricity in nuclear power reactors or produce atomic bombs. In nuclear chemistry, the process of nuclear fission is spontaneous or works through the excitation of the nucleus by particles like neutrons, protons, deuterons, or alpha. It is also excited by electromagnetic radiation obtained from gamma rays. Uranium-238 works through spontaneous radioactive decay to fission but uranium-235 does not work through spontaneous nuclear fission due to a lack of activation energy.
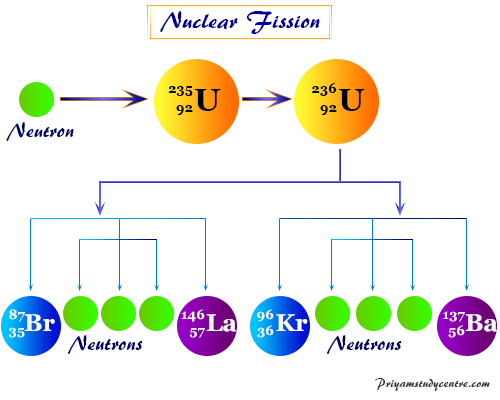
History of Nuclear Fission
In 1934, Italian physicist Enrico Fermi and his collaborators were engaged in studying neutron-induced radioactivity on heavy atoms. They study the chemical elements having an atomic number greater than 92.
They observed that such a type of nuclear reaction produced two atomic nuclei with different atomic numbers. These fragments are widely different from the nucleus of uranium. Therefore, uranium-235 is splitting or fission to form smaller fragments.
Energy From Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is carried out by a number of processes by releasing a large amount of energy. The amount of energy released by nuclear fission reactions is considerably greater than that of any other energy-releasing process.
Uranium-235 is split by slow or thermal neutrons to release the energy of 0.3 MeV. It is also split by a fast neutron to produce 1 MeV energy.
Nuclear fission reactions are accompanied by the release of a large amount of energy due to mass defects. The mass defect is converted to energy. It can be described by the Einstein relativity equation, E = mc2.
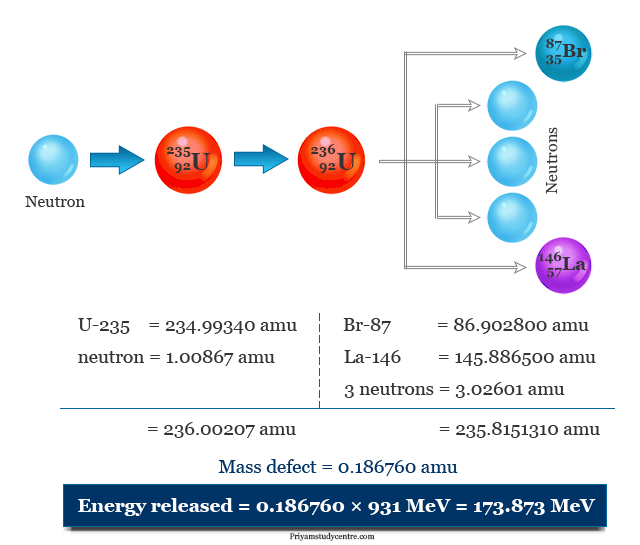
The energy released from the nuclear fission of one gram of uranium-235,
= (0.18676 × 931)/235 MeV
= 0.739887 MeV
During fission, some neutrons are lost. These neutrons can sustain further nuclear fission by developing a chain reaction. Therefore, fission can release a huge amount of energy.
Nuclear Fission Reaction
The nuclear fission of each heavy atomic nucleus releases 2 to 3 neutrons. When a small number of uranium-235 split up, the neutrons produce an infinite number of fusion reactions. Therefore, it leads to the form of a nuclear chain reaction. The chain reaction works through the emission of a large amount of energy.
Uranium-235 is split by slow or thermal neutrons to release 0.03 MeV energy and fast neutrons to release 1MeV energy. The radioactive isotope like uranium-238 fission by fast neutrons only but plutonium-239 undergoes nuclear fission by thermal neutrons only.
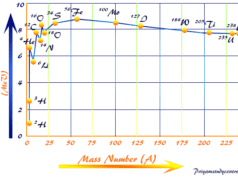
The product formed by the fusion reaction differs in mass numbers by a large margin. For example, during the fission of uranium-235, the fragments formed belong to two groups. One has a mass number near 140 and the other has a mass number near about 95.
How Does an Atomic Bomb Work?
The atomic bomb works by bombarding U-235 with neutrons. Every fission process produced approximately 200 MeV of energy.
- The process yielded 3 neutrons that attacked the fresh uranium-235 for fission.
- In this way, at every stage, the energy output is multiplied by two.
- The chain would be continued when U-235 is large enough and secondary neutrons are produced to find the fresh targets.
If we use a small piece of U-235, the produced neutrons will be escaped and the chain will be broken up. Therefore, there is a limit or critical size of the target for the production of energy by chain propagation.
If the size is below the critical size, there will be no explosion and the fission process is safe. For large species from which the secondary neutron cannot escape causes an explosion.
How does a Nuclear Bomb Work?
1 Kg of pure uranium-235 produced 2.2 × 107 KWH energy within 10−6 sec The heat formed by this fission process cannot escape. The atomic bomb’s work through fission produces a tremendous explosion. It resulted in a violent blast with an intense temperature of 107 °K with dangerous radioactive radiation.
The first effective bomb, called “lean boy” was released on Hiroshima in Japan at 8:11 A M on August 5, 1945, from an altitude of 31600 feet. The effects and pollution of the bomb are known to every human being now.
Fission Energy
In the fission process, longer chain propagation produces greater energy. In such cases, the energy is very large and cannot be used for any peaceful purpose for mankind.
The useful application of fission energy goes through the control of the propagation of the chain. Scientists have succeeded in controlling nuclear chain reactions. Therefore, fission is useful in creating energy or electricity for mankind.
Nuclear Fission Reactor
The nuclear fission process is worked through a nuclear reactor in a power plant to create electricity for mankind. A variety of nuclear reactors are operating in various parts of the world to create electricity. We used uranium-235 or plutonium-239 in the form of plates alloyed with aluminum as fuel.
- The energy produced in the reactor by nuclear fission is in the form of heat.
- The heat is obtained from reactors conducted away by the heat exchanger.
- The heat obtained from the heat exchanger is utilized to generate steam.
- The steam is used to drive a turbine or turbogenerator to create electricity for mankind.
Difference Between Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
Burning carbon materials or fossil fuels such as wood, coal, natural gas, and renewable energy such as sun, wind, and water are the main sources of energy that we use in our daily lives.
Fusion and fission reactions are produced a large amount of energy but the application of such energies is different.
- In the fission process, the heavy nucleus of a radioactive atom is split into lower nuclei to produce a large amount of energy but in a nuclear fusion reaction, two light nuclei combine by releasing vast amounts of energy.
- The fission process is used in the nuclear reactor for generating electricity for mankind but the fusion reaction does not utilize to produce electric power because the reaction is not easily controlled.