Structure of Alkanes
Alkanes (Paraffin) in organic chemistry are saturated hydrocarbons or organic compounds having the general molecular formula CnH2n+2. They are mainly two types, open-chain alkanes, and cycloalkanes. The properties like boiling and melting points, density, and viscosity of alkanes or paraffin regularly increase with the increasing carbon atom. The entire molecular structure of alkanes contains sp3 hybridized carbon atoms surrounded by the hydrogen atom with single covalent chemical bonding. In learning chemistry, the simplest alkane molecule like methane contains four equivalent hydrogen atoms in its structure. However, paraffinic or paraffin wax is a crystalline solid mixture of straight chain hydrocarbons with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)nCH3, where n = greater than or equal to 18. Paraffin wax obtained from alkanes has been uses mostly for the preparation of candles, wax paper, polishes, cosmetics, electrical insulators, perfumes, and medicine.
Paraffins occur in natural sources like natural gas, mineral oil, and petroleum oils. The higher members of the alkanes or paraffin wax generally contain zigzag chain structures.
Properties of Alkanes
- The boiling point of hydrocarbon regularly increases with the increasing carbon atom.
- Other physical properties like melting points, density, and viscosity of alkanes, or paraffin also increase in the same way as the boiling point of alkane.
- For alcohol, hydrogen bonding may be used for the association of molecules but in alkanes or paraffin, only weak Van der Waals forces or covalent bond is concerned for the association of molecules.
- They are almost insoluble in water but readily soluble in alcohol or ether.
- The solubility of these compounds decreases with increases in molecular weight.
- The normal alkanes or paraffin from C1 to C4 are colorless gases. However, from C5 to C17 are colorless liquids, and from C18 are colorless solids.
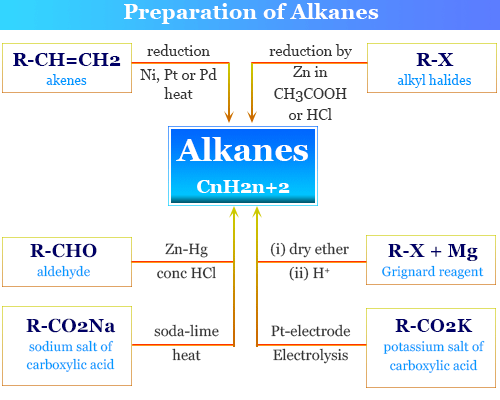
Preparation of Alkanes
The saturated hydrocarbons alkane or paraffin are prepared by different synthesis methods or from chemical compounds,
- Alkene or olefin
- Alkyl halide
- Alcohol
- Aldehyde
- Carboxylic acid
- Natural gas
- Paraffin wax may be prepared from petroleum oil during creaking
Reduction of Alkenes
Catalytic reduction of unsaturated hydrocarbons like alkene or olefin is used for the preparation of alkane. For example, the catalytic reduction of ethylene in the presence of the chemical catalyst nickel produces ethane.
C2H4 + H2 → C2H6
Reduction of Alkyl Halides
The reduction of an alkyl halide by dissolving metals like zinc in acetic acid or hydrochloric acid, zinc in sodium hydroxide, and the zinc-copper couple in ethanol is also used for the preparation of alkane.
Zn → Zn+2 + 2 e−
RX + e− → X− + R·
R: + e− → R−
R− + CH3CH2OH → RH + CH3CH2O−
Reduction of Aldehyde
Reduction of aldehyde in the presence of Zn-Hg in hydrochloric acid gives alkanes.
Preparation of Alkanes from Grignard Reagent
Alkyl halide in ether reactions with magnesium metals produces alkyl magnesium halide or Grignard reagents. When Grignard reagent is treated with water or dilute acid, it produces alkane molecules.
RI + Mg → RMgI
RMgI + H+ → RH
Electrolysis of Carboxylic Acid
The sodium salt of carboxylic acid and soda lime is used for the production of paraffin. A concentrated solution of the sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acid or a mixture of carboxylic acid electrolysis in the presence of a platinum (Pt) electrode is used mostly for the preparation of alkane or paraffin compounds.
Paraffin Wax
Paraffinic or paraffin wax is a crystalline solid mixture of straight-chain hydrocarbons with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)nCH3, where n = greater than or equal to 18.
After the removal of volatile compounds from crude petroleum oil, the residue contains a paraffinic or paraffin base. The low-boiling hydrocarbons are also separate from individual hydrocarbons like methane, ethane, propane, etc.
After separating low boiling alkanes or alkenes, crude oil is fractionalized distillation to produce four main fractions petrol (gasoline), kerosene (paraffin oil), gas oil (heavy oil), lubricating oil, paraffin wax, and asphaltic bitumen.
Uses of Paraffin Wax
- Chemically synthesized paraffin wax is used during the chemical preparation of candles, wax paper, polishes, cosmetics, electrical insulators
- Paraffin wax is used in perfumes due to its flower smell.
- It is a base material in medical ointments.
- It is used as a waterproof coating for wood.
- Paraffin wax is also used in wood or paper matches. It helps to ignite the matchstick due to the presence of easily vaporized alkane fuel.