Manganese Dioxide (MnO2)
Manganese dioxide is a slightly brownish black solid with the chemical formula MnO2. The naturally occurring mineral pyrolusite (present in the earth’s crust) is the main source of manganese dioxide. Naturally occurring manganese dioxide contains several number of impurities. It commonly contains a considerable amount of manganese(III) oxide. For the production of the electrochemical cell, high-purity manganese dioxide is required. Therefore, high-purity MnO2 is widely used for making dry cell batteries (Leclanché cell, or zinc–carbon batteries). The chemical MnO2 is also used in the synthesis of organic compounds. The reducing agent aluminum powder is used for the production of manganese from manganese dioxide. It is insoluble in water and inert to cold dilute acids. When heating a mixture of potassium hydroxide and MnO2 in air, it gives green potassium manganate that is used for the production of oxidant potassium permanganate.
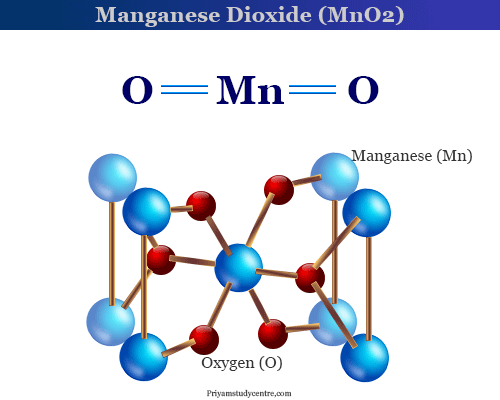
Structure of Manganese Dioxide
MnO2 has a rutile-type structure at high temperatures but tends to be nonstoichiometric at ordinary temperatures when it becomes polymorphic.
Properties
Manganese dioxide is amphoteric in nature. It forms oxomanganate (IV) with fused alkaline earth oxide which has varied compositions.
MnO2 + CaO → CaMnO3
| Chemical properties of manganese dioxide | |
| Chemical formula | MnO2 |
| Molar mass | 86.9368 g/mol |
| Density | 5.03 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 535 °C |
| Appearance | brown black solid |
| Odour | odourless |
| Solubility in water | insoluble in water |
| Oxidation number | +4 |
Chemical Properties
Manganese dioxide commonly participates in redox reactions (oxidation-reduction). In the chemical cell, MnO2 can participate in a one-electron reduction reaction.
MnO2 + e− + H+ → MnO(OH)
MnO2 also catalyzes the chemical reaction that forms oxygen. For example, MnO2 can catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water. It is also used in the laboratory for the production of oxygen from potassium chlorate.
2 H2O2 → 2 H2O + O2
MnO2 is a strong oxidant but it further oxidizes to Mn (VI) or Mn (VII) with strong oxidizing agents.
3 MnO2 + KClO3 + 6 KOH → 3 K2MnO4 + KCl + 3 H2O
2 MnO2 + 3 PbO2 + 6 HNO3 → 2 HMnO4 + 3 Pb(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
It is a stronger oxidant in an acid medium than in an alkaline medium. Therefore, it readily reacts with hot HCl by liberating chlorine gas.
MnO2 + 4 HCl → MnCl2 + 2 H2O + Cl2
On strong heating, concentrated sulfuric acid and nitric acid can also decompose by MnO2.
2 MnO2 + 2 H2SO4 → 2 MnSO4 + 2 H2O + O2
Careful heating of MnO2 with other metal oxides gives manganites. It has different types of formulas, the simplest formula is MnO2MIIO or MIIMnO3.
Manganese Dioxide Uses
MnO2 is widely used as a dipolar in dry cells. A high-purity MnO2 is widely used for making dry cell batteries (Leclanché cell, or zinc–carbon batteries). The common dry cell contains a zinc metal acting as a cathode while a central carbon rod as an anode with a paste of carbon dust, ammonium chloride, and manganese dioxide.
Zn → Zn+2 + 2e
Zn+2 + 2 NH4Cl + 2 OH− → [ZnCl2(NH3)2] + 2H2O
2 MnO2 + 2 H2O + 2e → 2 [MnO(OH)] + 2 OH−
MnO2 is used as an oxidant and chemical catalyst in the chemical industry.
It is also a precursor for the production of strong oxidant potassium permanganate (KMnO4). When heating a mixture of potassium hydroxide and MnO2 in air, it gives green potassium manganate.
2 MnO2 + 4 KOH + O2 → 2 K2MnO4 + 2 H2O
Potassium manganate is commonly used for the production of oxidant potassium permanganate.
MnO2 is used for making a natural pigment. Manganese dioxide can also used in the glass industry to decolorize glass and in the manufacture of matches.