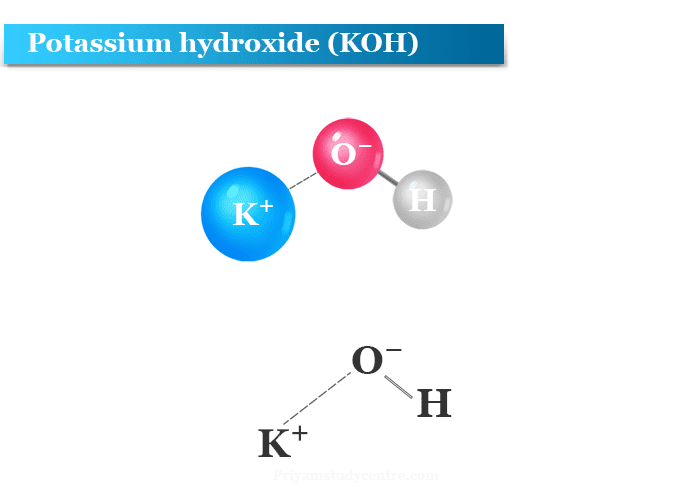
What is potassium hydroxide?
Potassium hydroxide (formula KOH), also called caustic potash or lye is a chemical compound which uses mainly for making soft soap. Like sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide is also a strong base that attacks aluminum and zinc. It is made by the electrolysis of potassium chloride solution.
Potassium hydroxide is a strong alkali which available in liquid and crystalline solid forms. The solid form is readily dissolved in water to form an aqueous KOH solution. Potassium hydroxide is marketed in several forms including pellets, flakes, and powders.
Potassium hydroxide and its solution are highly reactive and corrosive which irritates our skin, eyes, and other tissue.
Properties
At room temperature, caustic potash is a white crystalline solid that absorbs moisture from the air and attacks aluminum and zinc. It forms a clear solution with water. It is also dissolved in low molecular alcohols like methanol, ethanol, and propanol.
Some common properties of KOH are given below the table,
| Potassium hydroxide | |
| Chemical formula | KOH |
| Other names | caustic potash Potash lye Potassia Potassium hydrate |
| CAS number | 1310-58-3 |
| Molar mass | 56.11 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.044 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 360 °C, 680 °F, 633 K |
| Boiling point | 1327 °C, 2421 °F, 1600 K |
| Solubility | Soluble in water and alcohols (methanol, isopropanol), glycerol but insoluble in ether, liquid ammonia |
| Acidity (pKa) | 14.7 |
| Crystal structure | rhombohedral |
| Heat capacity | 65.87 J mol−1 K−1 |
| Standard molar entropy |
79.32 J mol−1 K−1 |
| Standard enthalpy of formation |
−425.8 kJ mol−1 |
| Gibbs free energy | −380.2 kJ mol−1 |
Chemical properties
Potassium hydroxide reacts violently with acid to form corresponding salts.
- It reacts with methanol to form potassium methoxide.
KOH + CH3OH → CH3OK + H2O - It is a highly nucleophilic anion that attacks polar bonds of inorganic and organic compounds. For example, aqueous KOH saponifies esters.
KOH + RCOOR’ → RCOOK + R’OH - KOH attracts SiO2 to give soluble potassium silicates.
- It reacts with carbon dioxide to produce potassium bicarbonate
KOH + CO2 → KHCO3 - Potassium hydroxide solutions react with the aluminum to form potassium tetra hydroxy aluminate (III) and hydrogen gas.
2 Al + 2 KOH + 6 H2O → 2 KAl(OH)4 + 3 H2
Potassium hydroxide preparation
Previously, KOH was produced by adding potassium carbonate to a strong solution of calcium hydroxide.
Ca(OH)2 + K2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2 KOH
Calcium carbonate was removed from the solution as a precipitate. After this, the solution boils to give potassium hydroxide or caustic potash.
Presently, the process is replaced by a new method where electrolysis of aqueous potassium chloride gives KOH.
2 KCl + 2 H2O → 2 KOH + Cl2 + H2
Hydrogen and chlorine gas are produced as a by-product during the electrolysis of KCl.
Uses of potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide has a wide variety of applications in various industries such as the cleaning industry, chemicals industry, agriculture industry, food processing industry, manufacturing industry, cosmetics, etc.
Potassium hydroxide for soap making
Soap is a salt product that is obtained by combining alkali with fats or fatty acids. The alkali used for making soap is NaOH or KOH.
KOH or caustic potash or lye is a chemical which use specifically for making soft soap. It induces saponification of the fats and oils to form liquid soap. It is softer than the more common sodium hydroxide soaps.
Uses in the chemical industry
- It is used for making many potassium salts and potassium chemicals such as carbonate, cyanide, permanganate, phosphate, bromate, bromide, potassium aluminate, laurate, formate, gluconate, etc.
- Aqueous potassium hydroxide solution is used as the electrolyte for the production of alkaline batteries such as nickel-cadmium, nickel-hydrogen, and manganese dioxide–zinc batteries.
- It is used for the production of various household cleaning products.
- In the petroleum and natural gas industry, potassium hydroxide helps remove organic acids and sulfur compounds.
- It is used as a catalyst in the production of biodiesel from fats and oils.
- In analytical chemistry, KOH is a useful agent which adjusts the pH of chemical solutions.
- It is used for semiconductor chip fabrication.
Uses in agriculture
- In agriculture, KOH is used to adjust and regulate the pH level of the soil.
- It is used for the production of fertilizers that supply potassium to crops.
- KOH is also used for making herbicides and fungicides. For example, phosphorous acid and KOH solutions may be sprayed for pest and disease prevention.
KOH in food
In the food industry, potassium hydroxide acts as a food thickener, pH controller, and food stabilizer agent. KOH is a common food additive to make soft drinks, chocolate, and cocoa. It acts as a thickener and stabilizer in ice cream.
It is also used for washing and the chemical peeling of fruit and vegetables. According to FDA consideration, it is a safe food ingredient when used in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices.
KOH in cosmetics
In cosmetics, KOH is used for making manicure products and shaving products. Potassium hydroxide is a basic material which use in the production of lotions, shampoos, hairspray, etc
Potassium hydroxide solution
Aqueous potassium hydroxide solution is a colourless inorganic liquid that is used as a strong base. The pH values in an aqueous solution depending on the concentration of KOH.
KOH in water dissociates completely to form K+ and OH− ions. Due to complete dissociation, the concentration of KOH is equal to the concentration of OH−.
Problem: If the concentration of an aqueous potassium hydroxide solution is 0.1 mol dm−3. How to calculate the pH value of such KOH solution?
Solution: The concentration of OH− of said solution = 0.1 mol dm−3 = 10−1.
∴ pOH = −log[10−1]
or, pOH = 1
From the equation, pH + pOH = 14
pH + 1 = 14
∴ pH = 13
Problem: How to calculate the pH value of 0.0001 mol dm−3 KOH solution?
Solution: The concentration of OH− of said solution = 0.0001 mol dm−3 = 10−3 mol dm−3.
∴ pOH = −log[10−3]
or, pOH = 3
From the equation, pH + pOH = 14
pH + 3 = 14
∴ pH = 10
From the above two problems, if the concentration of KOH lies between 0.0001 M to 0.1 M, the pH range of such solutions will be 10 to 13. When the concentration of potassium hydroxide increases, the pH value of the solution also increases.