Chemical Formula Drawing
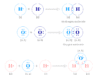
A chemical formula is the shortest way to represent a compound or molecule with the help of symbols and chemical proportions of atoms of participating periodic table elements. Most commonly, chemical formulas of compounds or molecules show their constituent elements and the number of atoms of each combining element. When writing a formula or drawing the structure of diatomic molecules such as methane, water, ammonia, hydrogen peroxide, and hydrogen sulfide, the valency of each participating atom is used to determine the chemical formula of a compound. For example, water is composed of hydrogen and oxygen with valencies one and two respectively and the chemical formula for water is H2O.
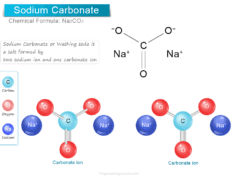
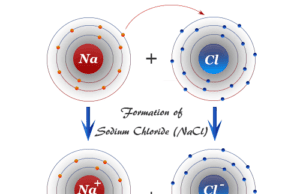
In ionic compounds, the charge on each ion is used to determine the chemical formula of a compound. For example, sodium chloride is formed by sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl−) with the chemical formula NaCl.
Chemical Formula for Methane
Methane is a covalent molecule made of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
The valency of carbon atom = 4
The valency of hydrogen atom = 1
Therefore, the chemical formula of methane is CH4
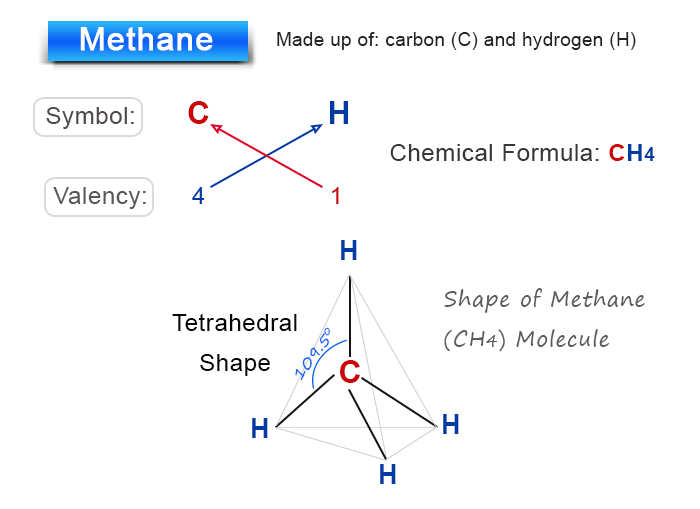
When drawing the chemical formula to structure, one carbon atom combines four hydrogen atoms by covalent bonding to form a tetrahedral methane molecule.
Chemical Formula for Ammonia
Ammonia molecule is formed by nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
The valency of nitrogen atom = 3
The valency of hydrogen atom = 1
Therefore, the chemical formula of ammonia is NH3.
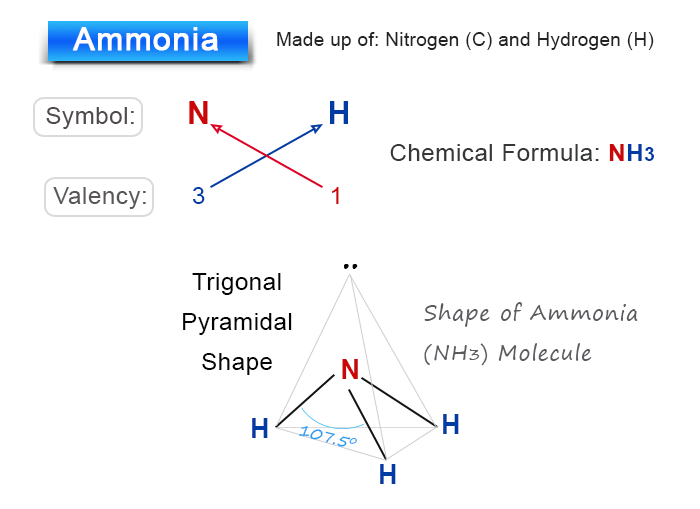
When drawing the chemical formula to structure, one nitrogen atom combines three hydrogen atoms by covalent bonding to form a trigonal pyramidal ammonia molecule.
Formula of Chemical Compounds
To write a chemical formula or drawing a structure of a compound, first, we see the constituent elements or ions with their valency and symbol or formula of constituent ions.
Sulfuric acid (dihydrogen sulfate) is one of the most widely produced chemicals in the world formed by the elements hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. It contains hydrogen with valency 1 and sulfate ion (SO4−2) with valency 2. Therefore, the chemical formula for sulfuric acid is H2SO4.
Valency
We can say valency is the combining power or capacity of an element. It can be used to find out how the atoms of an element will combine with the atom/atoms of another element to form a chemical compound. Therefore, it is important when we write the chemical formula of a compound.
Valency Chart
The valency of a cation or anion is equal to the charge on the ion. The valency of some common metallic, non-metallic, and polyatomic ions are given below in the table,
| Valency | Ion of metallic element | Symbol | Ion of non-metallic element | Symbol | Polyatomic ions | Symbol |
| 1 | Lithium | Li+ | Hydrogen | H+ | Ammonium | NH4+ |
| Sodium | Na+ | Hydride | H− | Hydroxide | OH− | |
| Potassium | K+ | Fluride | F− | Nitrate | NO3− | |
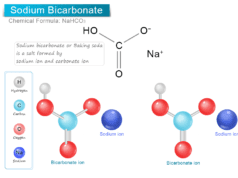
| Rubidium | Rb+ | Chloride | Cl− | Hydrogen Carbonate (bicarbonate) | HCO3− | |
| Cesium | Cs+ | Bromide | Br− | Cyanide | CN− | |
| Silver | Ag+ | Iodide | I− | Hydrogen sulfate (bisulfate) | HSO4− | |
| Copper (cuprous) | Cu+ | Hypochlorite | ClO− | |||
| chlorite | ClO2− | |||||
| Chlorate | ClO3− | |||||
| Perchlorate | ClO4− | |||||
| Permanganate | MnO4− | |||||
| Thiocyanate | SCN− | |||||
| 2 | Beryllium | Be+2 | Oxide | O−2 | Chromate | CrO4−2 |
| Magnesium | Mg+2 | Sulfide | S−2 | Dichromate | Cr2O7−2 | |
| calcium | Ca+2 | Selenide | Se−2 | Peroxide | O2−2 | |
| Strontium | Sr+2 | Telluride | Te−2 | Carbonate | CO3−2 | |
| Barium | Ba+2 | Peroxide | O2-2 | Sulfate | SO4−2 | |
| Radium | Ra+2 | Sulfite | SO3−2 | |||
| Iron (ferrous) | Fe+2 | Oxalate | C2O4−2 | |||
| Copper (cupric) | Cu+2 | Thiosulfate | S2O3−2 | |||
| Tin (stannous) | Sn+2 | Selenate | SeO4−2 | |||
| Mercury (mercuric) | Hg+2 | Silicate | SiO3−2 | |||
| Zinc | Zn+2 | Tartrate | C4H4O6−2 | |||
| 3 | Aluminum | Al+3 | Nitride | N−3 | Phosphate | PO4−3 |
| Iron (ferric) | Fe+3 | Phosphide | P−3 | Phosphite | PO3−3 | |
| Chromium (chromic) | Cr+3 | Arsenide | As−3 | Arsenate | AsO4−3 | |
| Manganese (manganic) | Mn+3 | Borate | BO3−3 | |||
| Gold (auric) | Au+3 | Aluminate | AlO3−3 | |||
| 4 | Tin (stannic) | Sn+4 | pyrophosphite | P2O5−4 | ||
| lead (IV) | Pb+4 | pyrophosphate | P2O7−4 |
Chemical Formula Writing
After knowing the valencies or charges of elements and ions, we can use some rules for writing the chemical formula of a compound.
- The valencies or charges on the ion must be balanced.
- When a compound contains a metal and a non-metal, the symbol of the metal is written first on the left, and the non-metal symbol is written on the right. In calcium oxide, we wrote CaO because calcium is a metal and oxygen is a non-metal.
- Then, they crisscross their charges or valencies to get the chemical formulas of a compound. For example, calcium chloride is written as CaCl2 because calcium contains the change +2 and chlorine ions contain the charge −1.
- The ion is enclosed in a bracket when compounds are formed with polyatomic ions. For example, calcium hydroxide is written as Ca(OH)2.
- The bracket is not required if the number of polyatomic ions is one. For example, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide are written as NaOH and KOH.
Chemical Formula for Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide molecule is formed by the silicon atom and the oxygen atom.
The valency of silicon atom = 4
The valency of oxygen atom = 2
Therefore, the chemical formula of silicon dioxide is Si2O4 or SiO2.
One silicon atom combines two oxygen atoms to form a silicon dioxide molecule.
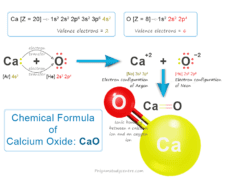
Chemical formula of calcium oxide
Calcium oxide is formed by the calcium ion and the oxygen ion.
The valency of calcium ion = 2
The valency of oxygen ion = 2
Therefore, the chemical formula of calcium oxide is CaO.
Chemical Formula Table
| Compounds | Combining ions | Chemical Formula | |||
| Cation | Anion | ||||
| Name and Symbol | Valency | Name and Symbol | Valency | ||
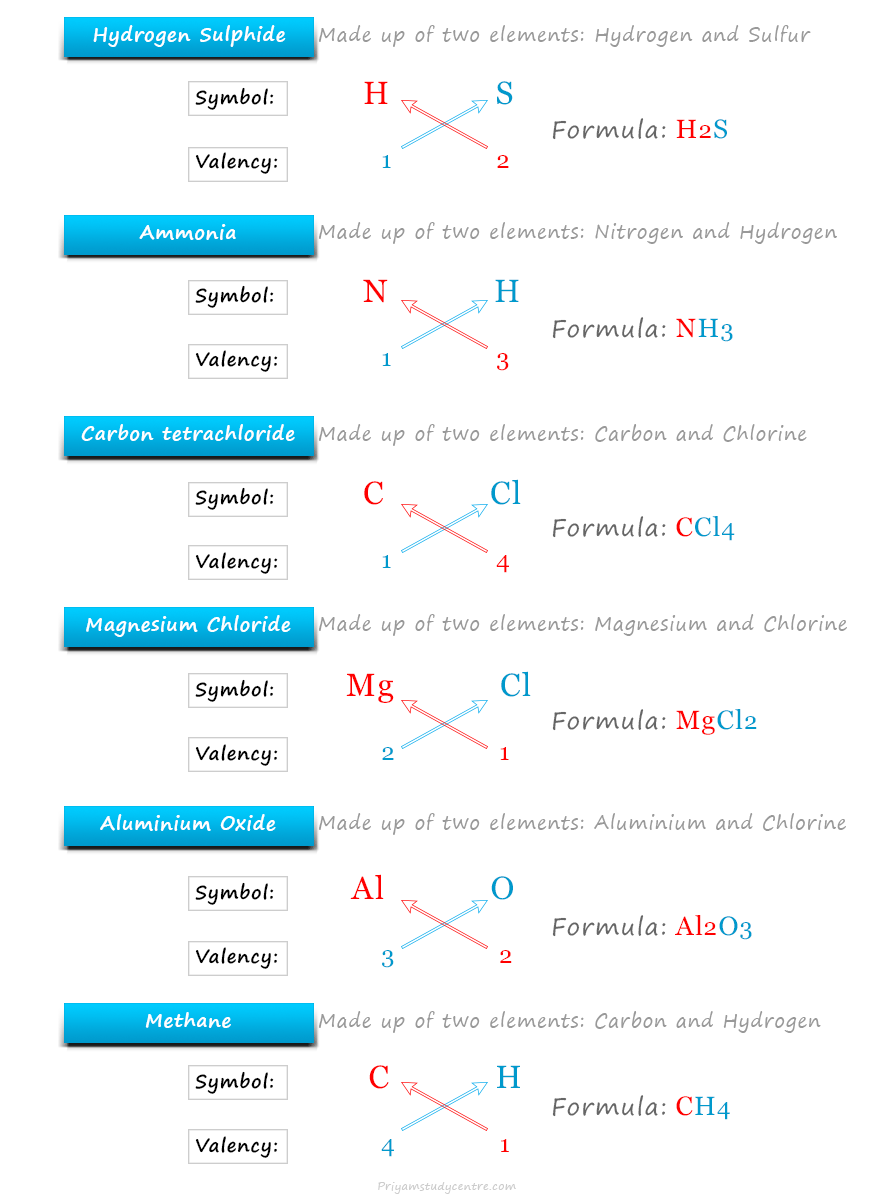
| Hydrogen sulfide | Hydrogen ion (H+) | 1 | Sulfide ion (S−2) | 2 | H2S |
| Carbon tetrachloride | Carbon (C) | 4 | Chloride (Cl−) | 1 | CCl4 |
| Magnesium chloride | Magnesium ion (Mg+2) | 2 | Chloride (Cl−) | 1 | MgCl2 |
| Calcium oxide | Calcium ion (Ca+2) | 2 | Oxide ion (O−2) | 2 | CaO |
| Aluminium oxide | Aluminium ion (Al+3) | 3 | Oxide ion (O−2) | 2 | Al2O3 |
| Sodium nitrate | Sodium ion (Na+) | 1 | Nitrate ion (NO3−) | 1 | NaNO3 |
| Potassium carbonate | Potassium ion (K+) | 1 | Carbonate (CO3−2) | 2 | K2CO3 |
| Aluminium hydroxide | Aluminium ion (Al+3) | 3 | Hydroxide (OH−) | 1 | Al(OH)3 |
| Ammonium sulfate | Ammonium (NH4+) | 1 | Sulfate (SO4−2) | 2 | (NH4)2SO4 |
| Tin (IV) oxide | Tin (Sn+4) | 4 | Oxide ion (O−2) | 2 | Sn2O4 or SnO2 |
| Sodium oxide | Sodium ion (Na+) | 1 | Oxide ion (O−2) | 2 | Na2O |
| Aluminium sulfate | Aluminium ion (Al+3) | 3 | Sulfate ion (SO4−2) | 2 | Al2(SO4)3 |
Chemical Formula Chart
| Sl No | Name of the Chemical Compound | Chemical Formula |
| 1 | Acetic acid | CH3COOH |
| 2 | Aluminium hydroxide | Al(OH)3 |
| 3 | Acetaldehyde | CH3CHO |
| 4 | Acetone | C3H6O |
| 5 | Aluminium chloride | AlCl3 |
| 6 | Aluminium oxide | Al2O3 |
| 7 | Amino acid | H2NCHRCOOH |
| 8 | Ammonia | NH3 |
| 9 | Ammonium chloride | NH4Cl |
| 10 | Ammonium hydroxide | NH4OH |
| 11 | Aluminium sulfide | Al2S3 |
| 12 | Ammonium sulfate | (NH4)2SO4 |
| 13 | Ascorbic acid | C6H8O6 |
| 14 | Barium chloride | BaCl2 |
| 15 | Benzene | C6H6 |
| 16 | Bleach | NaClO |
| 17 | Boric acid | H3BO3 |
| 18 | Borax | Na2[B4O5(OH)4]·8H2O |
| 19 | Bromocresol Green | C21H14Br4O5S |
| 20 | Calcium carbonate | CaCO3 |
| 21 | Calcium hydride | CaH2 |
| 22 | Calcium hydroxide | Ca(OH)2 |
| 23 | Calcium oxide | CaO |
| 24 | Carbon monoxide | CO |
| 25 | Carbon tetrachloride | CCl4 |
| 26 | Carbonic acid | H2CO3 |
| 27 | Carbon dioxide | CO2 |
| 28 | Chromic acid | H2CrO4 |
| 29 | Chlorine dioxide | Cl2O |
| 30 | Dihydrogen monoxide | H2O |
| 31 | Dinitrogen monoxide | N2O |
| 32 | Ethanol | C2H5OH |
| 33 | Ethylene glycol | C2H6O2 |
| 34 | Ethylene oxide | C2H4O |
| 35 | Formaldehyde | HCHO |
| 36 | Glycerol | C3H8O3 |
| 37 | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid | C10H16N2O8 |
| 38 | Formic acid | HCOOH |
| 39 | Hydrofluoric acid | HF |
| 40 | Hydroiodic acid | HCl |
| 41 | Hydrocyanic acid | HCN |
| 42 | Hydrogen peroxide | H2O2 |
| 43 | Hydrosulfuric acid | H2SO4 |
| 44 | Hexane | C6H14 |
| 45 | Heavy Water | D2O |
| 46 | Iron (ii) oxide | FeO |
| 47 | Iron (iii) oxide | Fe2O3 |
| 48 | Manganese dioxide | MnO2 |
| 49 | Methanol |
CH3OH |
| 50 | Nitrogen monoxide | NO |
| 51 | Nitrous acid | HNO2 |
| 52 | Nitric acid | HNO3 |
| 53 | Ozone | O3 |
| 54 | Oxalic acid | C2H2O4 |
| 55 | Potassium Chloride | KCl |
| 56 | Potassium Hydroxide | KOH |
| 57 | Potassium iodide | KI |
| 58 | Potassium dichromate | K2Cr2O7 |
| 59 | Phenol | C6H5OH |
| 60 | Sodium Chloride | NaCl |
| 61 | Phosphoric acid | H3PO4 |
| 62 | Propanol | CH3CH2CH2OH |
| 63 | Sodium hydroxide | NaOH |
| 64 | Sodium carbonate | Na2CO3 |
| 65 | Sugar | C12H22O11 |
| 66 | Sulfur dioxide | SO2 |
| 67 | Sulfur trioxide | SO3 |
| 68 | Starch | (C6H10O5)n |
| 69 | Tartaric acid | C4H6O6 |
| 70 | Toluene | C7H8 |
| 71 | Urea | CH4N2O |
| 72 | Zinc chloride | ZnCl2 |
| 73 | Zinc sulfate | ZnSO4 |
| 74 | Zinc sulfide |
ZnS |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Chemical Formula in Chemistry?
In chemistry, a chemical formula is the shortest way to represent a compound with the help of symbols and the valency or charge of the elements.
For example, methane is formed by carbon (symbol C and valency = 4) and hydrogen (symbol H and valency = 1). Therefore, the chemical formula of methane is CH4.
What is the chemical formula for hydrogen peroxide?
Hydrogen peroxide is formed by a hydrogen ion (H+) and a peroxide ion (O2−2). Therefore, the chemical formula of hydrogen peroxide is H2O2.
What are polyatomic ions?
Polyatomic ions are groups of atoms that carry a charge and behave like one entity. For example, one oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom combine to form a hydroxide ion (OH−). Similarly, one carbon atom and one three oxygen atom combine to form a carbonate ion with the chemical formula CO3−2.