Electrical Energy and Power
Electrical energy is the energy obtained from the electric potential or kinetic energy of the charged particles (electrons) while electric power is the amount of electric energy consumed or supplied to a circuit per unit time. If W is the amount of electrical energy consumed in a circuit in t seconds then electric power is measured by formula P = W/t. Therefore, when an electrical appliance of power 1 watt runs for 1 hour then electrical energy is measured by unit 1 watt-hour. Most commonly, electrical energy is generated in a power station through electromechanical generators driven by renewable and nonrenewable energy resources and nuclear power sources obtained from nuclear fission reactions.
Nonrenewable and renewable energy natural resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear power, solar radiation, wind energy, flow of water, and geothermal heat are examples of electrical energy sources that can be used to generate electricity.
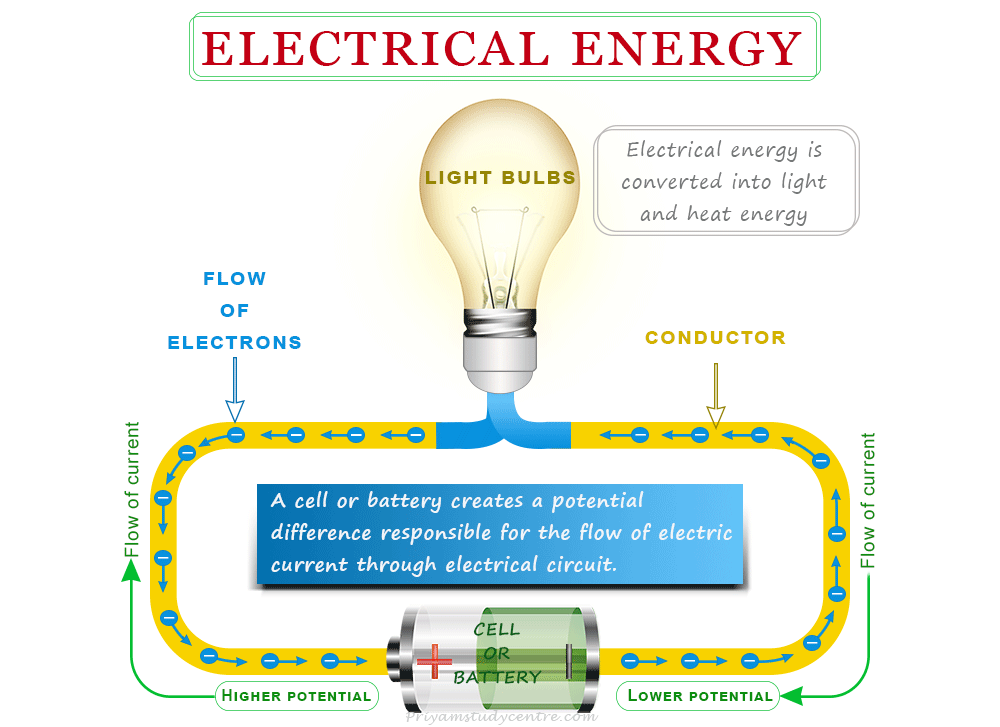
The electrical energy generated or stored within batteries creates an electric potential difference responsible for the flow of electric current through any electrical circuit. Therefore, a cell or battery is also a source of electrical energy generated by chemical reactions within them. However, in most cases, electricity is produced by converting mechanical energy using a generator through the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Inside metals, the atoms are packed together very closely to each other but electrons are able to travel through the metallic crystalline solids. When a steady current flows in a metallic conductor, the electrons in it move with an average speed of the order of 10−4 m/s. Therefore, the flow of charge or electron particles can produce current in a conducting wire.
Flow of Electricity
The flow of electricity can occur due to a difference in electrical potential between two points. It creates an electric field that drives electrons to move through the conducting wire or materials. The potential difference can be measured in volts while the flow of electric current is measured in amperes.
The direction of electric power is taken as opposite to the direction of the flow of electrons (negative charges). In an electric circuit, the current flows from the positive terminal of the electrochemical cell or battery to the negative terminal.
Electrical Energy Examples
Electrical energy is a versatile form of energy resulting from the flow of electrons through a conductor. Electricity can be easily transformed or converted into other forms of energy such as light, heat, or mechanical energy.
Electrical energy is an example or form of energy produced by electrical charges. If the electrical charge is moving, it is kinetic energy but when the charge is stored, it is potential energy. Electrical energy has the power to move an object or do some work. We can see such type of work completed by electricity every day in the surroundings around us.
Electrical energy can be obtained by converting other types or forms of energy. For example, solar cells convert sunlight into electricity, wind turbines turn kinetic energy into electricity, and hydroelectric power plants use the kinetic energy of moving water for the production of electricity. Another example of electricity is electrochemical energy obtained due to chemical reactions in batteries. Common examples of electrical energy are:
- Batteries: They produce and store energy due to chemical reactions within the cell.
- Electrical appliances: They use electrical power or electricity to perform different types of work.
- Solar cells: They convert solar energy into electricity.
- Wind turbines: Convert wind energy into electricity.
- Lightning: Lightning is a giant spark of electricity that forms in the atmosphere between clouds, the air, or the ground.
- Electric eels: They produce electrical charges in their bodies.
- Proton beams: Highly energetic particle beams composed of positively charged particles.
- A capacitor before it discharges can store electricity within it.
- Two ions that are held apart from each other can also generate electricity.
Electric Potential
Electric potential or voltage is defined as the difference in potential energy per unit charge between two points in an electric field. If work done in moving a positive charge q from one point to another point is W, then the electric potential V of that point is,
V = W/q
The SI unit of electric potential is volt (V) named after Italian physicist Alessandro Volta.
The electric potential difference between two points of a conductor is defined as the work done for moving a unit positive charge from one point to another point. When the potential difference between two points in a current carrying conductor is 1 volt, then 1 joule of work is done in moving 1 coulomb of electric charge from one point to another.
The potential difference between two points A and B in a circuit can be measured by using an electric device called a voltmeter. It is a high-resistance device that is always connected in parallel with the components through which potential differences can be measured.
Problem: How to calculate the potential difference between two terminals of a battery, if 100 J of work is required to transfer the charge of 20 C from one terminal of the battery to the other?
Solution:
From the problem,
Work done (W) = 100 J
Charge (q) = 20 C
The potential difference, ΔV =?
∴ ΔV = W/q = 100/20 = 5 V
Therefore, the potential difference between the two points of the battery is 5 V.
Unit of Electrical Energy
Electrical energy can be derived by SI unit joule (J) but it is most commonly sold in the commercial unit kilowatt hour (kWh).
1 kWh = 1000 Wh
= 1000 × 3600 Ws
= 3.6 × 106 J
Joule is defined as the amount of energy generated or consumed by an electrical conductor with a potential difference of 1 volt and current flow through the conductor 1 ampere for a time of 1 second.
If an electrical appliance of power p watt runs for t seconds then the amount of electrical energy consumed by such appliance,
E = P × t Ws = Pt Joule
- Watt-hour (Wh): 1 Watt-hour is the amount of energy consumed by an electrical appliance of power 1 watt running for 1 hour.
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh) or Board of Trade unit (BOT): 1 kilowatt-hour or Board of Trade Unit (BOT) can be defined as the amount of energy consumed by an electrical appliance of power 1 kilowatt running for 1 hour.
BOT unit or kWh unit is used by electric supply company to measure the amount of electricity consumed by the consumers in domestic supply. Therefore, the electric supply company installs a meter in the house to measure the electricity consumed in terms of BOT or kWh.
1 kWh = (1 watt × 1 hour)/1000
= (1 ampere × 1 volt × 1 hour)/1000
Problem: An electric device rated 500 W and operates 10 hours per day. What is the cost of the energy to operate it for 30 days at $4.5 per kWh?
Solution:
Energy consumed by refrigerator in 30 days,
= 500 W × 10 × 30 hours
= 150000 Wh = 150 kWh
∴ The cost of electrical energy to operate the refrigerator for 30 days,
= 150 kWh × $4.5 per kWh
= $675
Electrical Power
Electric power is defined as the amount of electric energy consumed or supplied to a circuit per unit time. It can be represented by the symbol P and measured by unit watt or joule per second. Therefore, like mechanical power, electrical power is the rate of doing work in watts.
Electric Power Formula
If W is the amount of electrical energy consumed in a circuit in t seconds then electric power,
P = W/t (where W = electric energy)
But W = VQ = VIt
Here, Q = electric charge in coulombs
V = electric potential in volts
I = electric current in amperes
∴ P = VIt/t = VI
According to Ohms law, V = IR
Here, I = electric current and R = resistance
∴ P = IR × I = I2R
Electric Power Unit
Electric power can be measured commonly by SI unit watt (W). If 1 ampere current flows through a circuit having 1 volt potential difference, the electric power is 1 watt.
1 watt (W) = 1 volt (V) × 1 ampere (A)
∴1 W = 1 VA
Electric power can also be represented by bigger units kilowatts, megawatts, gigawatts, and practical unit horsepower (HP).
- 1 kilowatt (kW) = 103 W
- 1 megawatt (MW) = 106 W
- 1 gigawatt (GW) = 109 W
- 1 horsepower (HP) = 746 W
Electrical Energy Sources
Electrical energy can generated from various renewable and non-renewable power sources present in our Earth. Hydroelectric, solar, wind, and geothermal heat are the main renewable resources that are used for generating electricity. Similarly, fossil fuels (coal, oils, and natural gas) and nuclear power are the main non-renewable resources that are used for generating electrical energy.
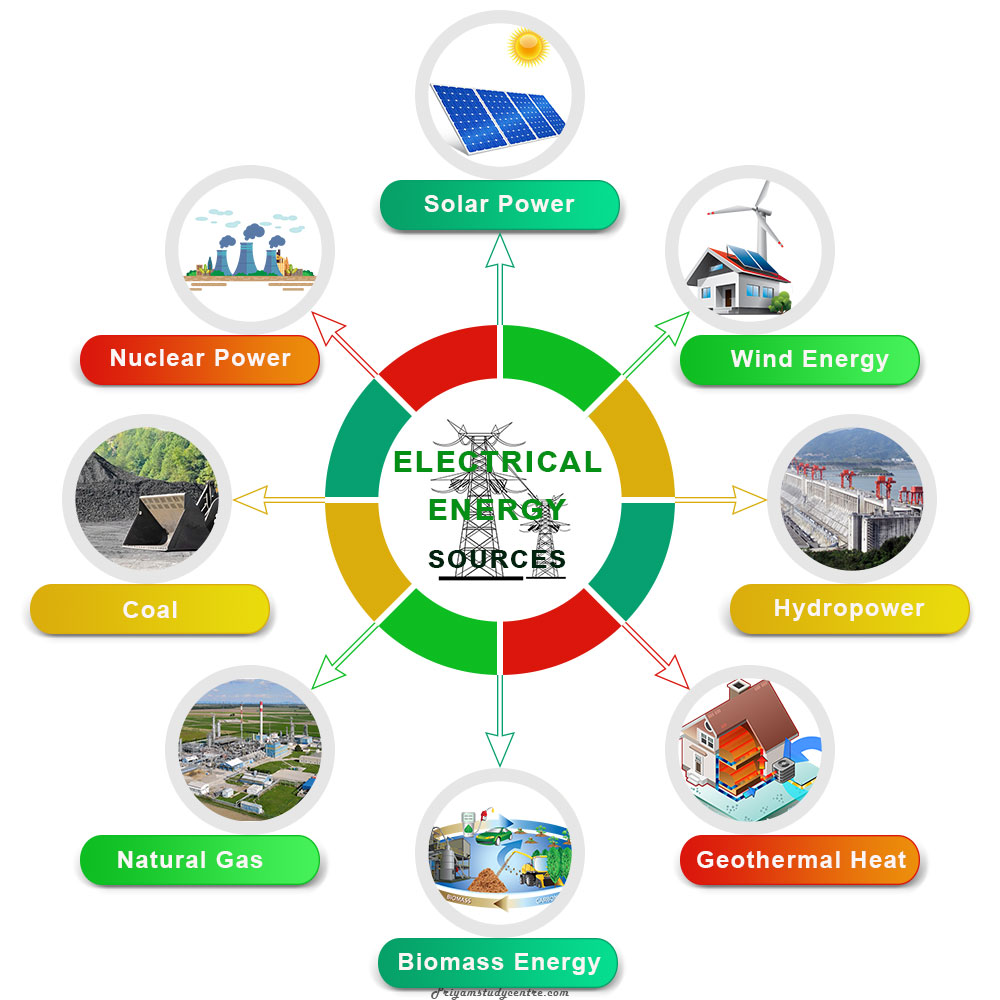
Electricity or electric power obtained from various sources moves electrons through all appliances installed in homes and factories. Therefore, it is used in a wide variety of household applications from lighting, heating, and running appliances. Electrical energy is also used as a source of power for large industries and transport systems.
Renewable Energy Resources
Electrical energy can be generated from a variety of renewable power sources, such as solar panels, hydropower, geothermal heat, and wind turbines.
Photovoltaic Solar Energy
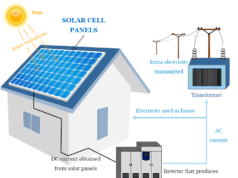
Photovoltaic solar energy obtained from the Sun can converted to electricity through photovoltaic solar panels. These solar panels contain photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight directly into electrical power. Photovoltaic cells use semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect for such conversion.
Wind Energy
The kinetic energy of the moving air or wind is converted into electricity by using wind turbines. When the wind turns the blades of wind turbines, they activate generators that produce electricity from the moving air.
Wind energy is a clean and renewable source for generating electricity that is installed either on land or offshore. It has very low maintenance costs but very high installation costs and also requires very large areas. The production of such type of energy is dependent on wind speed and direction.
Hydroelectric Energy
The kinetic energy of moving water can be used for generating electrical energy in hydroelectric power plants. The water is stored in a dam and released through pipes to turbine blades. It activated generators and produced electricity from moving water.
Hydroelectric power is a clean and renewable source of electrical energy but has very high installation costs. It also impacts our environment due to breaking down the natural flow of rivers.
Geothermal Energy
The heat from the Earth’s interior can be used for the production of electricity in the region of volcanic or tectonically active areas. In geothermal power plants, geothermal heat is used to generate streams that drive turbines connected to the electrical energy generator.
Electricity from geothermal heat cannot be produced in all regions of the world. It is only produced in the region of volcanic or tectonically active areas.
Nonrenewable Energy Resources
The generation of electrical energy from nonrenewable natural sources uses natural power resources that are limited in nature and degraded in quantity and quality by human activities. Although they still play an important role in electrical power generation in many parts of the world.
Conventional Thermal Energy
Coal, oil, and natural gas are common fossil fuels used in thermal power plants for generating electrical energy. They are the most common nonrenewable natural resources that are used widely for the production of electricity.
Such nonrenewable natural power resources produce heat that is converted to electrical energy by generating streams that drive turbines connected to the generator. They are the most important source of energy but they impact our environment by releasing greenhouse gases and causing environmental pollution.
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy can be generated by nuclear fission and converted to electrical energy in nuclear power plants. In nuclear fission, the heavy atomic nucleus such as uranium split into smaller atoms, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of heat. Such heat can be used to generate streams that drive turbines connected to the generator.
Although nuclear power plants do not emit any greenhouse gases during the electrical energy generation process. However, if proper safety is not taken it causes radioactive pollution.
Advantages of Electrical Energy
One of the most important parts of life in today’s world is electrical energy or electric power. It is a controllable and convenient form of energy because electricity is used in almost every sector (household, commercial, transport, industrial, etc) to make life faster and easier.
Electrical energy obtained from renewable sources provides a significant number of advantages and makes it a very attractive power source. Some common advantages of using electrical energy in power generation are:
- Electricity is a versatile form of energy because it can easily transform other forms of energy.
- The efficiency of such type of energy is very high compared to other forms of energy.
- When electric power is generated from renewable energy sources, it is a clean and pollution-free source of electrical energy.
- Electricity can easily to transported over long distances or areas through transmission and distribution networks.
- Electrical energy has high automation and controlling power. Therefore, it is used efficiently in industrial systems, manufacturing processes, or transport systems.
- It can reduce dependence on fossil fuels when generated from renewable energy sources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Definition of Electrical Energy?
Electrical energy is defined as the energy obtained from the electric potential or kinetic energy of the charged particles. Therefore, electrical energy is a form of energy obtained from the flow of charged particles (electrons) through metal conductors or any other conducting materials.
Why Electrical Energy is Important?
One of the most important parts of life in today’s world is electrical energy or electricity because it generates power for most of the appliances that we use. It is a controllable and convenient form of energy because electricity is used in almost every sector (household, commercial, transport, industrial, etc) to make life faster and easier.
What is Electrical Power?
Electric power is defined as the amount of electrical energy consumed or supplied to a circuit per unit time from the source of electricity. It is commonly measured by unit watt (W) or joule (J) per second.
Is Electrical Energy Potential or Kinetic?
Yes, electrical energy is either kinetic or potential. When the electrical power is stored in an atom, it is potential energy but when electrons are flowing, it is Kinetic energy. For example, a battery stores electrical energy in the form of potential energy but when we use a battery, the electrons flow out through a circuit and create kinetic energy.