Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
Greenhouse effect and global warming mean increasing the global temperature of the world which trapping specific heat from the earth’s surface by mainly carbon dioxide and other gas molecules like methane, CFC, ozone, etc. The harmful electromagnetic spectrum like UV light comes from sunlight shielding or absorbed by the ozone layer but visible or infrared rays pass through the layer and fall on the earth’s surface. The infrared spectrum has the heating of the earth and various particles of the earth. It warming the earth’s atmosphere and causes climate change. The contribution and effect of different greenhouse gases are different and their solutions to save our environment from global warming are the challenge today.
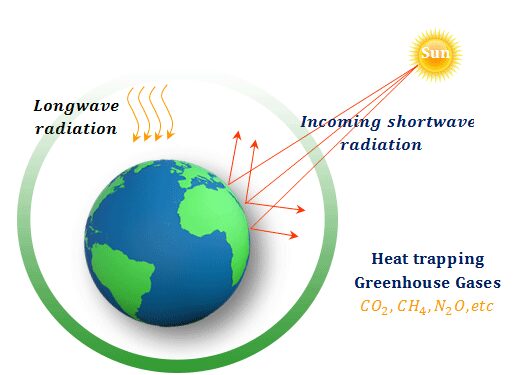
The name greenhouse effect comes from the fact that used in horticulture for the upbringing of green plants in the small glasshouse whose walls and roof are made of glass sheets. The glass sheet and roof of the house allow the short wavelength of heat that comes from the sunlight to go into the greenhouses freely and trap this heat coming from objects in houses. Such trapping of heat or infrared radiation increases the temperature inside the greenhouse. This is called the greenhouse effect.
Facts About Greenhouse Effect
There is a protective layer of ozone gas in the atmosphere at a height between 15 km and 60 km. The thick layer of ozone exists at a height of 23 km from the surface of the earth. Hence the blanket of carbon dioxide exists in the lower part atmosphere.
However, the long wavelength of particles that come from the soil, plants, and other contents of the earth does not allow them to go out from the earth’s atmosphere easily. Therefore, this trapping of heat or electromagnetic radiation raises the temperature of the earth’s surface.
Greenhouse Gases
The gases that trap heat or IR radiation that come from the earth’s atmosphere are called greenhouse gases in environmental chemistry or science.
Carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbon, ozone, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbon, PFC, sulfur hexafluoride, and water vapor are the greenhouse gases that increase global temperature.
The contribution to global warming of these gases is given below in the table.
| Greenhouse Gases | Contributions to global warming |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | 50% |
| Methane (CH4) | 16-20% |
| CFC | 13-18% |
| Ozone (O3) | 7-8% |
| Nitrous oxide (N2O) | 4-5% |
| Water vapor | ≈ 2% |
Positive Effects of Greenhouse Gases
The greenhouse effect in learning chemistry or biological chemistry is very important because this suggests the existence of life in the Earth’s atmosphere. The presence of these gas layers in the atmosphere does not allow heat rays to go out of the atmosphere. Hence the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere increases.
The rise in temperature of the earth’s atmosphere is very important for existence on earth. Without heating the whole earth would be converted into a cold planet, consequently, we would not be able to live a normal life.
Global Warming
Carbon dioxide contributes 50% of our greenhouse gases. When the atmosphere contains too much quantity of carbon dioxide, the effect of heating considerably rises. Hence the excess quantity of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases causes to warming of the global temperature to climate change.
This too much rises temperature that melts snow mountains of our environment. It causes floods in the low-lying areas of our earth. Also changes the biological activity of oceans and the patterns of cropping. Therefore, the presence of excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere brings about climate change.
What are the effects of greenhouse gases?
We have already said that air is pollution caused by the presence of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, ozone, unburned hydrocarbon, CFC, HFC, etc.
Some of the pollutants cause global warming but some cause soil pollution and water pollution through acid rain which decreases the pH scale of the earth’s soil and water. Therefore, we need proper solutions to decrease these pollutants.
Solution of Greenhouse Effect
- Adding lead tetraethyl to the petrol or by the catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons with a chemical catalyst like platinum or palladium. This method uses to save air from harmful gases released by vehicle engines.
- Balancing the quantity of carbon dioxide present in the earth’s atmosphere by growing plants. This is the natural process to remove greenhouse gases from the earth’s atmosphere.
- By using smoke free energy sources like solar energy, wind energy, nuclear power, etc.
- Using electrostatic precipitators. This method removes carbon dioxide produced by burning fuels like coal and oil.
- Stop the use of cooling agents like chlorofluorocarbons.
- To decrease the concentration of greenhouse gases on the earth’s surface, we need to use tall chimneys in homes and factories.