Maltose Malt Sugar
Maltose Sugar also called maltobiose or malt is a carbohydrate or monosaccharide formed by two α-D-glucose units held together by α(1→4) glycosidic bond. We use maltose powder or high maltose corn syrup to make various food items. Maltose has the molecular formula C12H22O11 and it can be hydrolysis by dilute acid or the enzyme maltase to form two molecules of α-D-glucose. Maltose and many other types of sugars are an important source of energy for human health. However, consuming too much sugar has negative effects on your health. Therefore, always avoid or eat a desired amount of processed foods that contain very high density of maltose or sucrose sugars.

Maltose can be made by breaking down starch, a long-chain carbohydrate that contains many glucose units. Such breaking down is carried out by enzymes present in your gut.
Plant seeds also produce enzymes that can convert starch into maltose during sprout. Such natural processes help us in the production of carbohydrate-rich food. Malt also plays an important role in brewing beer, whisky, and malt vinegar.
Maltose Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where a water molecule breaks down a chemical bond to form two or more chemical compounds. Maltose is a disaccharide that contains two glucose molecules linked by α(1→4) glycosidic bond.
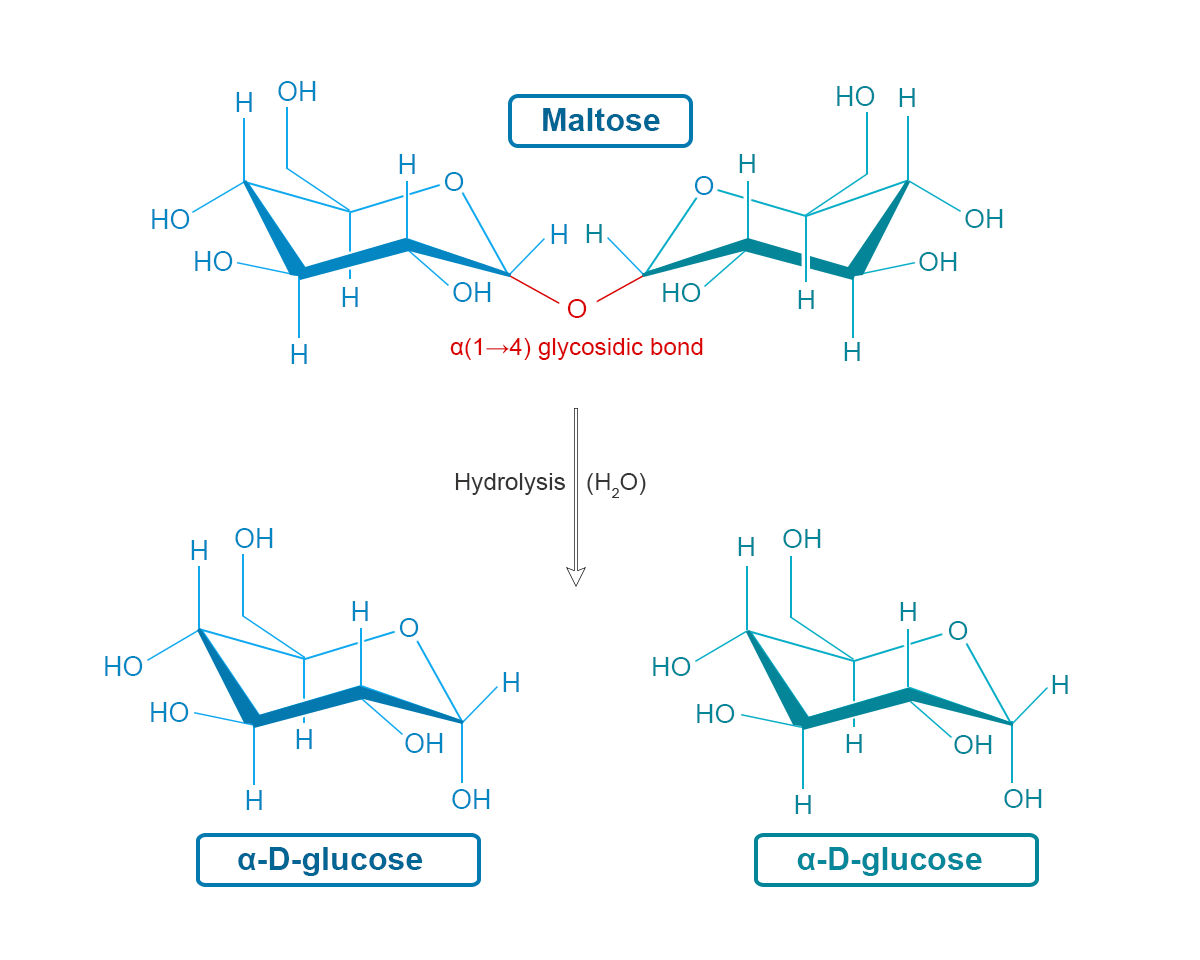
The chemical formula of maltose is C12H22O11 and is formed by two alpha D -glucose units where C1 of the first glucose unit is bonded to C4 of the second glucose unit. The hydrolysis reaction of maltose is given below:
C12H22O11 + H2O → 2 C6H12O6
On hydrolysis of disaccharide malt sugar, the α(1→4) glycosidic bond is broken down to form two monosaccharides α-D-glucose.
Maltose Chemical Structure
Like table sugar or sucrose, malt sugar also contains two monosaccharides. Table sugar is made of one glucose and one fructose but maltose has two glucose units. Maltose is a common type of disaccharide after sucrose and lactose. The chemical formula of maltose is C12H22O11. Therefore, it contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in its chemical structure.
Disaccharides are formed by the binding of two monosaccharide molecules with the liberation of a water molecule. Maltose, isomaltose, and cellobiose are three disaccharides that contain two glucose units held together by glycosidic linkage.
- The disaccharide, maltose is formed when the C1 carbon of one glucose bonded with the C4 unit of the second glucose molecule. The bond that joins two α-D-glucose units is called an alpha-glycidic bond.
- In isomaltose, the glucose units are held together by α (1→6) glycosic linkage.
- Cellobiose is identical in structure to maltose but formed by β (1→4) glycosidic linkage.
Food Source of Maltose
Plants contain maltose or malt sugar in their seeds and other parts of the body. Therefore, malt sugar can be found in various naturally occurring foods like cereals, certain fruits, sweet potatoes, etc. It can also made by the breakdown of biopolymer starch, a long-chain polysaccharide with a large number of glucose units.
We find high amounts of maltose sugar in various naturally occurring food items. Some foods that contain high amounts of maltose sugar are listed below:
- Glucose syrup
- Honey
- Caramels, snack bars, fruit-filled
- White bread, white flour, English muffins, and crumpet
- Liquorice, Sausage rolls, and Fillo pastry
Couscous - Savoury biscuits or crackers and sponge cake
- Muesli, Muesli bar and Orange marmalade
- Soy milk
- Pie
- Golden syrup
- Sundried tomato
- Water chestnuts
- Instant coffee
- Corn kernels
- Beer
- Bread crumbs, dry, grated, seasoned
- Fish, Fish fingers, and fish portions and sticks, frozen, preheated
Fruits such as peaches and pears are good sources of maltose sugar. Maltose is obtained in the market as a white crystalline powder but high maltose corn syrup is also available in the market.
High maltose corn syrup is an additive or food preservative obtained from corn starch that contains maltose and glucose. It is used widely for making various food items such as confectionery, breweries, chocolates, sweets, sauces, liquid foods, and ice creams.
Properties of Maltose Sugar
Maltose is a slightly sweet, water-soluble disaccharide that is generated during the brewing of beer and related beverages. It is a white crystalline powder or viscous liquid soluble in water. The reduced sugar, maltose is 30-60% less sweet than sugar.
Physical Properties
| Chemical formula | C12H22O11 |
| CAS Number | 69-79-4 |
| Molar mass | 342.297 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder or crystalline form |
| Odour | Sweet testing with no odour |
| Density | 1.54 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | Anhydrous form: 160 to 165 °C Monohydrate form: 102–103 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
Chemical Properties
The aldehyde group of one of the glucose in maltose remains free. It makes it a reducing disaccharide and allows it to have α and β forms.
Therefore, maltose shows optical rotation and forms α and β anomers. In an aqueous solution, α and β anomers are equilibrium in state.
Chemical Reactions
Maltose may participate in various chemical and biochemical reactions. The most common reactions are:
When malted sugar is treated with sulfuric acid, it forms carbon dioxide, water, and sulfur dioxide.
C12H22O11 + 24 H2SO4 → 12 CO2 + 35 H2O + 24 SO2
Hydrolysis in the presence of the maltase enzyme gives two molecules of α D-glucose.
C12H22O11 + H2O → 2 C6H12O6
Maltose also reacts with water to form ethanol and carbon dioxide.
C12H22O11 + H2O → 4 C2H5OH + 4 CO2
Uses of Maltose Sugar
Maltose, lactose, and sucrose are the most important disaccharides in human biochemistry. The sugars and proteins present in malt are very nourishing for yeast. Therefore, it is created in seeds during germination because they break down their stored energy to sprout.
Malt sugar is an important biomolecule used widely in brewing beer, whisky, and malt vinegar. Nutritionally, malt sugar provides the same number of calories to our bodies as starches and other sugars. Therefore, the healthier effect of maltose is similar to that of other sugars. Like other sugars, if you consume it in excess, it can lead to obesity, diabetes, and heart and kidney disease.
Malt sugar can be produced during hydrolysis of starch, catalyzed by the enzyme amylase. The most common general and biochemical uses of maltose are:
General Uses Maltose Sugar
We can use malt for brewing beer and other alcohol products or food additives. In the early stage of the plant harvesting process, seeds use malt sugar for the energy needed to germinate and grow.
High-maltose corn syrup is an important food additive made from corn starch that contains maltose and glucose. It is a refined starch used as an additive and preservative for food items such as confectionery, breweries, chocolates, sweets, sauces, liquid foods, and ice creams.
Biochemical Uses Maltose Sugar
In addition to forming melt, metlose is also formed in our gut during the breakdown of starch. Starch is a polysaccharide made up of smaller sugar units. Therefore, starch in our body is converted to smaller units and made available for the body to use.
Malt sugar is a common type of carbohydrate that is used as a source of energy for the body. Our body can break down carbohydrates into smaller units such as maltose or glucose for more easily used as fuel.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is malt sugar unhealthy?
Complex carbohydrates found in many foods can break down more slowly than refined or simple carbohydrates. Refined carbohydrates such as glucose, maltose, and fructose are easily digested or broken down by our bodies. Therefore, they can negatively impact our health by contributing to weight gain and promoting diabetes and heart disease.
Sucrose, maltose, and high-fructose corn syrup can be commonly added to processed foods that we eat daily. Consuming too much such type of processed foods can increses triglycerides in your blood. They also lead to weight gain and increased fat tissue around the muscles and liver.
What is high maltose syrup?
High-malt corn syrup is a food additive made from corn starch that contains maltose and glucose. It is a refined starch used as an additive and preservative for our food items.
High maltose corn syrup is a thick, viscous, odorless, colorless syrup extracted by biochemical technology through the Double Enzymatic process. It is less sweet than high fruitrose corn syrup and contains high concentrations of maltose in its composition. It can be added to various food items such as confectionery, breweries, chocolates, sweets, sauces, liquid foods, and ice creams.
What two monosaccharides make maltose?
Maltose is a disaccharide that is made by two glucose molecules linked by α(1→4) glycosidic bond. Therefore, during hydrolysis, the α(1→4) glycosidic bond is broken down to form two monosaccharides α-D-glucose.
Where to find maltose?
Malt sugar is a common disaccharide that is found in many plant-based food items and processed foods. The most common food items that contain high amounts of malt sugar may include seeds, germinating grains, wheat, cornmeal, barley, ancient grains, breakfast cereals, peaches, pears, sweet potatoes, honey, beer, bread, etc.
We also produced high-malt corn syrup that contains maltose and glucose in its composition.
What is the composition of maltose sugar?
Malt sugar is a double sugar composed of two glucose molecules joined by an α-(1,4) glycosidic bond. It is a white crystalline, odorless, sweet-tasting powder containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in its composition. Generally, maltose is found in various naturally occurring food items.