Recombinant DNA Technology
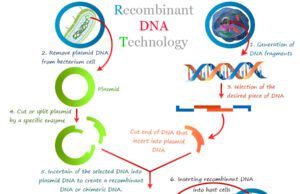
What is Recombinant DNA Technology?
Recombinant DNA technology (rDNA technology) is a process that is used for producing artificial DNA through the combination of different...
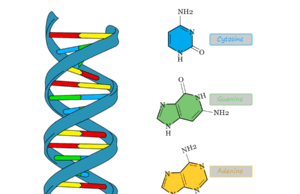
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Synthesis
Nucleotides that contain a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group in their structure are the basic building blocks of nucleic...
Nucleic Acids
What are Nucleic Acids?
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules that carry genetic information and participate in protein synthesis. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are...
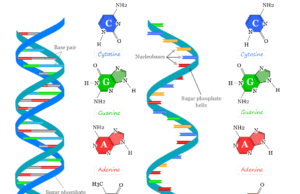
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Definition for Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the polymer of deoxyribonucleotides which is found in most animals, plants, and some viruses. Deoxyribonucleic acid carries...
Collagen Protein
Benefit of Collagen Protein
Collagen is the most vital protein in mammals which forms approximately one-third of the total body protein. Collagen is a type...
Carbohydrates
Metabolism of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates also called saccharides or carbs are the most abundant organic compounds in nature that provide energy for our bodies through metabolism....
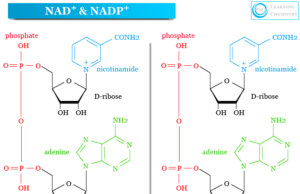
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADP)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) is a coenzyme formed by the addition of a phosphate group in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide...
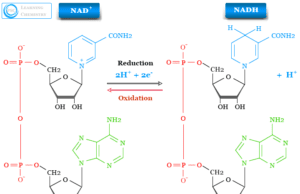
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme or electron carrier involved in the metabolism of all living cells. We used nicotinamide...
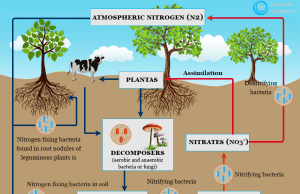
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen Fixation Definition
Nitrogen fixation is the process which fixing atmospheric dinitrogen (N2) in soil by any industrial and natural or biological processes to convert...
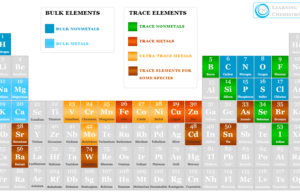
Essential Element
Essential Elements Nutrition
Essential element in biological science is the chemical elements that have biological functions to sustain the life of living organisms such as plants or...