Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Sulfur dioxide or Sulphur dioxide is a chemical compound of sulfur with the molecular formula SO2. It is a highly toxic and soluble gas in water. Liquid sulfur dioxide is a useful solvent that is used widely as a bleaching agent and refrigerant for food preservation. Sulfur dioxide is the most harmful gaseous pollutant which has adverse effects on our environment and human health. It causes air pollution, water pollution, and soil pollution in our environment. It can be easily liquefied by cooling or decreasing pressure. Volcanic activity and fossil fuels are the main natural sources of sulfur dioxide in the environment. The structure of the SO2 molecule contains sp2 hybridized sulfur atom bonding with two oxygen atoms. One sp2 orbital carries the lone pair of electrons and another sp2 orbital pairing with one oxygen through the coordinate bond.
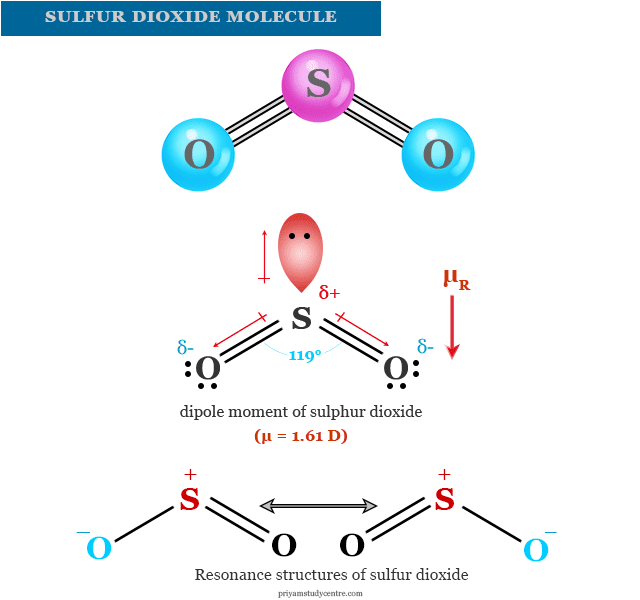
The electron in the third sp2 orbital overlaps with the unpaired electron in the second oxygen atom. The resonance structure of sulfur dioxide indicates the considerable double bond character of S-O bonds.
Sulfur Dioxide Sources
- Naturally, sulfur dioxide is released into the atmosphere by different types of volcanic activity.
- It is also generated when coal and oils are burnt in houses and industries. Coal always contains some sulfur as an impurity. When coal is burnt, sulfur present in coal is converted into sulfur dioxide. Oils also contain several types of sulfur compounds which give SO2 on burning.
- Sulfite ores such as iron pyrites (FeS2), copper pyrites (CuS), copper glance (Cu2S), zinc blende (ZnS), and galena (PbS) are other natural sources of sulphur dioxide. They produced SO2 when roasted in the air oxygen.
- A part of SO2 present in the atmosphere is oxidized to SO3 by photolytic and catalytic oxidation processes. Therefore, SO2 present in the atmosphere also contains SO3. Although the quantity of sulfur trioxide in the atmosphere is very low.
Properties of SO2
SO2 is a colorless heavy gas with a choking smell. It can be easily liquefied by cooling in a freezing mixture. It is highly soluble in water. The aqueous solution of sulfur dioxide contains unstable sulfurous acid.
Some common properties of sulfur dioxide are given below in the table,
| Properties | |
| IUPAC name | sulfur dioxide |
| Chemical formula | SO2 |
| Molar mass | 64.066 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Odor | choking smell like a struck match |
| Density | 2.6288 kg m−3 |
| Melting point | −72 °C |
| Boiling point | −10 °C |
| Critical temperature | 157.5 °C |
| Solubility in water | 94 g/L |
| Dipole moment | 1.62 D |
| Acidity (pKa) 1.81 | 1.81 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 12.19 |
Sulfur dioxide acts as an oxidizing or reducing agent because sulfur atoms in SO2 can be easily oxidized to the +6 state and reduced to the 0 oxidation state.
Oxidizing properties: It reacts with hydrogen sulfide to produce sulfur and water. Here, SO2 acts as an oxidizing agent.
2 H2S + SO2 → 2 H2O + 3S
Reducing properties: It reacts with chlorine to form sulfuryl chloride. Here, SO2 acts as a reducing agent.
Cl2 + SO2 → SO2Cl2
It acts as a Lewis acid or base when reacts with CH3CN, Me3N, SbF5, or BF3. The autoionization of liquid sulphur dioxide shows that the thionyl ion (SO+2) should be acid and the sulfite ion (SO3−2) should be a base.
2 SO2 → SO+2 + SO3−2
How to Detect Sulfur Dioxide Gas?
We can use potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) paper to detect the presence of sulfur dioxide gas. In the presence of SO2, potassium dichromate paper changes its colour from orange to green.
K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 + 3SO2 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + H2O
Production Process
Commonly, it is prepared by heating the element sulfur in the air. It is also produced by roasting sulfide minerals or burning sulfur containing fuels such as oil and coal which is a major pollutant in our environment.
S + O2 → SO2, ΔH = −297 kJ/mol
The roasting of sulfide ores such as iron pyrites (FeS2), copper pyrites (CuS), copper glance (Cu2S), zinc blended (ZnS), and galena (PbS) release SO2 gas into our environment.
4 FeS2 + 11 O2 → 2 Fe2O3 + 8 SO2
2 ZnS + 3 O2 → 2 ZnO + 2 SO2
HgS + O2 → Hg + SO2
4 FeS + 7 O2 → 2 Fe2O3 + 4 SO2
It is obtained as a by-product in the manufacture of cement by heating gypsum with clay, sand, and coke in a rotary kiln at 1200°C.
Uses of Sulfur Dioxide
- It is a toxic gas that causes various health problems but we use sulfur dioxide for the production of various industrial compounds such as sulfuric acid, sulfur trioxide, and sulfites. Sulfuric acid obtained from SO2 uses for the production of steel, fertilizers, medicines, fuels, batteries, paper, plastics, etc.
- It is used as a disinfectant or bleaching agent for removing excess chlorine.
- Liquid sulphur dioxide uses as a refrigerant for food preservation.
- It is used as a reducing agent or solvent for different types of chemical transformations in the laboratory.
- Due to its toxic nature, it is widely used for the production of pest control products.
Effects of Sulfur Dioxide on Environment
Most power plants and industrial units produce flue gases that contain SO2 and NO2. Both gases pollute our environment. The effects of sulphur dioxide on the environment or human health, animals, and plants are given below,
- It produces sulfur trioxide on photolytic and catalytic oxidation. Therefore, SO3 produced by this process reacts with rainy water or moisture to give sulfuric acid. It comes down to the atmosphere in the form of sulfuric acid rain or snow.
- It can affect the respiratory system of animals and human beings. In human health, sulfur dioxide may effects our lungs and cause coughing, wheezing, phlegm, and asthma attacks.
- It affects the production of chlorophyll in plants, Therefore, the green colour of plants is decolorized,
- Due to the corrosive nature of SO2 and sulfuric acid rain decolorized building materials such as limestone, marble, roof slate, and mortar.
- Paints, fabrics, leather, and paper fade their colour in the presence of sulfur dioxide.