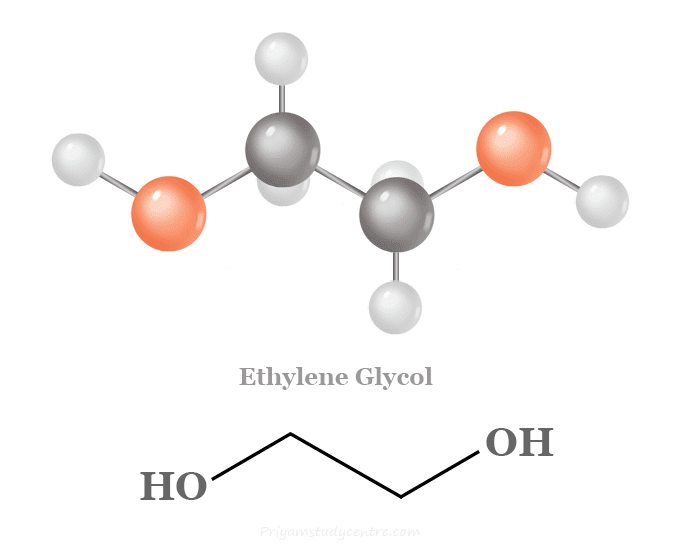
Chemical Formula for Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol or ethane-1,2-diol is a colourless viscous liquid with the chemical formula (CH2OH)2. It is missable in all proportions with water and alcohol but insoluble in ether. The prefix glyc in ethylene glycol indicates that the organic compound has a sweet taste. It is widely used as a solvent and antifreezing agent. Due to its low specific heat capacity, ethylene glycol is mixed with water to decrease the boiling point of water. Therefore, such a mixture helps in cooling many antifreezing systems. In chemistry, ethylene glycol has a high viscosity, boiling point, and solubility due to the hydrogen bonding of all hydroxyl groups. Industrially, ethylene glycol can be produced by treating ethylene oxide with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Ethylene Glycol Properties
It is a highly poisonous dihydric alcohol containing two hydroxyl groups. The chemical properties and reactions of ethylene glycol are similar to those of primary alcohol.
One hydroxyl group is always completely attacked before the other reacts.
| Ethylene Glycol | |
| IUPAC name | Ethane-1,2-diol |
| Other names | 1,2-Ethanediol Ethylene alcohol Hypodicarbonous acid Monoethylene glycol 1,2-Dihydroxyethane |
| Chemical formula | C2H6O2 |
| CAS Number | 107-21-1 |
| Molar mass | 62.068 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless viscous liquid |
| Density | 1.1132 g/cm3 |
| Solubility | Miscible in water and soluble in most organic solvents |
| Melting point | −12.9 °C |
| Boiling point | 197.3 °C |
| Viscosity | 1.61×10−2 Pa-s |
Production Process
It is the simplest glycol that may be prepared by various synthesis methods given below the picture,
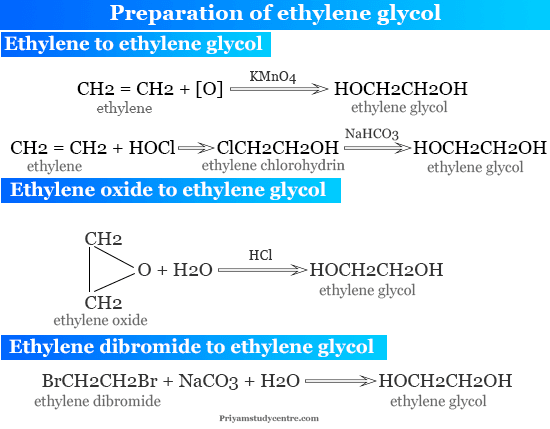
Ethylene Oxide to Ethylene Glycol
Industrially, it is produced by treating ethylene oxide with dilute hydrochloric acid. In the presence of concentrated halogen acids, ethane-1,2-diol is converted into ethylene halohydrins.
Ethylene to Ethylene Glycol
- It is prepared by passing ethylene into a cold diluted alkaline permanganate solution.
- Ethylene is also converted into chlorohydrin when passing hypochlorous acid.
- Hydrolyzing ethylene chlorohydrin by boiling with aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate produced ethane-1,2-diol.
- It can also be prepared from ethylene dibromide by boiling with aqueous sodium carbonate.
Reactions of Ethylene Glycol
In ethane-1,2-diol, one hydroxyl group readily reacts before another. Sodium at 50 °C forms the monosodium salt. The di-sodium salt is obtained only when the temperature is raised to 160 °C.
It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form chlorohydrin at 160 °C. Whereas at 200 °C, ethane-1,2-diol produced ethylene dichloride.
Some important chemical reactions are given below the picture,
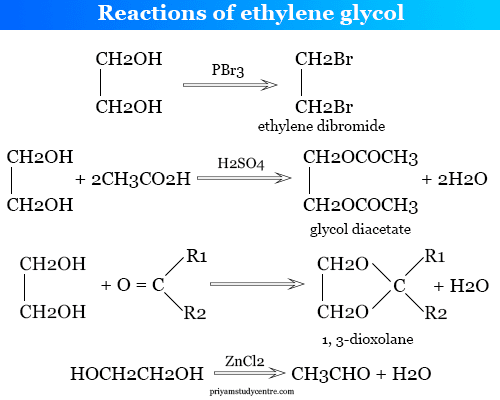
Ethylene dihalide is obtained when ethane-1,2-diol is treated with phosphorus trichloride or phosphorus tribromide.
Di-ester is obtained when ethane-1,2-diol is treated with organic acids or inorganic oxo-acids. The obtained product depends upon the relative amounts of glycol and acid.
For example, glycol diacetate is obtained when glycol is heated with acetic acid in the presence of a small amount of sulfuric acid.
When it is condensed with aldehydes or ketones in the presence of p-toluene sulphonic acid, forms respective cyclic acetals or cyclic ketals. It is converted into aldehyde when heated with dehydrating agents like zinc chloride (ZnCl2).
Oxidation Reactions
It is oxidized with nitric acid to obtain glycolic acid and oxalic acid. Oxidation of glycols with acid, alkaline or neutral permanganate, acid dichromate, chromic acid or lead tetra-acetate, or periodic acid gives aldehyde, acids, or ketones by fusion of C-C chemical bond.
Oxidation of cis-glycol occurs more rapidly than the corresponding trans-glycol due to the formation of a cyclic intermediate. These oxidations are also influenced by strict hindrances. It is oxidized much faster than pinacol by periodic acid.
Uses of Ethylene Glycol
- It is used as a coolant and antifreezing agent in industry and cars. It helps to freeze our car in the winter season and coolant to reduce overheating in the summer season.
- For the production of polyester, we used a large quantity of ethylene glycol as a raw material. This polyester is used for making different types of clothes, carpets, pillows, fiberglass, etc.
- In a geothermal pump, it is used as a fluid that transports heat through it.
- Due to its low specific heat capacity, it is mixed with water to decrease the boiling point of water. The mixture is used as a coolant solution in many antifreezing systems.
- When ethane-1,2-diol is heated with a dehydrating agent like phosphoric acid, it produces polyethylene glycols. These condensed polymers contain both alcohol and ether functional groups. They are soluble in water and used as solvents.
- Polyethylene glycols are widely used as solvents for gums, resins, cellulose esters, etc.
- A small amount of ethylene glycol is used for the manufacture of capacitors and 1,4-dioxane.