Starch
Healthy Starch Foods
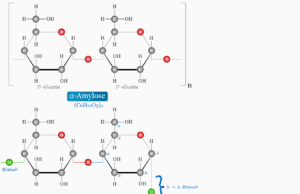
Starch is a soft, white powder and tasteless carbohydrate reserved in plants. Various types of starches found in plants are the most...
Recombinant DNA Technology
What is Recombinant DNA Technology?
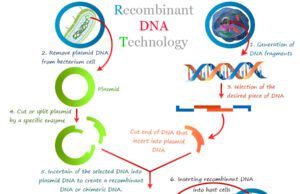
Recombinant DNA technology (rDNA technology) is a process that is used for producing artificial DNA through the combination of different...
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Synthesis
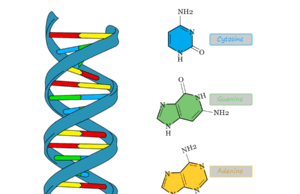
Nucleotides that contain a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group in their structure are the basic building blocks of nucleic...
Nucleic Acids
What are Nucleic Acids?
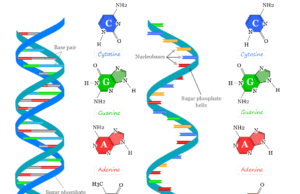
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules that carry genetic information and participate in protein synthesis. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Definition for Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the polymer of deoxyribonucleotides which is found in most animals, plants, and some viruses. Deoxyribonucleic acid carries...
Collagen Protein
Benefit of Collagen Protein
Collagen is the most vital protein in mammals which forms approximately one-third of the total body protein. Collagen is a type...
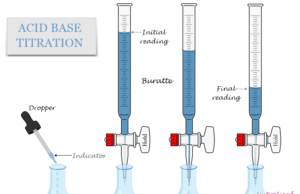
Acid Base Titration
What is Acid Base Titration?
Acid base titration in chemistry is an experimental procedure used to calculate the unknown concentration of an acid or base...
Carbohydrates
Metabolism of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates also called saccharides or carbs are the most abundant organic compounds in nature that provide energy for our bodies through metabolism....
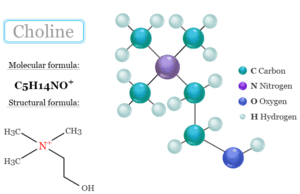
Choline
Choline Supplement Benefits
Choline is a quaternary ammonium cation that is naturally available in many foods and dietary supplements. The benefits of a dietary choline...
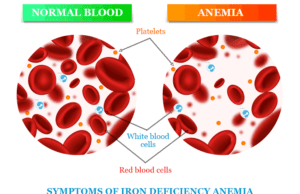
Iron Deficiency Anemia
What is Iron Deficiency Anemia?
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of nutritional disorder that occurs when your body doesn’t have an adequate...