Ion Exchange Resin Material
Ion exchange resin or ion exchange resin material is the types of resins molecules or polymers that are capable of exchanging cation and anion from a solution. Usually, ion exchange resins are examples of white or yellow fabricated organic compounds or polymers that are insoluble in common solvents. Ion exchange resins are widely used for the purification or separation of protein or amino acids, water softening, and separation of metal ions. The discovery of ion exchange resin material is accidental. England agricultural chemists, Thompson, and Way notice the ion exchange process of soil samples by adding fertilizer like ammonium sulfate. The exchange of sodium and calcium in soil indicates the phenomenon of ion exchange.
The electrically charged groups in ion exchange resins are commonly sulfonic or carboxylic acid salts or quaternary ammonium salts. In industrial and domestic applications, ion exchange resins are used for the removal of calcium, magnesium, iron, and manganese salts from water. It is also used for the purification of sugar in the sugar industry. For concentrating valuable metals such as gold, silver, and uranium from mineral ores, we also used an ion exchange process.
Cation Anion Exchange Resin
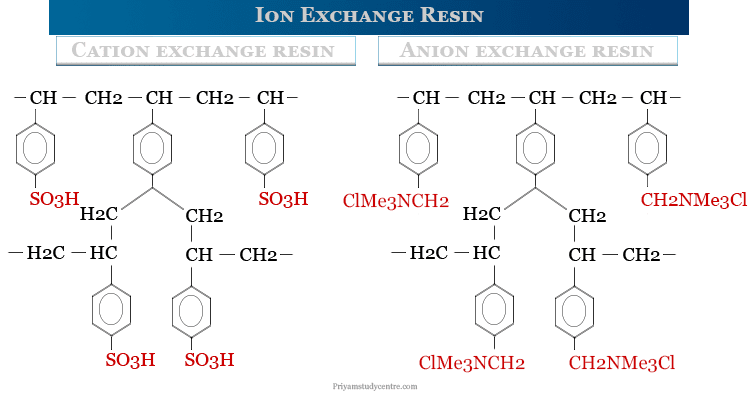
All the resins have reactive sulfonic (SO3H), quaternary amine or tertiary amine, carboxyl (-COOH), and hydroxyl (-OH) groups in exchange sites. The labile ion is a hydrogen ion in cation exchangers and a suitable anion in anion exchange resins. Resins with sulfonic groups or quaternary amine groups are highly ionized, insoluble, and reactive.
The resins commonly consist of a styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer, although other compositions, such as methacrylic acid–divinylbenzene and phenol-formaldehyde polymers. Depending upon the type of labile ions exchanged by the resins, they have been classified into two types,
- Cation exchange resin
- Anion exchange resin
Cation Exchange Resin
Cation exchange resins are anionic synthetic polymers that contain carboxyl or sulfate groups with hydrogen, potassium, and sodium as exchanger ions. Therefore, a common synthetic cation exchange resin material is obtained by polymerization of styrene and a small amount of divinylbenzene followed by sulfonation. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate are examples of cation exchange resin.
Normally, the H+ is the exchangeable cation in this type of resin. When we treat it with Na+ ions, the H+ ion is replaced by Na+ ions.
Cation exchanger → (Resin anion−)H+
(Resin anion−)H+ + Na+ → (Resin anion−)Na+ + H+
For the water softening, we used natural or artificial zeolites as synthetic cation exchange resin because they are regenerated many more times.
Strong Acid Cation Exchange Resin
Strong acid ion exchange resin material or polymer is a cation exchanger whose main exchange group is a sulfonic acid group (-SO3H). It has excellent physical and chemical stability. They are regenerated by either a sodium (Na+) salt solution for softening or an acid (H+) for demineralization applications.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate are examples of strongly acidic cation exchange resin. This type of resin can be used for softening and deionization of water, purification of water, wastewater treatment, separation of rare earth metals, separation of biomolecules such as peptides and amino acids, separation of inorganic ions, etc.
Weak Acid Cation Exchange Resin
Usually, weakly acidic cation exchange resin material contains the carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Wofatote C and Amberlite 45 C belong to this class of resin. Such types of resins are used for demineralization and dealkalization of water and regenerated by sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid.
They are a good choice for the removal of hardness due to alkalinity caused by divalent cations ions (Ca2+ and Mg2+). They have relatively high oxidation resistance and mechanical durability. Therefore, they are used in streams containing oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide and chlorine.
Anion Exchange Resins
An anion exchange resin material is a polymer having amines or quaternary ammonium groups in a polymeric network. In this resin, the chloride ion is the exchangeable ion while the rest is the non-exchangeable bulky polymeric cation.
Anion exchanger → (Resin cation+)Cl−
(Resin cation+)Cl− + OH− → (Resin cation+)OH− + Cl−
A significant application of both cation and anion exchange resin is softening or deionization of water. Depending upon the labile groups, ion exchange resins are broadly classified into four groups.
Strong Base Anion Exchange Resin
Strongly basic anion exchange resin is a polymer that containing quaternary or tertiary amine groups in their exchange site. In such type of a resin, quaternary ammonium groups are incorporated into the styrene frame.
A strong base anion exchange resin shows excellent physical and chemical stability. It also exchanges the different anions under a wide range of pH. Dowex IX8, Dowex 21K, and Amberlite IRA 400 are examples of strongly basic anion exchange resins.
Strong base anion exchange resins are strongly alkaline in nature and they can dissociate like sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide (strong bases). Therefore, such types of ion exchangers are used for sugar and antibiotics purification, removal of silica and organic substances, industrial demineralization, metal extraction, pure water production, etc.
Weak Base Anion Exchange Resin
Weakly basic anion exchange resin material containing an OH group as a labile group. They are typically regenerated with sodium hydroxide, ammonia, or sodium carbonate. Dowex 3 and Amberlite IR 4B are examples of weak base anion exchange resin.
Weak base ion exchange resins are used mainly for acid adsorption by removing chloride, sulfate, nitrate, and other anions. They are not effective for the removal of weak acidic compounds such as silica (SiO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Application of Ion Exchange Resin
The idea of ion exchange resin first comes from agricultural investigation. This time, the process is used widely for the analysis of micronutrients in soils.
- Presently, ion exchange resin is used mainly in water softening, purification, and separation of metal.
- In chromatography, ion exchange resin or polymer is also used in different fields of science such as medicine, agriculture, pharmaceutical, mining, and petrochemical industries.
- Ion exchange resin is used for the purification of sugar and the analysis and separation of amino acids.
- In the petrochemical industry, ion exchange resin is also used for the determination of sulfur compounds present in petroleum products.
- In mining, for analysis of inorganic anions of heavy metals, we used ion exchange resin or chromatography.
Ion Exchange Resin in Water Treatment
Ion exchange is a chemical process for removing unwanted dissolved ions in water and hard water by exchanging specific ions for ions that have a similar charge. A cation or anion exchange resin is used widely in the treatment of water such as softening and purification of water molecules.
Water Softening
A significant application of ion exchange resin is softening or deionization of water. Temporary hardness caused by calcium or magnesium bicarbonate can be easily removed by boiling or the addition of lime water.
Commonly, we used the ion exchange method for softening hard water by the removal of sulfates and chlorides of calcium or magnesium. For example, we used the hydrogen form of cation exchange resin and the hydroxyl form of anion exchange resin for the deionization of water. The principal merit of deionization is that it is not time-consuming like distillation.
Water Purification
Water purification is the process by which undesired chemical compounds, organic and inorganic materials, and biological contaminants are removed from drinking water.
Ion exchange resin is a wide variety of organic compounds synthetically polymerized and containing positively or negatively charged material. Therefore, they are used in water treatment to remove harmful contaminants and replace them with beneficial ions. Therefore, ion exchange resin is used for removing poisonous metal ions such as copper, lead, and cadmium from water. They can be replaced by sodium or potassium ions.
For the purification of domestic water, we also used activated charcoal mixed with resin. It can remove chloride ions and organic impurities from water.
Ion Exchange Resin in Metal Separation
We used different types of ion exchange resin material or polymer for the separation of transition metals and rare earth metals. It is also used for the separation of radioelement or actinides.
For example, the plutonium-uranium extraction process is used for the separation of plutonium and uranium. These two radioactive metals are widely used as fuel in nuclear power reactors.
Some examples of ion exchange resins and their applications are given below in the table,
| Resin | Application |
| Dowex 50W X12 | Used for separation of cobalt (Co) |
| Dowex 50W X8 | Used for separation of titanium (Ti), scandium (Sc), and manganese (Mn) |
| Dowex 21K | Used for separation of indium (In), thallium (Th), and Gallium (Ga) |
The cation exchange chromatographic method is used for the separation of magnesium, calcium, strontium, and barium by Dowex 50 with ammonium lactate buffer at pH scale 7.
The elements with similar chemical properties like zirconium, hafnium, niobium, and tantalum can be also separated by ion exchange resin.
Pharmaceutical Industry
For the purification and manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, we used wide ion exchange resin material or polymer. Resins like sodium polystyrene sulfonate, colestipol, and cholestyramine are used widely in pharmaceutical industries for the purification and separation of drug samples.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ion Exchange Resin?
An ion exchange resin or ion exchange polymer is a material that dissolves and removes ions from solution. Therefore, they commnly replaces other ions of the same or similar electrical charge. Usually, they are white or yellow fabricated organic compounds or polymers that are insoluble in common solvents.
Ion exchange resins are widely used for the purification or separation of protein or amino acids, softening and purification of water, and separation of metal.
How Ion Exchange Resin Works?
Ion exchange resin works by reversible chemical reaction where dissolved ions are removed from the solution and replaced with other ions of the same or similar electrical charge. Therefore, it is a medium that exchanges positively and negatively charged ions present in the solution.
Polymers containing acid groups are cation exchangers because they exchange positively charged ions such as hydrogen ions and metal ions. Polymers containing ammonium groups are anion exchangers because they exchange negatively charged ions such as hydroxide ions or halide ions.
What is Ion Exchange Resin Used For?
In industrial and domestic applications, ion exchange resins are used for the removal of calcium, magnesium, iron, and manganese salts from water. It is also used for the purification of sugar in the sugar industry. For concentrating valuable elements such as gold, silver, and uranium from mineral ores, we also used this technology.
In chemical analysis, ion exchange chromatography is used for the separation of ionic substances in a chemical solution. Some ion exchange resins are also used as effective catalysts, esterification, and hydrolysis reactions.
What is Cation Exchange Resin?
Cation exchange resins are anionic synthetic polymers that contain carboxyl or sulfate groups with hydrogen, potassium, and sodium as exchanger ions.
A common synthetic cation exchange resin material or polymer is obtained by polymerization of styrene and a small amount of divinylbenzene followed by sulfonation. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate are examples of cation exchange resin polymer.