Size Exclusion Chromatography
Size Exclusion Chromatography Instrumentation
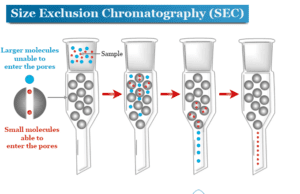
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic separation procedure that separates analyte molecules according to their size or geometry and some...
Benzene
What is Benzene?
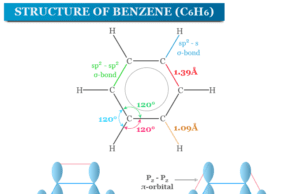
Benzene is a class of organic compounds or aromatic hydrocarbons having the chemical formula C6H6. It is a flammable and colorless or slightly...
Acetone (CH3COCH3)
Acetone Chemistry
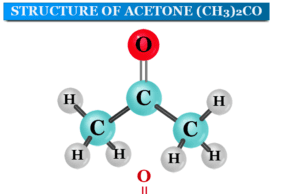
Acetone, 2-propanone, or dimethyl ketone in chemistry is a colourless and highly flammable organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COCH3. Commercially acetone can...
Gel Permeation Chromatography
Gel Permeation Chromatography Analysis
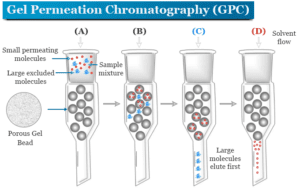
Gel permeation chromatography (GPC) or gel filtration chromatography is an example of size exclusion chromatography (SEC) that analysis substances largely according...
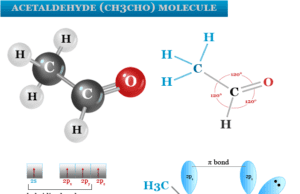
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde Molecular Formula
Acetaldehyde (also called ethanal) is a colurless, pungent-smelling organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CHO or C2H4O. It is prepared industrially by...
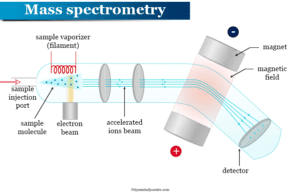
Mass Spectrometry
Mass Spectrometry Principle
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical principle that uses for the analysis of charged gas molecules (ions) according to their weight or...
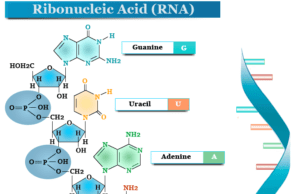
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymer of ribonucleotides that help in protein synthesis and the production of new cells in our body....
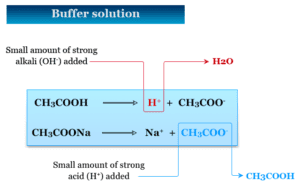
Buffer
Buffer Solution and pH
Buffer solution simply called buffer in analytical chemistry or biology is a solution whose pH remains virtually unchanged upon the addition...
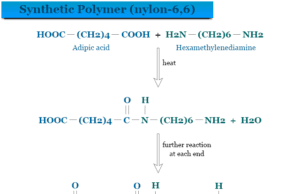
Polymers
Polymers in Chemistry
Polymers in chemistry are big molecules made by the repeated joining of simpler molecules by covalent bonding. They are macromolecules and complex...
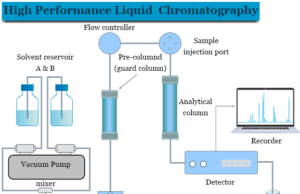
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
High Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLC
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) principle is a modification of liquid chromatography used in analytical chemistry for the separation and...