Properties
Properties of Matter
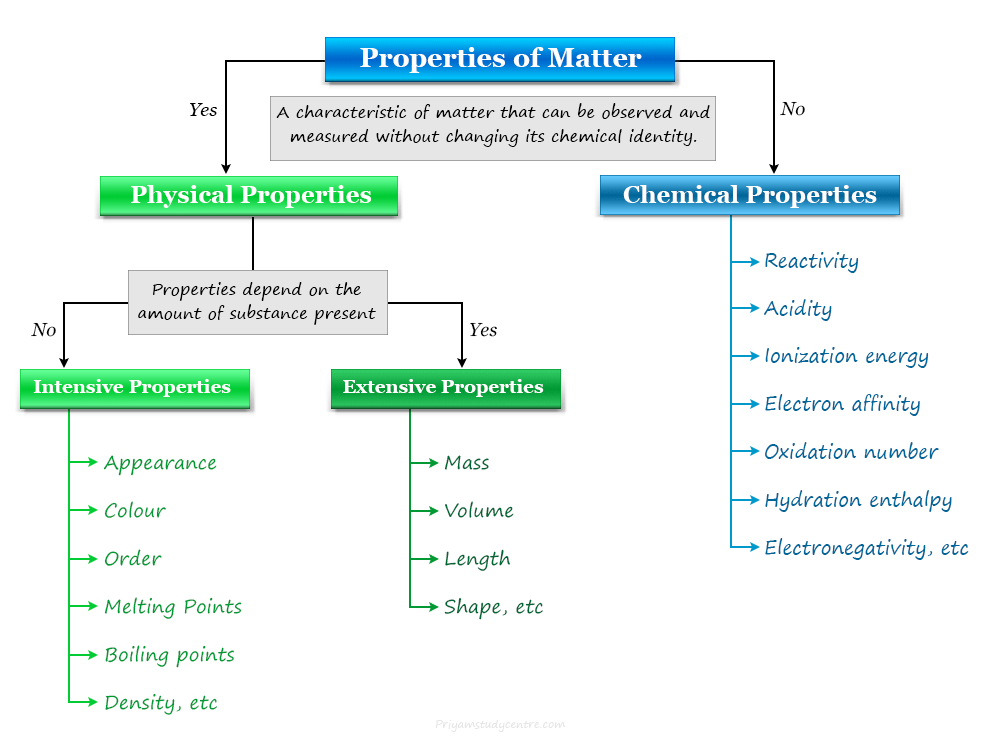
Properties of matter or physical and chemical properties in chemistry or chemical science are considered a key to understanding chemical elements (atoms, molecules), and substances present in our earth’s environment. In our daily life, we see a variety of changes which may be physical and chemical. Physical and chemical properties are the characteristics of a material that enable us to differentiate one matter or substance from another. The common properties of substances may include,
- Density
- Colour
- Mass
- Volume
- Length
- Malleability
- Melting point
- Hardness
- Odour
- Temperature
- Reactivity
- Acidity
- Ionization energy
- Electron affinity
- Hydration enthalpy
- Electronegativity
Physical Properties Examples
A physical property is a characteristic of matter that can be observed and measured without changing its chemical identity. Therefore, appearance, color, order, melting and boiling points, atomic weight, molecular weight, density, and electrical conductance are examples of physical properties of matter.
Chemical Properties Examples
A chemical property is a characteristic of matter that can be observed and measured when a substance undergoes a chemical change. Reactivity, acidity, ionization energy, electron affinity, oxidation number, hydration enthalpy, electronegativity, and chemical bonding are common examples of chemical properties of matter.
Physical and Chemical Changes
In our daily life, we come across a variety of changes which may be physical and chemical. A physical change can be easily reversed but a chemical change cannot be reversed easily. Evaporation, melting of wax, and freezing of water are examples of physical changes. However, the conversion of milk to curd, rusting or iron, and the digestation of food items are examples of chemical changes.
- An observable physical change is a characteristic of materials that we can describe using our five senses.
- We can also use our senses to observe colour, texture, hardness, and flexibility of a material.
- All chemical changes are accompanied by chemical reactions and are represented with the help of chemical equations. Therefore, we use various types of chemical equations to represent chemical changes.
Reactivity is an important property of matter in learning chemistry that generally derives the tendency of matter to combine chemically with other substances. Therefore, certain substances are highly reactive while some are inactive. In this part of learning chemistry, we study various physical and chemical properties and changes of matter.