Ozone Layer Depletion
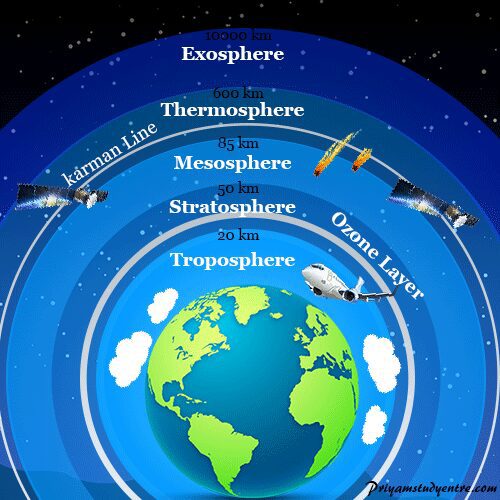
Ozone layer or ozonosphere is a region found in the upper atmosphere that contains relatively high concentrations of ozone gas (O3) to protect the earth’s environment and its biosphere from harmful ultraviolet electromagnetic radiation. The region lies in the stratosphere or is between 20 km to 60 km above the earth’s surface. The thickest layer of ozone lies at a height of 23 km from the distance of the earth’s surface. A steady concentration is maintained in the ozone layer by the destruction and generation of ozone molecules. Lowering the steady concentration or thinning of ozone molecules in the ozone layer is called ozone layer depletion. It causes various health problems in human beings and commonly effects our skin, eyes, DNA molecules, and immune systems.
Unfortunately, the thickness of the ozone layer has been decreased by several human activities. Due to environmental pollution, ozone layer depletion started in the 1980s. It is mainly due to the large use of synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). It can used as a coolant in refrigerators and in fire extinguishers.
Ozone Layer Formation
About 90% of the ozone molecules of the earth’s atmosphere are present in the stratosphere. When UV light from the Sun strikes the earth’s atmosphere, ozone in the stratosphere is continuously created and destroyed by solar radiation.
In the upper atmosphere, ozone gas is formed by solar uv radiation of very high energy. The ozone molecules absorb moderately high energy uv radiation with a very long wavelength to form oxygen atoms.
O2 + hν (UV radiation) → 2O
Such oxygen atoms are highly reactive and combine with molecular oxygen in the stratosphere to form ozone molecules. Therefore, ozone is formed and distributed in the stratosphere.
O2 + O → O3
In the stratosphere, an equilibrium is established between the destruction and generation of the ozone molecule. Therefore a steady concentration is always maintained in the ozone layer of the upper atmosphere.
If the ultraviolet electromagnetic radiations reach the earth, it will cause skin cancer and destroy different types of organic biomolecules necessary for life.
Importance of Ozone Layer
The ozone layer is important for us because it can shield or protect the surface of our earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation emitted from the Sun. If the protective ozone layer in the atmosphere completely disappears, then all the harmful ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun would reach the earth’s environment. It can damage the DNA of cells, cause skin cancer in human beings, damage eyes, decrease crop yields, and disturb the global ecosystem.
The ozone layer is important for us because depletion of such stratospheric layer can cause various health problems in human beings and other animals along with plants. Therefore, such depletion is a serious environmental threat that is happening due to several human activities.
In 1980, scientists showed that there is a hole in the O3 layer. This hole was detected over the region of Antarctica. Due to the presence of ozone holes in the stratosphere, the concentration of ozone gas is reduced day by day. Unfortunately, several human activities permanently damage the ozone balance in the upper atmosphere.
Ozone Depletion
Ozone layer depletion is a serious environmental threat that is caused due to several human activities. It happens commonly due to the high use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) in refrigerators and air-conditioners, and the emission of nitrous oxide during combustion of fossil fuels.
Nitrous dioxide (N2O) from supersonic aircraft, industrial chemical catalysts, and chlorocarbons (CFCs) is the main source of ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere or stratosphere. Photochemically nitrous oxide (N2O) and chlorine atoms are continuously regenerated in the ozone depletion process causing permanent damage in the ozone balance.
Ozone Depletion by CFC
Chlorofluorocarbons are the stable compounds of methane like freon-1 (CFCl3) and freon-12 (CF2Cl2). These are emitted from different types of organic spray aerosol, refrigerants, firefighting reagents, and solvents for cleaning electric components. It has been observed that one molecule of CFC can destroy about one lakh ozone molecules in the stratosphere.
The extreme stability of CFCs enables them to be active for years in the atmosphere. When they enter the stratosphere, they absorb ultraviolet radiation and get broken down into free atomic chlorine in a cycle process.
CF3Cl → Cl. (free radical) + CF3
Such atomic chlorine continuously causes to depletion of ozone into oxygen in a cycle that damages the ozone layer. One chlorine radical can destroy a huge number of ozone molecules by following chain reactions.
Cl. + O3 → ClO. + O2
ClO. + O → Cl. + O2
Nitrous Oxide and Ozone Depletion
The oxides of nitrogen present in the atmosphere decompose ozone gas into oxygen gas and continuously regenerate. The presence of nitrous oxide (N2O) destroyed the ozone layer found in the stratosphere.
In recent years, the presence of nitrous oxide may constantly increase due to the large-scale combustion of fossil fuels and increasing use of nitrogenous fertilizer in soil. It is also emitted by supersonic transport aircraft. When they enter the stratosphere, nitrous oxide photochemical convert to more reactive nitric oxide.
N2O + E → NO + N
Such nitric oxide continuously causes to depletion of ozone into oxygen in a cycle that damages the ozone layer. Present evidence suggests that the ClOx cycle can be three times more active to the destroyed ozone molecules than the NOx cycle. Nitric oxide can destroy ozone molecules by following chain reactions.
NO + O3 → NO2 + O2
O3 + hν → O2 + O
NO2 + O → NO + O2
Ozone hole caused by nuclear testing
Different types of nuclear reactions for generating nuclear power or weapons in the world generate high temperatures in the earth’s environment. Therefore, it accelerates the production of nitric oxide in the stratosphere. At high temperatures, atmospheric nitrogen oxidizes to form nitrogen oxides which generally destroy the ozone layer found in the upper atmosphere.
Effects of Ozone Layer Depletion
The ozone layer is important for us because it shields the surface of the earth from harmful energetic ultraviolet (UV) radiations coming from the Sun. Such radiations highly affect living organisms by breaking down their biomolecules.
- They can damage the DNA of living organisms.
- Direct exposure to UV radiation damages the connective tissue of human beings. Therefore, it leads to an increase in the probability of skin cancer.
- Direct UV radiation can damage the lens of our eyes.
- Leaves of plants are decolored by direct UV radiations. Therefore, photosynthesis can be affected due to ozone depletion.
- Excessive UV radiation can inhibit the growth of almost all plants that we use for the production of food. Therefore, agricultural productivity or crop yield can be reduced.
- Marine and aquatic life will be destroyed because plankton and small aquatic animals are highly sensitive to UV radiation.
Protection of Ozone Layer
Scientists are worried about the effects of the gradual destruction or depletion of the ozone layer by the oxides of nitrogen and chlorofluorocarbons (CFC).
- Air pollution, water pollution, or acid rain can increses the concentration of nitrous oxide in the upper atmosphere. It can be controlled by reducing these gases to convert ammonia by the reaction with hydrogen in the presence of finely divided platinum metal before they enter the atmosphere.
- To save ozone layer destruction or depletion by chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), the use of such types of substances would be banned. Therefore, we need to discover some new types of substances in aerosol spray or refrigerants that do not react with the O3 layer of the upper atmosphere.
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) succeeded in forming an agreement to freeze chlorofluorocarbons (CFs) production at 1986 levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ozone Layer?
The layer of the atmosphere in which most of the atmospheric ozone is concentrated is called the ozone layer. It is found mostly in the stratosphere and protects the surface of the earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiations coming from the Sun.
How Ozone Layer is Formed?
Ozone is a deadly poisonous gas formed by three oxygen molecules with the chemical formula O3. Ozone at the higher level of the atmosphere is the product of the UV radiation coming from the Sun. The high-energy UV radiations split apart some molecular oxygen in free oxygen atoms.
O2 + hν (UV radiation) → 2O
Such atoms are highly reactive and combine with molecular oxygen in the upper level of the atmosphere to form ozone molecules.
O2 + O → O3
Therefore, the ozone layer is formed by concentrating ozone molecules in a region of the atmosphere.
What is the Importance of Ozone Layer?
The ozone layer is important for us because it shields the surface of the earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiations coming from the Sun. Such radiations are highly damaging to the living organisms of our earth. They damage the DNA of cells, cause skin cancer in human beings, damage eyes, decrease crop yields, and disturb the global environment.
What is Ozone Depletion?
Ozone layer depletion is the thinning of the ozone layer that is found in the stratosphere and protects the surface of the earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiations coming from the Sun.