Argon Gas
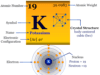
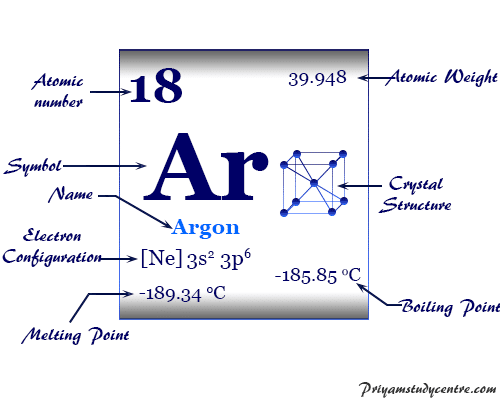
Argon is a chemical element or inert or noble gas of Group 18 of the periodic table with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is the most abundant noble gas which is used widely in metallurgy and other industry due to its cheap price. Due to the filled valence shell orbital, the oxidation number or state of argon is zero and the ionization energy is very high. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, monoatomic gas that occurs to the extent of 93 ppm by volume in dry air and 4 × 10−2 ppm by weight in igneous rocks. The name of the lighter gas, argon derived from the Greek letter Argos meaning idle. In solid-state, it forms a face-centered cubic crystal lattice. The most abundant inert gas, Ar has a valence shell electron configuration [Ne] 3s2 3p6, and a heat capacity ratio (Cp/Cv) close to 1.66.
Argon on the Periodic Table
Argon is placed in the p-block of the periodic table with other noble gases like helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
Discovery of Argon
It was discovered nearly one hundred years after the English natural philosopher and scientist Henry Candavis’s observation. He observed that a sample of air always leaves a small residue of about 1/120 part of inert gases after repeated sparking with air oxygen.
British scientist Lord Rayleigh observed that nitrogen isolated from atmospheric gases was about 0.5 percent heavier than nitrogen prepared chemically. He identified a new element (argon = idle) in the residue left after heating atmospheric nitrogen with magnesium.
Sir William Ramsay suggested that helium and argon belong to the new group (group zero) in the periodic table.
When the residual gas was subjected to spectroscopic analysis, a new characteristic electromagnetic spectrum was obtained. British scientist Lord Rayleigh was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for the investigation of gas density and the discovery of argon.
Sir William Ramsay gets a Nobel Prize in chemistry for the discovery of inert gas in the air and its place on the periodic table.
Isotopes
It is the most abundant noble gas in the air with 93 ppm in dry air. However, in igneous rocks, it is present to the extent of 4 × 10−2 by weight.
Natural argon is a mixture of isotopes like 40Ar (99.6 percent), 36Ar (0.063 percent), and 36Ar (0.337 percent). 40Ar prepared by nuclear reaction or electron capture reaction of 40K.
Properties of Argon
| Argon | |||
| Symbol | Ar | ||
| Discovery | Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay in 1894 | ||
| Name derived from | The Greek word argos means idle | ||
| Common isotope | 18Ar40 | ||
| Oxidation states | 0 | ||
| CAS number | 7440-37-1 | ||
| Periodic properties | |||
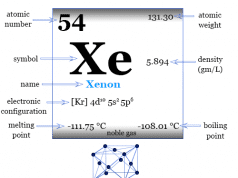
| Atomic number | 18 | ||
| Relative atomic mass | 39.948 | ||
| Electron per cell | 2, 8, 8 | ||
| Electronic Configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p6 | ||
| Block | p-block | ||
| Group | 18 | ||
| Period | 3 | ||
| Physical properties | |||
| State at 20 °C | Gas | ||
| Melting point | −189.34 °C, −308.81 °F, 83.81 K | ||
| Boiling point | −185.85°C, −302.53°F, 87.30 K | ||
| Molar heat capacity | 20.85 J mol−1 K−1 | ||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) | ||
| Density | 0.001633 g/cm3 | ||
| Critical temperature | 150.69 K | ||
| Atomic properties | |||
| Atomic radius (non-bonded) | 1.88 Å | ||
| Covalent radius | 1.01 Å | ||
| Electronegativity | unknown | ||
| Electron affinity | unknown | ||
| Ionization energy (kJ/mol) | 1st | 2nd | 3rd |
| 1520.57 | 2665.86 | 3930.81 | |
Facts About Argon
The chemistry of argon or other noble gases is different from other elements of the periodic table. All of them contain a filled valence shell configuration.
The promotion of electrons to the next available orbitals needs very large energy. The facts suggest that the covalent bonding in Ar is highly unfavorable.
The ionic compounds with the most electronegative fluorine are unlikely due to high positive entropy and free energy for the formation of such a chemical bonding. Therefore, no true chemical compounds of Ar are known.
Chemical Compounds
The only clathrates or cage compounds of argon formed with para quinol and water. The noble gas molecule is trapped within the cavities formed by quinol crystals through a hydrogen bonding network.
Water and zeolite also produce such types of clathrates compounds with Ar molecules. These compounds are not called true chemical compounds. Since weak Van der Waals forces operate between the gas molecule and quinol or water.
What is Argon Used for?

- Argon is the most abundant and cheapest noble gas mostly obtained on a large scale by fractional distillation of air. It is used to protect metal surfaces from oxidation during the welding of steel, aluminum, and magnesium.
- It is widely used in electrical equipment like filament bulbs and radio tubes.
- We used argon gas in different types of industrial production processes, scientific research, and medicine.
- Argon atmosphere is used in some high-temperature industrial processes, for the production of metals like titanium, vanadium, zirconium, uranium, etc.
- The non-toxic argon is also used for packing food materials to extend the food life.
- We also used it for the preservation and packaging of chemicals like varnish, polyurethane, and paint.
- It is used for thermal insulation in energy-efficient windows.
- The blue argon gas laser is generally used in medicine to destroy the tumors of the human body.