Electrode
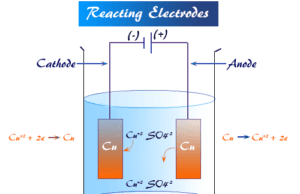
What is Electrode in Chemistry?
Electrode is the type of electronic conductor, usually metals partly immersed in an electrolytic solution, and imparts or receives electrons...
Electrolysis
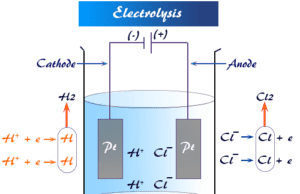
Electrolysis Definition in Chemistry
Electrolysis in chemistry is defined as a process where chemical changes occur at the electrodes (cathode or anode) due to the...
Gold
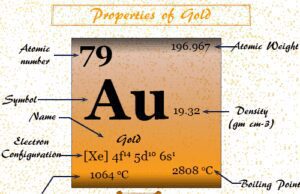
Gold Metal
Gold is a chemical element or yellow precious d-block metal of Group 11 or 1B of the periodic table with the symbol Au...
Copper
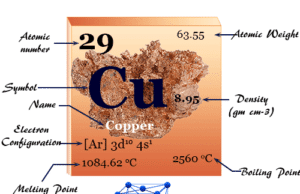
Copper Element
Copper is a chemical element or reddish-brown transition metal of Group 11 or IB of the periodic table with the symbol Cu and...
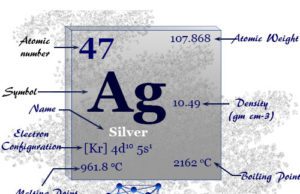
Silver
Silver Element (Ag)
Silver is the shiny white chemical element or lustrous transition metal of Group 11 or IB in the periodic table with atomic...
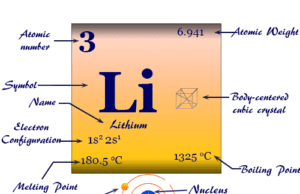
Lithium
Lithium Metal
Lithium is the lightest solid chemical element or alkali metal of Group 1 or IA in the periodic table with the symbol Li and atomic...
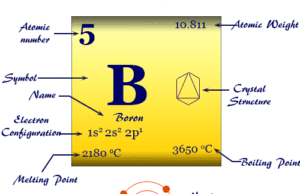
Boron
What is Boron?
Boron (symbol B), atomic number 5, is the first chemical element of Group 13 or Group IIIA in the periodic table. The...
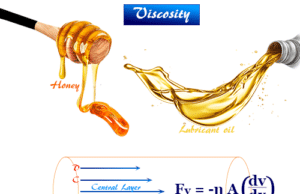
Viscosity of liquids
Measuring Viscosity of Liquids
Viscosity of liquids in chemistry is measuring the resistance to flow exhibited by fluids (liquids or gases) like glycerol, ester, oils,...
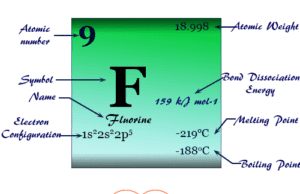
Fluorine
Fluorine Element
Fluorine (chemical symbol F), chemical formula F2, atomic number 9 is the most electronegative and most chemically reactive member of the halogen family...
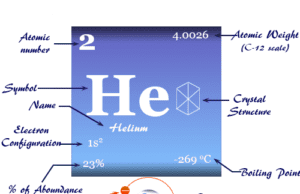
Helium
Helium Gas
Helium is a noble gas or group-18 element of the periodic table with the chemical symbol He and atomic number 2. It is the second most...