Cubic Crystal
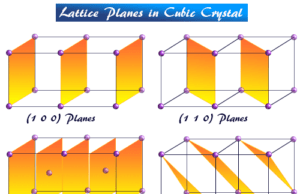
Cubic Crystal System
Crystal lattice or cubic crystal lattice is formed by the orderly arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in space or a three-dimensional...
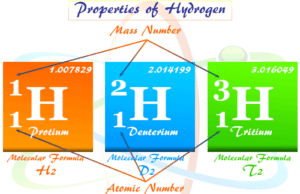
Hydrogen
Facts About Hydrogen Element
Hydrogen is the only chemical element in the periodic table in which the valence electron is under the direct influence of the...
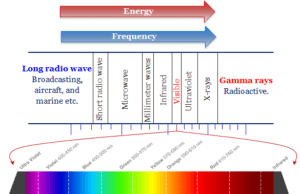
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electromagnetic Waves and Spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum and waves diagram or entire chart represent the number of radiation spectra (frequency, wavelength, and energy) formed by the...
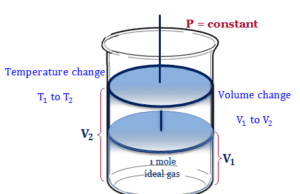
Conservation of Energy
Law of Conservation of Energy
Law of Conservation of energy or conservation of energy in thermodynamics states that the total heat or energy of our...
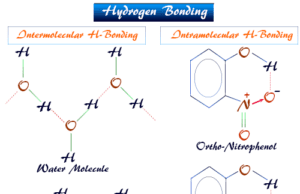
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen Bonding Examples
Hydrogen bonding or intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bond is a weak type of chemical bond due to very unstable attractive forces responsible...
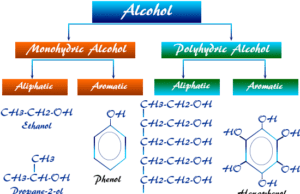
Alcohol
Different Types of Alcohol
Types of alcohol uses for the manufacture of drinks or beer, vodka, and brandy include ethyl alcohol or ethanol. Alcohol is...
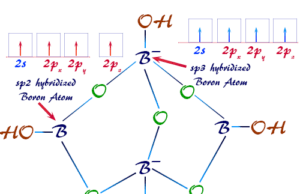
Borax
Uses of Borax Powder
Borax or borax powder (chemical name sodium tetraborate decahydrate) has the chemical formula Na2B4O7.10H2O, or Na2.8H2O and has a wide variety...
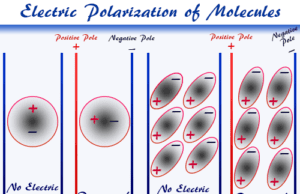
Electric Polarization
What is Electric Polarization?
Electric polarization occurs when a non-polar molecule is placed between two parallel plates with an applied electric field. The electric field...
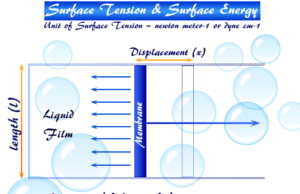
Surface Tension
Surface Tension of Liquid
Surface tension or surface energy is the most important characteristic property of liquid origin at the surfaces and is displayed when...
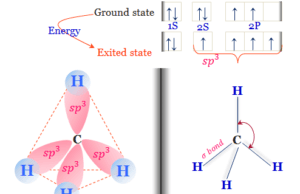
Methane Gas
Sources of Methane Gas
Methane gas (chemical formula CH4) also called marsh gas is the simplest hydrocarbon compound of the alkanes or paraffin with a...