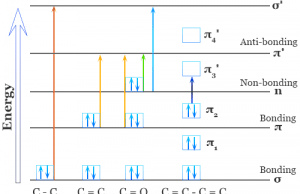
Ethanol
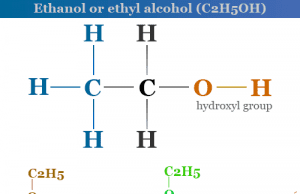
Ethanol (Ethyl Alcohol)
Ethanol or ethyl alcohol is a colorless, inflammable simple alcohol or organic compound used as a fuel and solvent in chemistry. It...
Manganese Dioxide
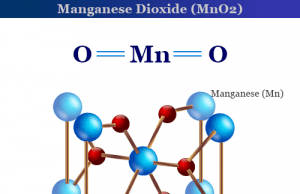
Manganese Dioxide (MnO2)
Manganese dioxide is a slightly brownish black solid with the chemical formula MnO2. The naturally occurring mineral pyrolusite (present in the earth's...
Spectrophotometry
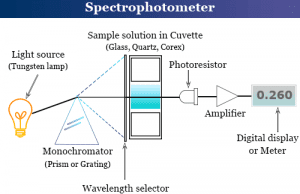
Definition of Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is an instrument in the electromagnetic spectrum for the measurement of relative energy (emitted, transmitted, or reflected) as a function of...
Optical Fiber
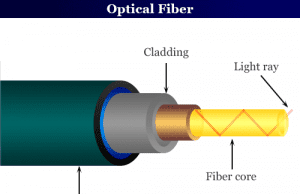
Optical Fiber Cable
Optical fiber cable or optical fiber cable is a new development in the field of communication technology that can transmit light along...
Ultraviolet Visible Spectroscopy
Ultraviolet Visible (uv vis) Spectroscopy
Ultraviolet visible spectroscopy or uv vis spectroscopy involves the measurement of absorption or transmittance of energy in the ultraviolet and...
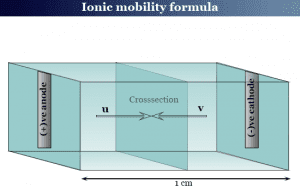
Ionic Mobility
Ionic mobility in electrochemistry
Ionic mobility in chemistry is the velocity of an ion under a unit potential gradient or field strength. Therefore, ionic mobility...
Tin
Tin Element
Tin is a chemical element or group 14 metal of the periodic table with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is...
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colurless, odourless, poisonous gas produced by burning carbon in insufficient oxygen. In the laboratory, carbon...
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Gas
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO2) is a colorless, orderless gas that can be easily liquefied under critical temperature and pressure. It is...
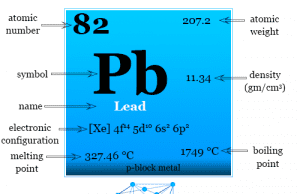
Lead
Lead Metal
Lead is a chemical element or group-14 metal of the periodic table with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. It has been...